Test your knowledge with the 10 questions below on hydrocarbon nomenclature. Clear your doubts about the topic with the comments after the feedback.
In the nomenclature of organic compounds, the suffix indicates the corresponding organic function, which in the case of hydrocarbons is:
to
b) OL
c) AL
d) ON
The suffix is the last element in the nomenclature of an organic compound. Check out the examples below.
methaneO
EthanO
propaneO
ButanO
Therefore, the ending with “o” indicates that the substances are hydrocarbons.
In the official nomenclature, according to IUPAC, AN, EN and IN are infixes that indicate in hydrocarbons
a) the type of bond between the atoms of the compound.
b) the type of bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
c) the type of bond between carbon atoms in the main chain.
d) the type of bond between the side chain radicals.
The bonds between the carbon atoms in the main chain can be:
AN: single link
Example: ETANO
EN: double bond
Example: ETENO
IN: triple bond
Example: ETHINE
The nomenclature of hydrocarbons has three basic elements: prefix + infix + suffix. For example, the name of a compound prefixed with BUT indicates that
a) the hydrocarbon has 2 carbon atoms in the main chain
b) the hydrocarbon has 3 carbon atoms in the main chain
c) the hydrocarbon has 4 carbon atoms in the main chain
d) the hydrocarbon has 5 carbon atoms in the main chain
The prefix in hydrocarbon nomenclature indicates the number of carbons. Therefore, BUT informs that there are 4 carbon atoms in the main chain.
Example: BUTYEAR
The correct name of the branched hydrocarbon, whose formula is outlined below, is:
a) isobutane
b) 2-methylbutane
c) Pentane
d) 1,1 dimethylpropane
Analyzing the main chain, we identified that the hydrocarbon is butane.
Prefix: BUT, which indicates the existence of 4 carbons in the main chain.
Intermediary: AN, which corresponds to single bonds.
Suffix: O, which corresponds to the hydrocarbon function.
In addition, there is a branch on carbon 2 of the main chain and its name is METHYL ().
Therefore, the name of the compound is 2-methylbutane.
Correctly match the hydrocarbon in column 1 to the corresponding classification in column 2.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
| I. Methane | ( ) alkane |
| II. Benzene | ( ) alkene |
| III. cyclobutene | ( ) Alkyne |
| IV. ethnicity | ( ) Cyclone |
| v. cyclopentane | ( ) Cyclene |
| SAW. propadiene | ( ) Cycle |
| VII. cyclohexine | ( ) Alcadiene |
| VIII. propylene | ( ) Aromatic |
a) I, VIII, IV, V, III, VII, VI and II
b) II, VI, VII, III, I, IV, VIII and V
c) I, II, III, IV, V, VIII, VI and VII
d) VI, VII, I, II, III, VIII, V and IV
alkane: open-chain hydrocarbon with single bonds, such as methane.
alkene: open-chain hydrocarbon with a double bond, such as propylene.
alcino: triple-bonded open-chain hydrocarbon, such as ethnic.
cyclane: closed-chain hydrocarbon with single bonds, such as cyclopentane.
Cyclene: closed-chain hydrocarbon with a double bond, such as cyclobutene.
cycle: triple-bonded closed-chain hydrocarbon, such as cyclohexine.
alkadiene: open-chain hydrocarbon with two double bonds, such as propadiene.
Aromatic: closed-chain hydrocarbon with alternating single and double bonds, such as benzene.
Build the structure of the hydrocarbon with the indications below.
- The main chain contains 5 carbon atoms;
- All links in the main chain are single;
- There are 3 methyl radicals in the structure: two on carbon 2 and one on carbon 4.
The official nomenclature of the compound is:
a) trimethylpentane
b) 2,2,4 methylpentane
c) 2,2 methylpent-4-ane
d) 2,2,4 trimethylpentane
The compound presented in the question is a branched alkane, whose official name is 2,2,4 trimethylpentane.
