Learn to apply the first law of thermodynamics in different situations, solve exercises and test your knowledge with solved and explained exercises.
question 1
The first law of thermodynamics states that:
a) Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another.
b) Energy is always conserved, but it cannot be converted from one form to another.
c) Energy can be created or destroyed, but it cannot be converted from one form to another.
d) Energy cannot be conserved, but it can be converted from one form to another.
The first law of thermodynamics is the principle of conservation of energy, so in a system closed, the amount of energy remains constant and can only be transformed from one form to another. other.
question 2
Assume a closed system that receives 100 J of heat while doing 50 J of work. What is the change in internal energy of the system?
a) -50J
b) 0 J
c) 50J
d) 100J
e) 150J
Checking the signs:
Heat received is positive Q > 0.
Work done is positive W > 0.
According to the first law, we have:
question 3
An ideal gas system exchanges 500 joules of heat with the external environment. Assuming this process to be an isometric cooling, determine the work and internal energy, respectively.
a) 500 J and 0 J
b) - 500 and 0 J
c) 0 J and 500 J
d) 0 J and - 500 J
e) -500 J and 500 J
Since the process is isometric, there is no change in volume, so the work is zero.
According to the first law of thermodynamics:
As it is a cooling, the system loses heat, therefore:
question 4
8 moles of an ideal gas in a piston-cylinder system are compressed by doing 1000 J of work. During the process, 400 J of heat are lost to the external environment. Its internal energy and the change in its temperature are respectively equal to
Given: R = 8.31 J/mol. K
a) - 1400 J and approximate variation of 6 K
b) 600 J and approximate variation of 6 K
c) 600 J and approximate variation of 14 K
d) - 1400 J and approximate variation of 14 K
internal energy
As the system receives work, its sign is negative, as well as the heat, which in this process is lost.
The first law of thermodynamics is:
Substituting the values, we get:
R = 8.31 J/mol K
Temperature
By Joule's law, we have:
question 5
A perfect gas undergoes compression, doing 500 J of work. At the end of this transformation, the internal energy of the system changed 200 J less than at the beginning. The amount of heat exchanged by the gas was
a) - 700 J
b) - 300 J
c) 300J
d) 0J
e) 700 J
Since the work was received, that is, resistant work, its sign is negative.
Substituting the values into the equation of the first law of thermodynamics:
question 6
(CEDERJ 2021) In a stage of the cycle executed by an ideal gas in an air conditioner, the gas pressure is increased keeping its volume constant. At this stage of the cycle, the work W done by the gas, the amount of heat Q absorbed by it and the change ΔT in its temperature are, respectively:
a) W < 0, Q < 0 and ΔT < 0
b) W = 0, Q > 0 and ΔT > 0
c) W = 0, Q = 0 and ΔT = 0
d) W > 0, Q > 0 and ΔT > 0
Data:
Pressure P increases;
Volume remains constant;
Work
As the volume is constant, the work W is equal to zero.
The first law of thermodynamics goes like this:
Since heat is positive, the change in internal energy will also be positive.
Heat
Since heat is absorbed, it is positive.
Temperature
By the gas law:
Where,
n is the number of moles
R is the universal gas constant
Thus, the temperature depends only on the pressure, since the volume is constant, being positive.
question 7
(UNICENTRO 2018) According to the First Law of Thermodynamics, the change in the internal energy of a system, ΔU, is given by the difference between the heat exchanged with the outside environment, Q, and the work, W, done in the process thermodynamic. Considering this information, if a monatomic gas expands so as to always remain at the same temperature, this transformation can be represented by the equation
a) ΔU + W = 0
b) ΔU − W =0
c) Q − W = 0
d) Q + ΔU = 0
Isothermal process occurs without temperature change.
Energy is related to temperature by:
Where n is the number of moles and R is the universal gas constant. Since n and R are constant, there is only temperature variation, and
The first law of thermodynamics goes like this:
question 8
(URCA 2016) According to the first law of thermodynamics if, during an isothermal process undergone by an ideal gas of fixed mass, the gas releases an amount of heat whose magnitude is 50 cal then the change in internal energy and the work done by the gas in this process are, respectively:
a) 0 and 50 cal.
b) 50 cal and 0.
c) 0 and 0.
d) 50 cal and -50 cal.
e) 0 and -50 cal.
The change in internal energy is directly related to the change in temperature. As the process is isothermal, there is no temperature change, so .
From the first law of thermodynamics:
Since heat is released, its sign is negative.
question 9
(UFRN 2012) Biomass is one of the main sources of renewable energy and, therefore, machines that use it as fuel for power generation are important from an environmental point of view. A very common example is the use of biomass to drive a steam turbine to generate work. The figure on the side schematically shows a simplified thermoelectric power plant.
In this thermoelectric plant, the burning of biomass in the furnace produces heat, which heats the water in the boiler and generates high pressure steam. The steam, in turn, is conducted through pipes to the turbine which, under its action, starts to rotate its blades.
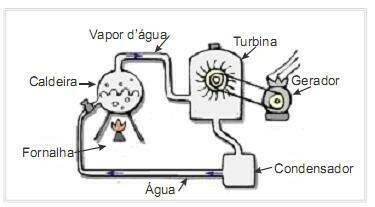
Assume heat losses due to temperature differences between the parts of this heat engine and the environment to be negligible. In this context, the variation in the internal energy of the boiler water
a) is greater than the sum of the heat supplied to it by burning the biomass and the work done on the turbine.
b) is equal to the sum of the heat supplied to it by burning the biomass with the work done on the turbine.
c) is equal to the difference between the heat supplied to it by burning the biomass and the work done on the turbine.
d) is greater than the difference between the heat supplied to it by burning the biomass and the work done on the turbine.
The water in the boiler receives energy in the form of heat from burning the fuel and releases energy in the form of work done on the turbine.
question 10
(UECE 2021) Regarding the properties of gases, pay attention to the following statements:
i. For an ideal gas, internal energy is a function of pressure only.
II. The heat absorbed by a gas when changing its state is independent of the process.
III. The internal energy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature only and is independent of the process.
IV. In an isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, the work done by it is equal to the heat absorbed.
It is correct what is stated only in
a) I and II.
b) III and IV.
c) I and IV.
d) II and III.
III. CORRECT. The internal energy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature only and is independent of the process.
The change in internal energy is directly related to the change in temperature.
Where n is the number of moles and R is the ideal gas constant, being constants, only the temperature determines the internal energy of the gas.
IV. CORRECT. In an isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, the work done by it is equal to the heat absorbed.
Since it is isothermal, there is no change in temperature, so the change in internal energy is zero. By the first law of thermodynamics:
Learn more with:
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics: laws, concepts, formulas and exercises
- Exercises on thermodynamics
- gas law
ASTH, Rafael. Exercises of the first law of thermodynamics.All Matter, [n.d.]. Available in: https://www.todamateria.com.br/exercicios-da-primeira-lei-da-termodinamica/. Access at:
See too
- Exercises on thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics
- adiabatic transformation
- Exercises on Thermochemistry
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- Natural sciences and their technologies: Enem
- Thermal energy
- Second Law of Thermodynamics

