Economic blocs consist of the union of different countries that wish to establish a strengthened economic relationship with each other.
The economic blocs aim to facilitate trade between their respective member countries and this is usually the case. give, for example, through the reduction of import and export taxes and the reduction of customs duties between they.
Main world economic blocks
You world economic blocks, that is, economic blocs formed by the union of different countries, emerged taking into account the globalization of the trade, in order to strengthen their own economies in trade relations among themselves and with other countries in the world.
In the case of some economic blocs such as the European Union, the member countries are part of the same region, that is, with regard to geography, they are located close to each other constituting thus regional economic blocks.
Economic blocs usually have countries in their formation that have cultural and commercial affinities.
See below some examples of the main economic blocks and their characteristics.
APEC

APEC logo
APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation) was created in 1993 and is formed by the United States of America, Japan, China, Formosa Island (Taiwan), South Korea, Hong Kong (Chinese administrative region), Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Brunei, Philippines, Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Canada, Mexico, Russia, Peru, Vietnam and Chile.
One of the main objectives of this bloc is to support the sustainable economic growth of the Pacific region, as well as its prosperity. through assistance among member countries.
This occurs mainly through the reduction of customs duties among member countries.
APEC is an economic bloc of extreme importance worldwide, as the industrial production of all member countries that comprise it corresponds to practically half of the world's industrial production.
This economic bloc, which has the potential to become the largest economic bloc in the world, does not have a treaty among its member countries; all decisions are made through consensus and non-binding declarations.
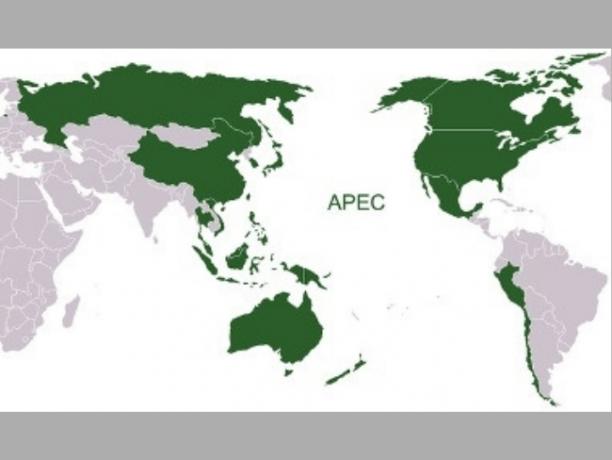
APEC Map
Since its foundation, APEC has held annual meetings to bring together the leaders of its member countries.
These meetings are usually hosted alternately by the member countries themselves, and it is a tradition for leaders to attend wearing typical attire from the host country.
It is not, however, a requirement and thus not everyone adheres to the custom.
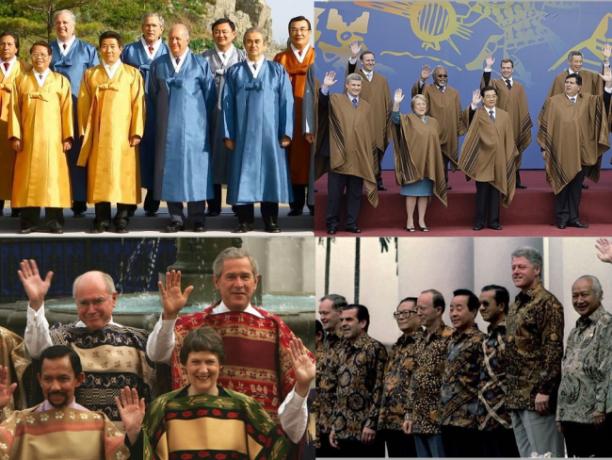

APEC Peru 2008 (top right), APEC Korea 2005 (top left), APEC Indonesia 1994 (bottom right) and APEC Chile 2004 (bottom left).
ASEAN

ASEAN Flag
ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) was founded in 1967 and comprises Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Brunei, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos and Cambodia.

ASEAN Map
One of the characteristics of this economic bloc is the concern with guaranteeing peace and stability in its territory.
As a result, member countries signed a treaty banning all nuclear weapons in the region.
CIS

Flag of CIS
The CIS (Community of Independent States) was founded in 1991 and is formed by Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine and Uzbekistan.
One of the main objectives of the creation of the CEI was to preserve the ties and collaborative relationships between the nations that emerged as new countries after becoming independent from the Soviet Union, even though they were under a great influence of the Russia.

CIS map
Russia had influence, for example, with regard to the language adopted, as it exerted some pressure for Russian to receive official language status from all CIS member countries.
However, Russian is only an official language in some countries, such as Belarus, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
Despite being often seen as an economic bloc, the CEI cannot receive such a classification as it does not have any type of trade policy among its members.
Andean Community of Nations - Andean Pact

Founded in 1969, the Andean Community of Nations is made up of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru.

