Work and energy are directly proportional quantities. This is the definition for work when studying mechanical energy.
We also see in mechanical energy that work is performed by a constant force parallel to the displacement of a body corresponding to the variation of mechanical energy suffered by the body.
Having made these necessary observations about working in mechanical energy, let us now understand how the Work of the Electric Power.
A fixed electric charge Q creates an electric field. If we abandon a test charge q within this field, the charge q will be influenced by the electrical force F, which will move this test charge q in the same direction and in the same direction as this strength.
Motor work – When the electric force F displaces the test charge q in the direction of the force itself.
Resistant work - When work is performed against the forces of the electric field, that is, when the force is contrary to the direction of displacement of the field.
Electric Force = Conservative Force
This equality occurs because the work performed is stored in the form of energy.
Characteristics of Conservative Forces
The work of the electric force does not depend on the trajectory, it only depends on the starting and ending points.
Work expression of electrical force
The mathematical representation of the Electric Power Work is given by the equation:
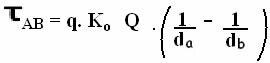
Where:
τ = work of electrical force
q = proof load
Ko = electrostatic constant
Q = fixed load
d = distance
By Talita A. angels
Graduated in Physics
Brazil School Team
Electricity - Physics - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/trabalho-forca-eletrica.htm
