To the oxygen function are a group of organic compounds that have oxygen atoms attached to the carbon chain. Are they:
alcohol;
ketone;
aldehyde;
carboxylic acid;
ester;
ether.
Read too:Hydrocarbons — compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen
Summary on oxygen function
Oxygen functions are a group of compounds that contain an oxygen atom. oxygen attached directly to the carbon chain.
The different oxygen functions are characterized by a specific structural arrangement of atoms, called a functional group.
The functional groups are responsible for the properties of each organic function.
The oxygen functions are: alcohol, ketone, aldehyde, carboxylic acid, ester and ether.
Video lesson on oxygen function
What are the oxygen functions?
Oxygenated body functions are those that have an oxygen atom bonded to an oxygen atom carbon of the carbon chain.
The oxygen functions are:
alcohol;
ketone;
aldehyde;
carboxylic acid;
ester;
ether.
The organic functions are identified by their functional group, which is a structural arrangement of atoms or bonds, responsible for the characteristic properties of that set of compounds.
Importance of oxygen functions
The presence of oxygen functions in organic compounds is able to change the properties of compounds, compared to the respective hydrocarbon, with an equal number of carbons.
Oxygen functions are characterized by the occurrence of hydroxyl, carbonyl or carboxyl groups. A presence of the oxygen atom increases the polar character compounds, making them more hydrophilic, that is, increasing their affinity for water.
Occurrence of oxygen functions is also responsible for the type of intermolecular forceacting between molecules. The nature and intensity of intermolecular forces affect the solubility and the melting and boiling temperatures.
The table below brings a comparison between some properties of three compounds that have the same number of carbon atoms, but differ by the presence of oxygenated functional groups.
Organic compost | |||
Butane (C4H10) |
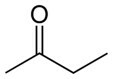
Butanone (C4H8O) |
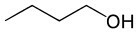
Butanol (C4H10O) |
|
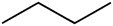 |
 |
 |
|
organic function |
Hydrocarbon |
ketone (oxygen function) |
Alcohol (oxygen function) |
Polarity |
apolar |
Polar |
Polar |
melting temperature |
-138.3°C |
-86°C |
-89°C |
boiling temperature |
-0.5°C |
80°C |
118°C |
Predominant intermolecular force |
Induced dipole |
permanent dipole |
hydrogen bonds |
Alcohol
The organic function alcohol has a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded directly to saturated carbon, that is, that carbon atom that establishes only single bonds.
Functional group of alcohols: R-OH (hydroxyl).
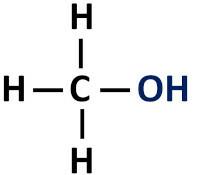
alcohols are classified according to the type of carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Primary alcohols have the hydroxyl attached to the primary carbon. Secondary alcohols have the hydroxyl group attached to a secondary carbon, and tertiary alcohols have their -OH group attached to tertiary carbons.
An organic compound that has only one hydroxyl is called a monoalcohol. If it has two hydroxyl groups, it is called a dialcohol. Above that, the molecules are called polyalcohols.
A nomenclature for alcohols follows the recommendation of Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry), considering the assembly of the name of chemical structures in three parts:
Prefix – related to the number of carbons.
Infix – refers to the type of chemical bond established between carbon atoms.
Suffix – related to the functional group. In the case of alcohols, the suffix used is -hello.
See examples:
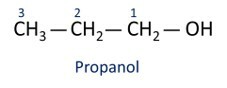
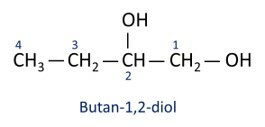
O main alcohol is ethanel (CH3CH2OH), used as a fuel, in alcoholic beverages, as a chemical solvent, cleaning agent and disinfectant.
ketone
The organic ketone function corresponds to the carbonyl functional group (C=O), located between two carbon atoms of the carbon chain.
Functional group of ketones: R1–(C=O)–R2.

Ketones are classified according to the number of carbonyl groups:
Monoketones – have a single carbonyl group.
Diketones – have two carbonyl groups.
Polytones – have more than two carbonyl groups.
A nomenclature for ketones follows the Iupac rules, but with a difference in the spelling of the suffix. Ketones are identified by the suffix -ona.
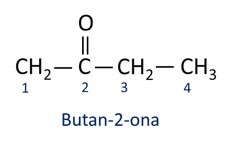
In general, ketones find application in the manufacture of other chemicals and pharmaceuticals. In industry, ketones are used as solvents for paints, dyes and varnishes. One of the most well-known ketones is propanone, which is popularly known as acetone. Acetone solutions are used for removing nail polish.
Read too:Amides — compounds that have a nitrogen attached to the carbonyl
Aldehyde
The organic aldehyde function is characterized by the presence of the carbonyl functional group, whose carbon atom has a hydrogen bond.
Functional group of aldehydes: H–C=O (formyl).
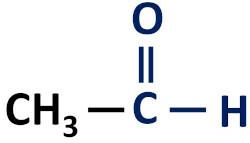
Aldehydes always occur at the end of carbon chains because their carbon atom needs to be bonded to at least one hydrogen atom.
A nomenclature for aldehyde compounds follows the IUPAC rules, differing by the suffix. Aldehydes are identified by the suffix -al.
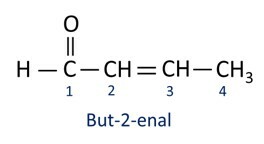
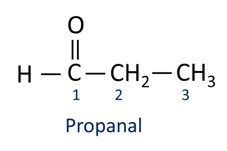
Aldehydes are used industrially in the manufacture of perfumes and flavoring, as its smell and taste vary according to the length of the carbon chain. Aldehyde compounds are also used in the manufacture of cleaning products, medicines, polymers, among others. Short carbon chain aldehydes can be used as a conservation agent, such as the famous formalin, which is an aldehyde named methanal.

carboxylic acid
The organic carboxylic acid function is identified by the presence of the carboxyl functional group (-COOH).
Functional group of carboxylic acids: –(C=O)OH or –COOH.