Andean Community Map
In addition to the member countries, the Pacto Andino also has the interaction of Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Paraguay and Uruguay as associated countries and, in addition, has Mexico and Panama as countries observers.
One of the main objectives of the creation of the Andean Pact was to promote regional integration, in order to provide balanced development between countries members, thus reducing the economic and social differences between them, enabling the improvement of the quality of life and the economic position of these countries in a context global.
The free commercialization of products among member countries was also one of the main objectives of the Andean Community of Nations.
Another highlight was the permission, made possible by the pact, for the free circulation of citizens between member countries. The simple presentation of the national identity card allows an individual to move freely between all member countries, as a tourist without the need for a visa.
Despite no longer being a member of the Andean Community of Nations, Venezuela was also, to some extent, covered by this permission. However, citizens visiting or coming from that country must present their respective passports.
In 2001 the Andean Passport was created. This identification document is issued by all member countries of the Andean Pact and allows the free movement of its citizens among them.
Some of the physical characteristics of the document:
- Standard size 88mm by 125mm.
- Security elements based on the ICAO (Organización de Aviación Civil Internacional – International Civil Aviation Organization).
- Text “Communidad Andina” (Andean Community) recorded on the cover in gold letters.
- Image of the member country's coat of arms on the cover, in gold.

Andean passport cover
Mercosur

Mercosur logo
Mercosur (Southern Common Market) was founded in 1991 and is formed by Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay and Paraguay.
Venezuela, a member that joined the bloc in 2012, was suspended in 2016 for having failed to comply with the Accession Protocol and in 2017 for having violated the bloc's Democratic Clause.
The bloc also has Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Suriname and Guyana as associate members and Mexico and New Zealand as observer members.
Mercosur was created with the aim of establishing regional integration in Latin America.
One of its main objectives was to create a common market to enable the free internal circulation of goods, services and factors of production among member countries.
Regarding trade with other countries, a Common External Tariff (TEC) was created, establishing that the export of a given product must have the same cost regardless of the member country to export it.
Considered as a whole, Mercosur is the fifth largest economy in the world. With the increase in the economic integration agenda, there was a significant increase in investments by member states in the group's partners.
Brazil is of great importance in Mercosur's economic scenario, as its GDP corresponds to almost 55% of the bloc's GDP.
With regard to languages, Mercosur includes Portuguese, Spanish and Guarani. The language used in the documents varies depending on the country where the meetings are held.
Mercosur has a Free Residence Area with the right to work. This makes it easier for nationals of another member country to apply for temporary residence in a particular member country of the bloc, for a period of up to two years.
To enjoy this Free Residence Area, citizens of Mercosur member countries only need a passport valid, birth certificate, negative criminal record certificate and, depending on the country, medical certificate of authority migration.

In 2015, the cover of the Brazilian passport was marked “Passaporte Mercosul”.
Learn more about Mercosur.
SADC

SADC logo
The SADC (Southern Africa Development Community) was founded in 1992 and comprises 15 countries. They are: South Africa, Angola, Botswana, Democratic Republic of Congo, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Seychelles, Swaziland, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe.

SADC map
SADC member countries face a major challenge with regard to development, economy, trade, education, health, diplomacy and security and not all of them manage to resolve these issues properly. efficient.
Two of the main problems are the existence of organized crime gangs and the fact that some member countries also integrate other types of regional economic organizations, which end up undermining or competing with the objectives of the SADC.
European Union

