O Phases diagram is a graph that allows you to define what physical state a substance is in at any given time, knowing its temperature and pressure.
Laboratory measurements are used to build the phase diagram of a given substance.
The diagram is divided into three regions, which represent the solid, liquid and vapor state.
The dots on the lines that delimit these regions indicate the values of temperature and pressure that the substance can be in two states.
A phase diagram has the following elements:
- curve of Fusion: separates the areas corresponding to solid and liquid states.
- curve of vaporization: separates the areas corresponding to the liquid and vapor phases.
- curve of sublimation: separates the areas corresponding to the solid and vapor phases.
- triple point: intersection point of the three curves (fusion, vaporization and sublimation). This point indicates the temperature and pressure values that the substance can simultaneously be in the three states.
- Critical point: indicates the highest temperature that the substance is vapor. From that point on, it is no longer possible to differentiate between liquid and vapor states. At temperatures above the critical point, the substance becomes a gas.
In the figure below, we present a representation of a phase diagram:

Read more at: Physical state changes.
melting curve
Substances, in general, increase in volume when they undergo fusion and, on the contrary, decrease in volume when they solidify. As a consequence, an increase in pressure leads to an increase in the melting point (melting temperature).
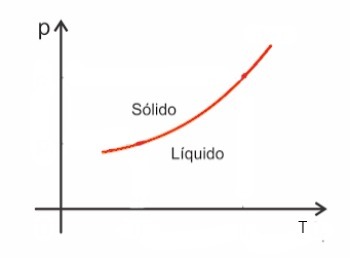
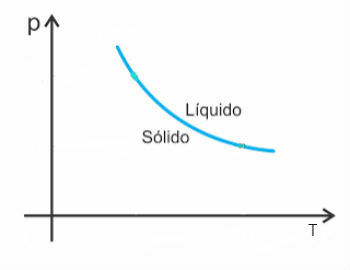
However, there are some exceptions among them water, which in melting decreases in volume. In this case, an increase in pressure causes a decrease in the melting point.
Thus, the melting curve of these substances will look like this:
Example
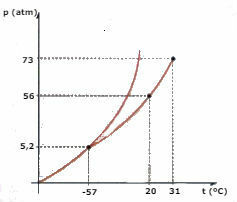
Consider the CO phase diagram2 (carbon dioxide) represented below and answer the questions:
a) What phase is the CO2 , when its temperature is -60 ºC and the pressure is 50 atm?
b) A certain amount of CO2 liquid is subjected to a pressure of 56 atm, and is confined in a container. If the liquid is heated, keeping the pressure constant, what is the temperature value at which vaporization will occur?
c) What is the temperature and pressure value of the triple point of CO2?
d) A piece of dry ice (CO2) is subjected to a pressure of 2 atm. It is heated, maintaining constant pressure. At a certain moment a phase change begins to occur. What is the name of this change?
Resolution:
a) Observing the diagram, we conclude that the CO2 will be in the solid phase.
b) Vaporization will occur when the temperature reaches 20°C.
c) The triple point corresponds to the intersection of the three curves, in the case of CO2, when it has a temperature of -57°C and a pressure of 5.2 atm, the three physical states can coexist.
d) Sublimation will occur
To learn more, read also:
- Solidification
- Melting and boiling point
- Evaporation
- Condensation
Solved Exercises
1) Enem - 2000
Even today, it is very common for people to use earthenware containers (jars or unglazed ceramic pots) to conserve water at a temperature lower than that of the environment. This is because:
a) clay isolates water from the environment, always keeping it at a lower temperature than its own, as if it were Styrofoam.
b) clay has the power to “freeze” water due to its chemical composition. In the reaction, water loses heat.
c) the clay is porous, allowing water to pass through it. Part of this water evaporates, taking heat from the moringa and the rest of the water, which are then cooled.
d) the clay is porous, allowing water to settle on the outside of the jug. The outside water is always at a higher temperature than the inside.
e) Moringa is a kind of natural refrigerator, releasing hygroscopic substances that naturally lower the temperature of the water.
Alternative c: clay is porous, allowing water to pass through. Part of this water evaporates, taking heat from the moringa and the rest of the water, which are then cooled.
2) Ita - 2013
Consider the hypothetical phase diagram schematically represented in the following figure:

What do points A, B, C, D and E represent?
point A: sublimation point
point B: triple point
C point: melting/solidification point
point D: vaporization/condensation point
point E: critical point
3) UECE - 2009
Looking at the PT phase diagram shown below. It can be concluded, correctly, that a substance that has gone through the sublimation process follows the trajectory:

a) X or Y
b) Y or U
c) U or V
d) T or X
Alternative b: Y or U


