Chemical kinetics studies the speed of chemical reactions and the factors that influence the rate of those reactions.
Use the questions below to test your knowledge and check out the comments on the resolutions.
question 1
Regarding the factors that influence the speed of a chemical reaction, it is INCORRECT to state that:
a) The greater the concentration of reactants, the greater the reaction rate.
b) The larger the contact surface, the greater the reaction speed.
c) The higher the pressure, the faster the reaction.
d) The higher the temperature, the faster the reaction.
e) The presence of a catalyst keeps the reaction rate constant.
Incorrect alternative: e) The presence of a catalyst keeps the reaction rate constant.
Catalysts increase the reaction speed, as they facilitate the formation of the activated complex between the reactants.
With this, the catalysts create a shorter mechanism for the reaction to develop, causing the speed to increase.
question 2
According to _____________ effective collisions must occur between the reagents for the formation of the products. In addition, there is enough ___________ to break the chemical bonds of the reactants and form a ___________, which is an intermediate state prior to the formation of products.
The words that correctly fill in the blanks are, respectively:
a) enthalpy, kinetic energy and catalyst variation.
b) collision theory, activation energy and activated complex.
c) reaction speed, enthalpy and inhibitor.
d) partial pressure, entropy and substrate.
Correct alternative: b) collision theory, activation energy and activated complex.
According to the collision theory, the collisions between the reactants are necessary for a chemical reaction to occur. For this, the substances must be in a favorable position for the shocks to be effective.
Activation energy acts as an energy barrier that must be overcome to break the bonds of reacting compounds. The lower the activation energy, the faster the reaction.
The activated complex is an unstable intermediate species formed before the products.
question 3
The following four statements are made about catalysts:
I. A catalyst works by increasing the speed of a reaction, but it does not change its performance.
II. In a chemical reaction the catalyst is not consumed in the reaction path.
III. Catalysts create an alternative route for transforming reactants into products. For this, greater activation energy is needed.
IV. The catalyst is only able to speed up the reaction in the forward direction.
The options that present correct information about catalysts are:
a) I and II
b) II and III
c) I and IV
d) All
Correct alternative: a) I and II.
Catalysts are used to speed up chemical reactions. The reaction using the catalyst does not change its yield, that is, the expected amount of the product is produced, but in less time.
Catalysts are not consumed during the chemical reaction, they aid in the formation of the activated complex. Therefore, a catalyst can be recovered at the end of the chemical reaction.
Catalysts are able to reduce the reaction time by creating an alternative mechanism for the formation of products with lower activation energy. Therefore, the reaction occurs faster.
Catalysts act both in the forward and in the reverse direction of the reaction.
question 4
How quickly a chemical reaction takes place depends on:
I. Number of effective collisions between reagents.
II. Enough energy to rearrange the atoms.
III. Favorable orientation of molecules.
IV. Formation of an activated complex.
a) I and II
b) II and IV
c) I, II and III
d) I, II, III and IV
Correct alternative: d) I, II, III and IV.
Effective collisions occur when the reactants are in positions favorable to shocks, which will promote the rearrangement of atoms.
The activation energy must be sufficient for the collision between the reactants to result in the breaking of bonds and the formation of the activated complex.
Not all collisions between reacting particles cause the reaction to take place. The orientation with which the collision occurs is important for the formation of the products to occur.
The activated complex is an intermediate and unstable state before the formation of products. It is created when the activation energy for the reaction is exceeded.
question 5
Carbon dioxide is a gas formed by the reaction between carbon monoxide and oxygen gases, according to the chemical equation below.
CO(g) + ½ the2(g) → CO2(g)
Knowing that in 5 minutes of reaction 2.5 mol of CO were consumed, what is the rate of development of the reaction according to the consumption of O2?
a) 0.2 mol. min-1
b) 1.5 mol. min-1
c) 2.0 mol. min-1
d) 0.25 mol. min-1
Correct alternative: d) 0.25 mol. min-1
To answer this question we must look at the chemical equation.
CO(g) + ½ the2(g) → CO2(g)
Note that 1 mole of carbon monoxide reacts with ½ mole of oxygen to form 1 mole of carbon dioxide.
The amount given in the statement refers to carbon monoxide, but the answer must be in terms of oxygen. For this we must perform a rule of three and find the amount of oxygen.