Compounds belonging to this organic function are weak acids, as they easily release H ions+ in aqueous solution.
A nomenclature for carboxylic acids follows the IUPAC rules, however the term “acid” appears before the prefix that indicates the carbon number, and the suffix used is -oic.
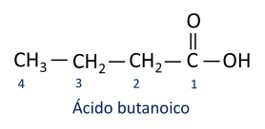
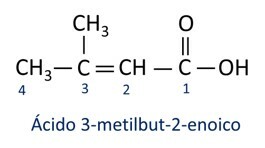
O most common carboxylic acid in everyday life is the Acetic Acid, substance present in vinegar. Vitamin C, abundant in many citrus fruits, is an organic molecule called ascorbic acid.
Ester
The organic ester function is identified by the presence of the carbonyl functional group, whose carbon atom has an oxygen ligand.
Functional group of esters: –R–(C=O)O–R'.
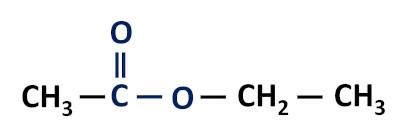
The esters are derivatives of carboxylic acids, differing from these in that they have an alkyl radical attached to the oxygen atom instead of the hydrogen atom.
Molecules belonging to the ester function are formed by the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, a reaction known as esterification.
The rules for nomenclature of esters defined by Iupac consider that the molecule is formed by two parts:
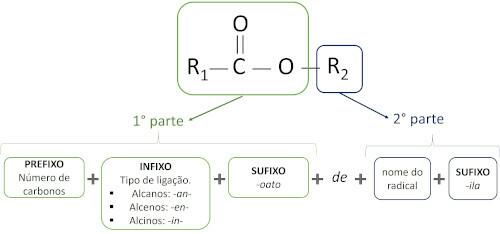
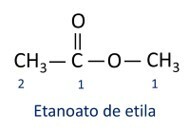
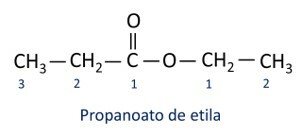
The main characteristic of esters is their ability to simulate taste and aroma of natural foods, according to the length of carbon chains (R1 and R2). Because of this, esters are widely used as flavoring agents in the food industry, in the production of pharmaceuticals, perfumes and cosmetics.
Ether
The ether organic function is characterized by having an oxygen atom between two carbon chains.
Functional group of ethers: R–O–R.

Ethers are highly flammable substances, with a characteristic and strong odor.
A official Iupac nomenclature for ethers follows the order prefix + infix + suffix. However, the side of the molecule that has the fewest carbons receives the suffix -oxy while the longer carbon chain is named as if it were a hydrocarbon, receiving the suffix -o.
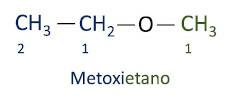
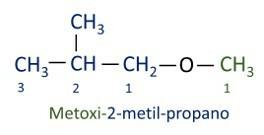
The ethers are used as solvents for paints, resins, oils and fats. As a result, they are used in different industrial and pharmaceutical processes. Ether was once used as an anesthetic, being replaced by other safer substances these days.
Read too:Nitro compounds — compounds that contain nitro (NO2) groups in their molecule
Solved exercises on oxygen functions
question 1
(Uece) In Organic Chemistry, a functional group is defined as a molecular structure that gives substances similar chemical behavior. The set of compounds that have the same functional group is called organic function. Mark the option that correctly presents the compound and the organic function to which it belongs.

Resolution:
Letter C
Among the alternatives, the only one that correctly expresses the functional group to the name of the chemical function is item C. The organic ester function is defined by the carbonyl functional group, whose carbon atom also has an oxygen ligand.
In item A, the ether functional group is expressed.
In item B, the ketone functional group is expressed.
In item D the amide functional group is expressed. amines It is amides belong to the nitrogen functions.
question 2
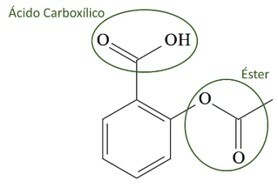
(UCS-RS) In the 5th century BC. C., Hippocrates, Greek physician, wrote that a willow bark product relieved pain and lowered fever. This same product, an acid powder, is even mentioned in texts from the ancient civilizations of the Middle East, from Sumeria, Egypt and Assyria. Native Americans also used it against headaches, fever, rheumatism and tremors. This drug is a precursor to aspirin, the chemical structure of which is shown below.
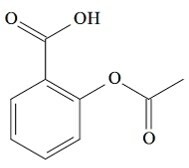
The organic functions present in the structure of aspirin, represented above, are:
a) carboxylic acid and ester.
b) alcohol and ether.
c) amine and amide.
d) amine and ether.
e) amino acid and alcohol.
Resolution:
Letter a
By Ana Luiza Lorenzen Lima
Chemistry teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/funcoes-oxigenadas.htm
