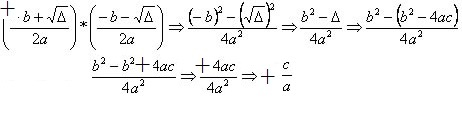An important relationship existing in trigonometry was elaborated by Pythagoras, based on right triangle (triangle with legs forming a right angle). See the relationship that became known as "Pythagorean theorem”:
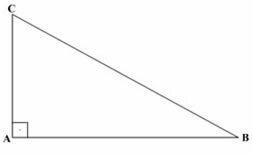
AB = collared
AC=catheto
BC = hypotenuse
avg (AB)² + avg (AC)² = avg (BC)²
At the trigonometric circle, the vertical axis is represented by the sine and the horizontal axis by the cosine. When we determine any point on the extremity of the circle, we have its projection on the axis of sines and cosines. When we draw a straight segment from the axis of the circle's origins to the given point, we form an angle Ө, as shown in the following diagrams:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

Based on the right triangle formed, let's apply the fundamentals of Pythagoras' theorem:

sin² Ө + cos² Ө = 1
Application of the fundamental relationship
Example 1:
Whereas 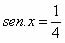 , with
, with  , determine cos x.
, determine cos x.

Example 2:
Whereas  , with
, with  , determine sin x.
, determine sin x.

by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Trigonometry - Math - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Marcos Noé Pedro da. "Fundamental Relation of Trigonometry"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/relacao-fundamental-trigonometria.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.