European Union flag
The European Union was founded in 1993 and is made up of 28 countries. They are: Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Croatia, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands (Netherlands), Poland and Portugal.
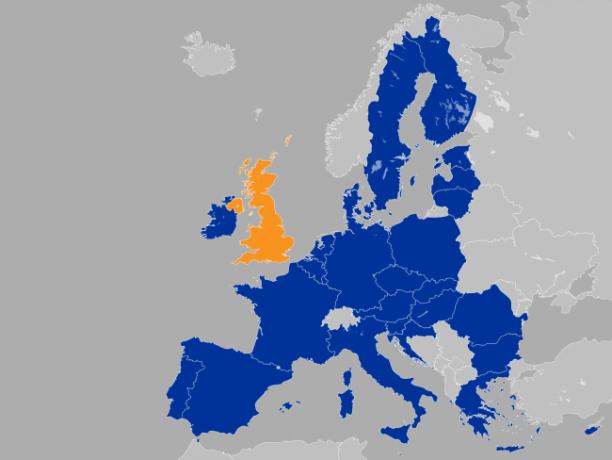
In 2016 a popular referendum approved that the United Kingdom (in orange) would no longer be part of the European Union (EU). The UK exit process will be completed in the year 2020.
With regard to the prosperity of its member countries, one of the main objectives of the European Union is to benefit sustainable development, based on balanced economic growth that provides prices stable.
With this, the aim is to achieve a highly competitive economy in favor of social progress and always taking into account the protection of the environment.
The European Union also aims to promote peace and the well-being of its citizens, seeking ensuring freedom, security and justice for all and fighting social exclusion and discrimination.
There is no border control between EU countries. In this way, its citizens can not only move freely between member countries but also live and work.
With regard to currency, in 1999 the euro was introduced as a single currency, initially as a virtual currency and in 2002 it was introduced in the form of banknotes and coins.
The main objective of introducing a single currency was to end exchange costs and exchange rate fluctuations. To join, countries must comply with a number of economic and legal conditions.
Check out the list of countries that could not adopt the currency because they did not meet all the requirements:
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Hungary
- Poland
- Czech Republic
- Romania
- Sweden
Two nations, however, negotiated a clause for not participating in the so-called “eurozone” and did not adopt the currency by choice. They are the United Kingdom (whose currency is the pound sterling) and Denmark (whose currency is Danish Crown).
Overall, 19 of the 28 EU member countries have the euro as their official currency.
Learn more about European Union.
UMSCA
The UMSCA (United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement – Agreement between the United States, Mexico and Canada) is an economic agreement established in 2018 between the three countries mentioned, which replaces the NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement - North American Free Trade Agreement business).

Flag of the NAFTA secretariat
The NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) entered into force in 1994 had as its main objective to strengthen the commercial relations between its member countries. To this end, customs duties on imports between them were reduced and the transit of goods and services between these nations was facilitated.
The creation of NAFTA was an American strategy whose intention was to face the competition of the Asian market and the European market.
The bloc's ideals were strictly economic and, for this reason, there were no major investments in the integration of citizens. Unlike the reality of some blocs, in NAFTA there was no free movement of national citizens between member countries.
During the term of NAFTA, there has always been a great deal of disparity between the member countries' economies. there has always been a certain dependence of the Canadian and Mexican economies on the American one.
In 2018, member countries agreed a renegotiation to replace NAFTA with UMSCA.

NAFTA map
UMSCA is considered a new and modernized agreement. One of its main objectives is to create conditions for all parties to emerge as winners and establish freer markets.
The main novelty at UMSCA regarding NAFTA is the unprecedented establishment of rules covering financial services and digital matters. An example of this is the treatment of copyright. Websites that infringe copyright will be removed, as is customary in the US.
Learn more about NAPHTHA.
BENELUX