1 mol CO - ½ mol O2
2.5 mol CO - x of O2
x = 1.25 mol
Now we apply the values in the formula for the rate of reaction development.
Therefore, the rate of reaction development with respect to oxygen is 0.25 mol.min-1.
question 6
Note the graphical representation of the development of a hypothetical chemical reaction, which relates energy and reaction path.
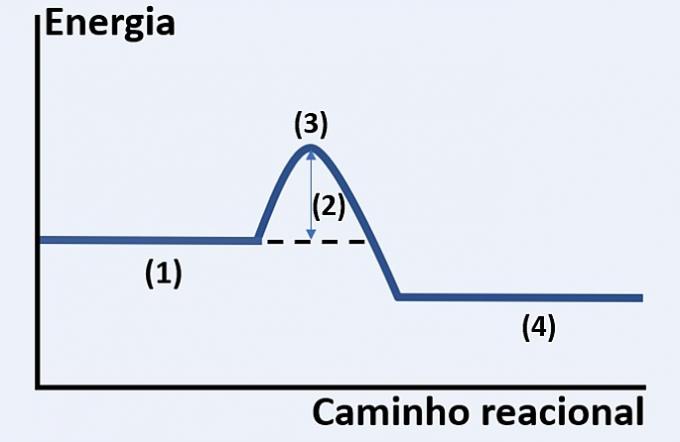
Check the alternative that correctly replaces (1), (2), (3) and (4), respectively.
a) substrates, released heat, maximum energy state and end of reaction.
b) reagents, activation energy, activated complex and products.
c) reactants, kinetic energy, catalyst and substrates.
d) reactants, absorbed heat, thermal energy and products.
Correct alternative: b) reagents, activation energy, activated complex and products.
The graph shown is of an endothermic reaction, that is, there is energy absorption for the reaction to occur.
You reagents (1) are at the beginning of the graph and the activation energy (2) corresponds to the difference between the energy stored in the reactants and in the complex activated (3). Finally, after passing the intermediate state, the formation of products (4).
Therefore, the reactants need to overcome the activation energy to rearrange their atoms into an intermediate structure called an activated complex in order for the products to form.
question 7
Substance A is capable of decomposing and becoming substance B. Observe the development of this reaction in the image below.

Regarding the reaction speed, we can say that:
a) Substance A decomposes between 0 and 15 s at a rate of 0.35 mol.s-1.
b) Substance A decomposes between 15 and 30 s at a rate of 0.02 mol.s-1.
c) Substance A decomposes between 0 and 15 s at a rate of 0.04 mol.s-1.
d) Substance A decomposes between 15 and 30 s at a rate of 0.03 mol.s-1.
Correct alternative: d) Substance A decomposes between 15 and 30 s at a rate of 0.03 mol.s-1.
The rate of decomposition of substance A can be calculated by the formula:
Let's calculate the speed of reaction in terms of substance A between the given intervals.
Range between 0 and 15:
Range between 15 and 30:
Therefore, alternative d is correct, as substance A decomposes between 15 and 30 s at a rate of 0.03 mol.s.-1.
question 8
Consider the following hypothetical reaction.
aA + bB → cC + dD
Note the variation in the concentration of A and C below.
| Time(s) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption of A (mol/L) | 7,5 | 6,0 | 4,5 | 3,0 | 2,5 | 1,0 |
| Formation of C (mol/L) | 0 | 0,5 | 1,0 | 1,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 |
Based on the information provided in the question, what is, respectively, the rate of consumption of A and the rate of formation of C in the interval between 5 and 25 min?
a) 0.3 mol. L-1.s-1 and 0.1 mol. L-1.s-1
b) - 0.1 mol. L-1.s-1 and 0.3 mol. L-1.s-1
c) - 0.25 mol. L-1.s-1 and 0.1 mol. L-1.s-1
d) 0.1 mol. L-1.s-1 and 0.3 mol. L-1.s-1
Correct alternative: c) - 0.25 mol. L-1.s-1 and 0.1 mol. L-1.s-1.
A consumption rate:
C training rate:
Therefore, in the reaction, A is consumed at a rate of 0.25 mol.s-1, so its value is negative, while B is formed at a rate of 0.1 mol. L-1.s-1.
Read too:
- Chemical Kinetics
- Thermochemistry
- Chemical balance
- Chemical reactions

