You plant tissueform the body of plants. Each type of tissue is organized within a group of systems, which are continuous throughout the plant, but with specificities depending on the organ analyzed. We will learn more about plant tissues below and understand which system they are part of.
vegetable tissue
Plant tissues can be defined, in a simplified way, as an association of cells that form structural and functional units. They are called plain fabrics when formed by only one type of cell, and from complexes, when formed by two or more cell types. The parenchyma, colenchyma and sclerenchyma are considered simple tissues. The epidermis, xylem and phloem, in turn, are complex tissues.
We'll talk more about each type of plant tissue below.

meristems
They are one living tissuenot yet differentiated. They have the ability to multiply and give rise to other tissues. We can classify meristems into two types: apical and lateral. The apexes are located at the apex of the root and stem and are involved with long-term growth of the plant (primary growth). The laterals (vascular cambium and phelogen) are related to the growth in thickness (secondary growth).
Epidermis
It is a plant tissue that covers the body of the plant. The cells of this tissue are arranged in a compact manner, and this characteristic is important in the protective function performed by it. Epidermal cells are alive and vacuolated, and may contain different substances, such as pigments. At epidermis we find some cells with specific functions, such as the guard cells of the stomata, lithocysts, suberous cells and trichomes.
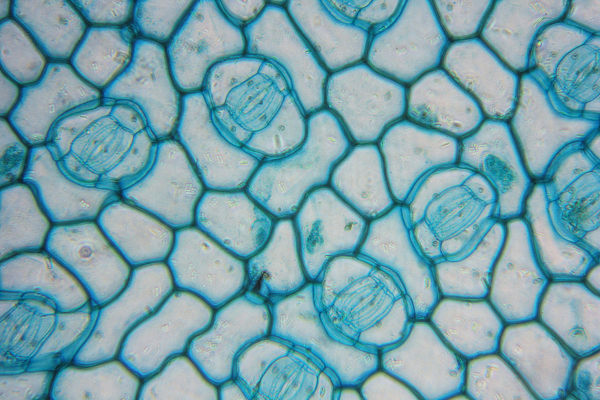
periderm
It replaces the epidermis in plants with secondary growth. Unlike what many people think, the periderm it is not a single fabric, it is, in fact, a set of lining fabrics that have a secondary origin. The periderm is formed by the suber, the phelogen and the pheloderm. The phelogen is a meristematic tissue of secondary origin, which produces the suberum to the outside, and to the inner region, the pheloderm.
Read too: Difference between periderm, bark and rhytidome
Parenchyma
It is a plant tissue formed by living cells and which usually have an isodiametric shape. This tissue has the ability to resume its meristematic activity, and is therefore important in processes such as healing and regeneration. We can classify the parenchyma in three basic types: parenchyma of fill, parenchyma chlorophyll and parenchyma of reserve.
colenchyma
It is a plant tissue that has living cells with thickened cell walls that are not lignified. When observed under a photonic microscope, the cells of this tissue have a characteristic bright white color. As well as the parenchyma, the collenchyme can resume meristematic activity. It is a tissue related to thesupport from the plant's body, in particular, the support of young, growing organs. It is classified, according to the type of thickening it has, in: angular, lamellar, lacunar and annular.

sclerenchyma
It's a fabric support related, just like the collenchyma. However, the sclerenchyma it is a tissue that has dead cells at maturity. In addition, it has a thickened secondary wall, which can be lignified or not, with uniform thickening. Two types of cells are identified in it: the fibers and the sclereids. Fibers are cells, generally longer than they are wide, and sclereids tend to be smaller.
Xylem
It is a complex tissue formed by several cell types, such as parenchymal cells, fibers and conductive elements. O xylem presents as a function ensure the transport of water and solutes, the so-called raw sap.
There are two basic types of tracheal elements (the more specialized cells of the xylem): the vessel elements and the tracheids. THE main difference among them is that those are provided with perforation plates (regions with one or more perforations, that is, without primary and secondary walls), while these are imperforate.
The xylem can originate from the procambium, being a primary xylem, or from the vascular cambium, being a secondary xylem.
Also access:Water transport through the vegetable body
Phloem
Like xylem, it is a tissue related to conduction of substances, however, it conducts organic and inorganic materials in solution (elaborated sap). Phloem is a complex tissue with several cell types, such as parenchymal cells, fibers, sclereids and cells specialized in conduction. The latter are the sieved elements, and it is possible to distinguish two types of them: the sieve cells and the elements of the sieve tube.
The sieve cells have sieve areas (set of pores) on all walls, while the tube elements sieve have sieve plates (region with larger pores) on the end walls and sieve areas on the walls sides. As well as the xylem, there is the primary phloem that originates from the procambium and the secondary phloem that originates from the vascular cambium.
Tissue Systems

Plant tissues are organized in three systems: dermal system, fundamental system and vascular system. In the plant body, generally, what is observed is the presence of the vascular system being involved by the fundamental system, which is involved by the dermal system, which covers the entire body of the plant.
O dermal system is the most external observed in the plant's body, protecting it against physical damage and herbivory. The epidermis is part of it, as well as the peridermis, which is found in plants with secondary growth.
Read more:Human tissues - set of organized cells that perform a function together
O fundamental system, in turn, is related to various functions, such as filling, booking, sustaining and performing photosynthesis. This system is formed by three types of fundamental tissues: the parenchyma, the colenchyma and the sclerenchyma.
Lastly we have the vascular system of the vegetable that guarantees the conduction of substances through the plant's body. Two types of tissue are part of it: xylem and phloem.
By Vanessa Sardinha
Biology teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/tecidos-vegetais.htm