BENELUX Flag
Benelux is an economic block founded in 1944. The bloc's designation comes from the names of its member countries in English: Belgium (Belgium), Nederlands (Netherlands) and Luxembourg (Luxembourg).
The Benelux consists of a trade agreement that includes mainly minerals and products for the industry, a sector considered one of the most important for the three member countries.
The main objective of creating the bloc was to make trade between member countries increase and become less bureaucratic. One of the measures taken to assist the process was the reduction of foreign trade fees and taxes.
The block has three official languages: Dutch, French and German.
Benelux is considered to have been the starting point for the emergence of the European Union; in 1951, the three Benelux countries united with West Germany, France and Italy and created the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), thus establishing a common steel market. Later, in 1957, the six countries signed the Treaty of Rome, which gave rise to the EEC (European Economic Community), also known as the MCE (European Common Market). Over the years, England, Ireland, Denmark, Greece, Spain and Portugal joined the EEC and the group became known as the Europe of 12.
The EEC promoted the integration of countries through the free movement of capital, products and people.
The integration promoted by the EEC came to fruition in 1992, when a treaty called the Maastricht Treaty was signed. This treaty entered into force the following year, giving rise to the European Union.
The rise of the European Union did not extinguish Benelux; the blocks began to coexist.
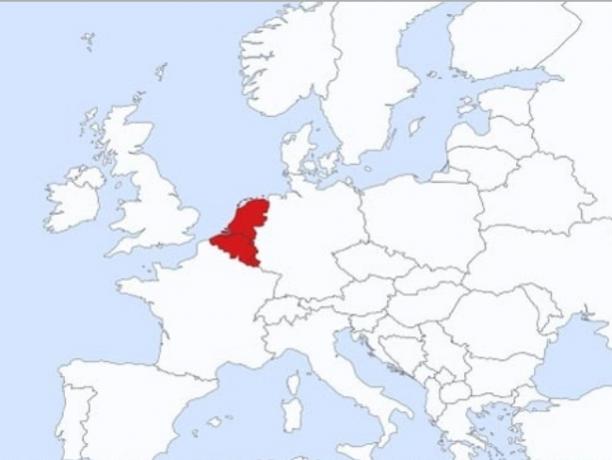
BENELUX Map
Formation of economic blocks
The formation of the first economic blocs took place after World War II.
With Europe devastated and the United States in a process of increasing economic growth, the European economy was threatened.
The first economic bloc then appears in 1944, with the union of Belgium, Holland and Luxembourg, giving rise to the BENELUX bloc, whose objective was to help these countries recover from the war.
Later, Germany, France and Italy joined BENELUX, thus forming a new block, called ECSC (European Coal and Steel Community).
Over the years and the integration of more and more countries, the CECA became what we know today as the CEE (European Economic Community).
In addition to being generally formed by neighboring countries, economic blocs usually have countries that have cultural and commercial affinity in their formation.
Main objectives of economic blocks
Check below some objectives of the economic blocks.
- Reduce import and export taxes and customs duties between member countries.
- Improve economic dynamics among member countries.
- Expand the consumer market of member countries to intensify the economy in a globalized context.
Types of economic blocks
The classification of the types of economic blocks is based on the characteristics that each one has.
Characteristics of economic blocks
Some of the characteristics of economic blocks are:
- Free Comerce.
- Free movement of persons and goods.
- Adoption of the same currency.
- Common commercial conduct among member countries.
See more about free Comerce.
Taking these characteristics into account, the economic blocks are classified into four categories, as explained below.
free trade area
The economic blocks that have this classification have a free trade agreement, which means that what is produced in a member country can enter another member country without any problem, thus being exempt from the fees of the usual bureaucratic process concerning the import.
customs union
In this type of economic bloc, commercial conduct and rules for the sale of products between the bloc's members and non-member countries are defined.
common market
In the common market, the free movement of capital, people and services is allowed. In this sense, a market is created that allows for greater integration between the economies and the rules of this internal market constituted by the member countries.
economic and monetary union
In the economic and monetary union system, the member countries of the economic bloc adopt the same currency and follow the same development policy.
Economic blocks and globalization
It is considered that the beginning of globalization took place at the time of the great navigations, when the vessels took and brought products and information from geographically distant places from one of the others.
However, the existence of economic blocks is, without a doubt, a form of globalization. The creation of trade agreements between countries ends up bringing nations closer and establishing peaceful relations between them.
With regard to the creation of economic blocs, globalization is beneficial in fighting inflation and in importing and exporting products, and in maintaining a good relationship between countries.
One point that could turn out to be negative, however, is the risk of wealth becoming more concentrated in some nations than in others.
know more about globalization and characteristics of globalization.
Advantages and disadvantages of economic blocks
The advantage of the formation of economic blocs is the reduction in import and export taxes and in the customs tariff. This reduction has a direct impact on the price of the final product.
How producers benefit from the lower prices paid for used imported materials as a raw material, the value of the final product ends up being reduced, which also benefits the consumer.
The downside of economic blocs is that companies that are not consistent enough to compete with other member countries' companies run the risk of having to go out of business.
List of current economic blocks
List of current economic blocks:
- ACP countries (79 countries in Africa, the Caribbean and the Pacific)
- ACP-EU (Cotonou Agreement: trade agreement between the European Union and the ACP countries)
- AEC (Association of Caribbean States)
- AELC (European Free Trade Association)
- ALADI (Latin American Integration Association)
- ALBA (Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas)
- APEC (Economic Cooperation of Asia and the Pacific)
- ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)
- CEFTA (Central European Free Trade Agreement)
- CAFTA-DR (Free Trade Community between the United States, Central America and the Dominican Republic)
- CAN (Andean Community of Nations)
- DOG (East African Community)
- CARICOM (Caribbean Community)
- CEA (African Economic Community)
- ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States)
- EAEC (Eurasian Economic Community)
- ECCAS (Economic Community of Central African States)
- CIS (Community of Independent States)
- CEMAC (Central African Economic and Monetary Community)
- IBSA (India, Brazil and South Africa Dialogue Forum)
- COMECOM (Council for Mutual Economic Assistance)
- EAT (Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa)
- MERCOSUR (Southern Common Market)
- OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development)
- OECO (Organization of Eastern Caribbean States)
- SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation)
- SADC (Southern African Development Community)
- UA (African Union)
- UAA (Southern African Customs Union) also known by the acronym in English SACU (Southern African Customs Union)
- HUH (European Union)
- UEMOA (West African Economic and Monetary Union)
- ONE (Union of Arab Maghreb)
- UNASUR (Union of South American Nations)
