One mixing of solutions of the same solute without chemical reaction it consists of bringing together in the same container two solutions with, for example, potassium chloride (Kcl). In this type of mixture, there will never be a chemical reaction due to the presence of equal solutes, that is, both have the same cation and the same anion. Thus, we can say that when we perform a mixture with these characteristics, we are just adding the amounts of solute and solvent that make up both solutions.
If we mix, for example, a solution of 1L of water and 4 grams of KI (potassium iodide) with another solution of 2L of water and 6 grams of KI, we will have a new solution of 3L of water and 10 grams of KI.
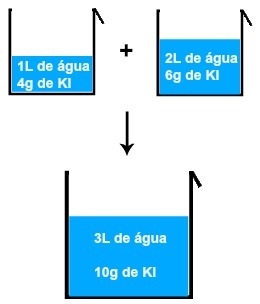
Result of mixing two potassium iodide solutions
Analyzing the image, we can conclude that the mass of the solute (m1') of the first solution is added to the mass of the solute (m1'') of the second solution, resulting in the mass of the solute (mF) in the final solution (Mix):
m1' + m1'' = mF
In the example:
4 + 6 = 10 grams
The same happens with the volume of water present in each solution, that is, the volume of the first (V') added to the volume of the second (V'') results in the final volume (V'F):
V' + V'' = VF
In the example:
1 + 2 = 3 L
As every solution has an amount of dissolved solute and here we have a mixture of solutions of the same solute, we can then, from the above, determine the concentration (common, molarity) of each of the mixed solutions and also of the final solution.
Therefore, we must remember the formulas to calculate these concentrations:
Common concentration:
C = m1
V
m1 = mass of solution solute
V = solution volume
NOTE: isolating the m1 in the formula, we have: m1 = CV
Molarity:
M = m1
M1.V
M1 = molar mass of the solute.
NOTE: isolating the m1 in the formula, we have: m1 = M.M1.V
As the mixture of solutions of the same solute addresses the sum of the mass of the solute of the solutions, we can substitute each of the observations in the following expression:
m1' + m1'' = mF
C'.V' + C''.V'' = CF.VF
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
C' = common concentration of solution 1
C'' = common concentration of solution 2
If the calculation of the mixture of solutions involves molarity:
m1' + m1'' = mF
M'.V' + M''.V'' = MF.VF
NOTE: Since the solute is the same, the molar mass is the same in each of the solutions; therefore, it is neglected in the calculation.
now see examples that cover calculations in a mixture of solutions of the same solute without chemical reaction:
Example 1: (Mackenzie-SP-Adaptada) Adding 600 mL of a 14g/L KOH solution to a certain volume (v) of 84 g/L solution of the same base, a 67.2g/L solution is obtained. The added volume (v) of the 84 g/L solution is:
a) 0100 mL
b) 3000 ml
c) 2700 ml
d) 1500 ml
e) 1900 mL
The data provided by the exercise were:
V' = 600 mL
C' = 14 g/L
V'' = ?
C'' = 84 g/L
VF = ?
CF = 67.2 g/L
Before determining the added volume of solution 1, we must initially determine the final volume by means of the following expression:
V' + V'' = VF
600 + V'' = VF
Substituting the values given in the mathematical expression below, we have:
C'.V' + C''.V'' = CF.VF
14. 600 + 84.V'' = 67.2.(600 + V'')
8400 + 84.V'' = 67.2. 600 + 67.2.V''
8400 + 84.V'' = 40320 + 67.2.V''
84.V'' – 67.2.V'' = 40320 – 8400
16.8.V'' = 31920
V'' = 31920
16,8
V'' = 1900 mL
Example 2: (UFOP) In a 1000mL volumetric flask, 250mL of a 2M sulfuric acid solution were added with 300mL of a 1M solution of the same acid and the volume was made up to 1000mL with distilled water. Determine the molarity of the resulting solution.
The data provided by the exercise were:
V' = 250 mL
M' = 2 M
V'' = 300 mL
M'' = 1 M
VF = 1000ml
MF = ?
To determine the molarity of the final solution, just use the mathematical expression that represents the process:
M'.V' + M''.V'' = MF.VF
2. 250 + 1. 300 = MF.1000
500 + 300 = MF. 1000
800 = MF
1000
MF = 0.8 mol/L
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "Mixture of solutions of the same solute without chemical reaction"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/mistura-solucoes-mesmo-soluto-sem-reacao-quimica.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.