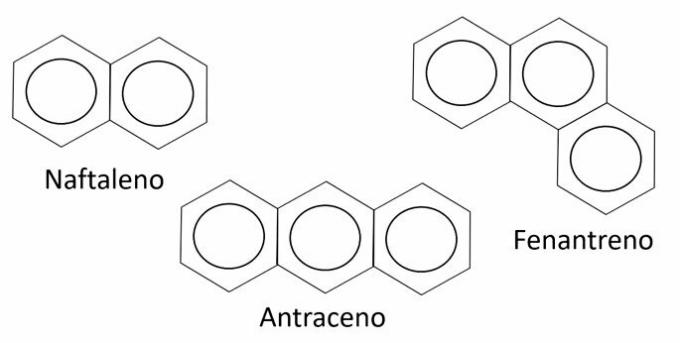
Naphthalene, anthracene and phenanthrene are names for hydrocarbons
a) Saturated
b) Aliphatic
c) Aromatics
d) cyclic
Aromatic hydrocarbons are compounds formed by at least one benzene ring, which consists of a closed chain with 6 carbon atoms and alternating single and double bonds.
The nomenclature of aromatic hydrocarbons is done differently and does not follow the general rules. Therefore, each compound has a specific name, as is the case with naphthalene, anthracene and phenanthrene. Note that the only similarity is in the suffix, as the names end in “eno”.
In the nomenclature of aromatic hydrocarbons ortho, goal and for indicate
a) the number of benzene nuclei
b) the location of the branches
c) the number of alternate connections
d) the type of alkyl radical
Aromatic hydrocarbons are designated by particular names, that is, they do not follow a specific nomenclature like other compounds with carbon chains.
As these compounds are subject to two or more substituents, it is necessary to enumerate the carbon atom as a way of indicating where the substitution occurs.
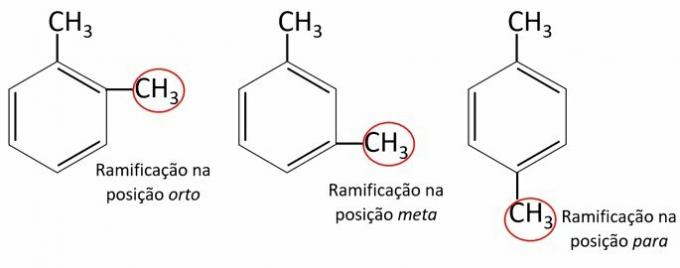
Look at the following structures and analyze the statements

I. The carbon chains of compounds are aliphatic, as they have alternating double bonds.
II. The hydrocarbons shown are polynuclear, as they have more than one radical.
III. The correct nomenclature of the compounds is 1,2 methylbenzene, 1,3 methylbenzene and 1,4 methylbenzene.
IV. The compounds present methoxy as ligands in the ortho, meta and para positions.
The statements are correct
a) only I
b) III and IV
c) I, II and III
d) None of the statements are correct.
I. WRONG. The carbon chains of the compounds are aromatic.
II. WRONG. The aromatic hydrocarbons presented are mononuclear, that is, they have only one benzene ring.
III. WRONG. The correct nomenclature of the compounds is 1,2 dimethylbenzene, 1,3 dimethylbenzene and 1,4 dimethylbenzene.
IV. WRONG. The radical present in the compounds of the image is methyl (-CH3) in the ortho, meta and para positions. The methoxy radical is -OCH3.
(UECE/2021-Adapted) The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature of organic compounds is very important to identify them internationally. This nomenclature follows rules that allow determining its structural formula. Thus, it is correct to say that the compound 5-ethyl-4-phenyl3-methyl-hex-1-ene contains
a) four π(pi) bonds.
b) only three tertiary carbon atoms.
c) a saturated main carbon chain.
d) fifteen carbon atoms and twenty-one hydrogen atoms.
a) CORRECT. One π(pi) bond is located on the main chain and the other three on the phenyl radical.
b) WRONG. There are 4 tertiary carbon atoms: 3 on the main chain and 1 on the phenyl radical.
c) WRONG. The carbon chain has unsaturation, that is, a double bond at carbon 1.
d) WRONG. There are 15 carbon atoms and 22 hydrogen atoms.