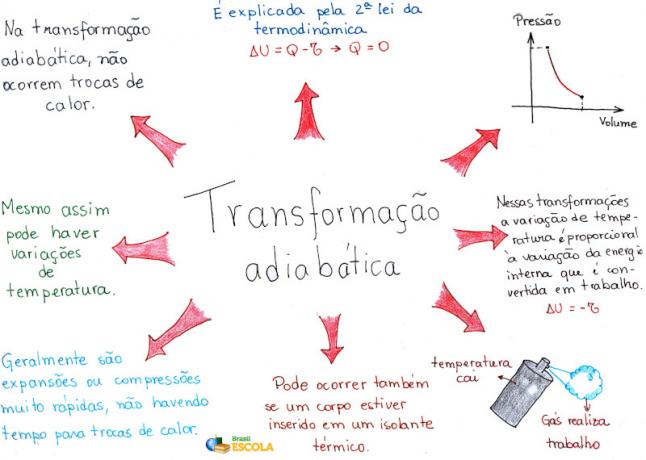
In the study of Thermology we call it adiabatic transformations those gaseous transformations where there is no heat exchange with the external environment. Therefore, in the adiabatic transformation the heat is zero.
Q = 0
If we apply the First Law of Thermodynamics, we have:
Q = ∆U+τ
∆U = - τ
But what does it mean that there is no heat exchange between the external environment? It means that if a gaseous expansion happens and the gas performs a 300 J job, it does not if there is heat exchange with the medium, the variation of the internal energy of the gas will be negative, therefore, we will have:
∆U = - 300 J
Now, if there is a decrease in the internal energy of the gas, we can say that there was also a decrease in the temperature of the gas. From the general law of gases

we can say that if the volume increases and the gas temperature decreases, necessarily the gas pressure will also decrease. In general, we can say that the same happens with compression, because if there is compression, the internal energy of the gas will increase, so the pressure will also increase.
Mind Map: Adiabatic Transformation
* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
Briefly, we can say that:
- in adiabatic expansion, temperature and pressure decrease;
- in adiabatic compression, both temperature and pressure increase.
The chart below gives us an overview of the adiabatic transformation:
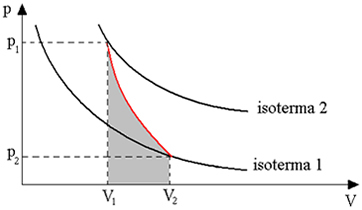
Adiabatic transformations are obtained using thermally insulated containers, or also through compression or very rapid expansion.
Thus, we can conclude that when a gas exchanges heat with the external environment, it takes some time for the heat to propagate through the gaseous mass and for it to come into equilibrium. Therefore, when both expansion and rapid compression are carried out, there is practically no heat exchange with the external medium.
* Mind Map by Me. Rafael Helerbrock
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/estudo-transformacao-adiabatica.htm
