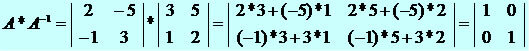It is possible to solve a system using Cramer's rule, but this rule only allows solving systems that have the same number of unknowns and the same number of lines (if a system of type n x n), that is, if the linear system is of type m x n with Cramer's rule it is not possible to resolution.
To solve both the m x n and n x n systems, the diagonalization process is used. This process consists of simplifying, that is, finding equivalent systems (Equivalent systems are systems that have the same solution) and with simpler resolution.
Equivalent systems also have equivalent complete matrices. If system A is equivalent to system B we represent this equivalence as follows A ~ B.
See the example:
Given the system A = 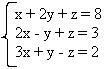 it will be equivalent to the system
it will be equivalent to the system
B =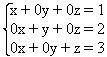 , as they have the same solution set {(1,2,3)}.
, as they have the same solution set {(1,2,3)}.
We can make one system equivalent to another in three different ways:
• Swap two lines of position with each other.
• Multiply (or divide) any row by a non-null real number.
• Multiply any row by a non-null real number and add the result to the other row.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
by Danielle de Miranda
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Matrix and Determinant - Math - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
RAMOS, Danielle de Miranda. "Process for solving an m x n linear system"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/processo-para-resolucao-um-sistema-linear-m-x-n.htm. Accessed on June 29, 2021.