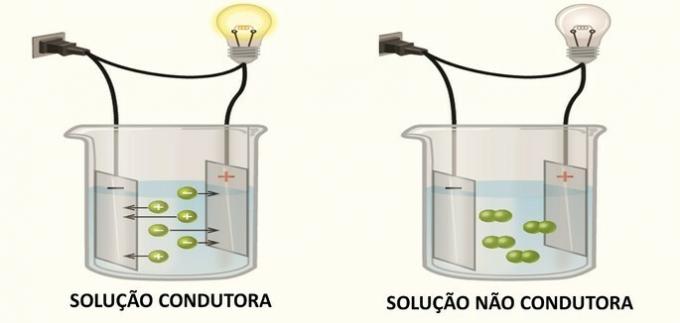
The plasma membrane is a thin cell envelope, mainly responsible for the flow of substances in the cell.
Check out the questions below to test your knowledge of the topic. The commented resolutions will help you to acquire more knowledge.
question 1
Identify in the alternatives below which does NOT have a plasma membrane function.
a) Control of the entry and exit of substances from the cell.
b) Protection of the internal structures of the cell.
c) Delimitation of intracellular and extracellular content.
d) Recognition of substances.
e) Cellular respiration and energy production.
Answer: e) Cellular respiration and energy production.
Cellular respiration and energy production is the responsibility of the mitochondria, organelles located inside the cell.
The cell membrane is located on the cell surface, delimiting it and allowing the passage or not of substances. Therefore, it protects the cell interior and controls what enters and leaves the cell, by recognizing substances.
question 2
American biologists Seymour Jonathan Singer and Garth L. Nicolson, in 1972, identified that the plasma membrane had a structure they named fluid mosaic.
Check the alternative that justifies the choice of the model to represent the membrane.
a) The membrane has discontinuities.
b) The membrane has flexible and fluid structures.
c) The membrane has few and equal elements.
d) The membrane has a high level of disorganization.
e) The membrane has rigid and fixed structures.
Answer: b) The membrane has flexible and fluid structures.
The plasma membrane is identified by the fluid mosaic model for having flexible structures and in constant movement.
Basically, the cell membrane is formed by a lipid bilayer with proteins distributed in the organization of the film around the cell.
question 3
In the plasma membrane scheme below, the sequence that correctly fills in the spaces numbered 1 to 5 is:

a) 1 - protein bilayer; 2 - whole protein; 3 - transmembrane protein; 4 - channel protein and 5 - carbohydrates.
b) 1 - lipid bilayer; 2 - transmembrane protein; 3 - whole protein; 4 - channel protein and 5 - amino acids.
c) 1 - lipid bilayer; 2 - peripheral protein; 3 - whole protein; 4 - channel protein and 5 - carbohydrates.
d) 1 - protein bilayer; 2 - peripheral protein; 3 - whole protein; 4 - channel protein and 5 - lipids.
e) 1 - lipid bilayer; 2 - peripheral protein; 3 - transmembrane protein; 4 - channel protein and 5 - amino acid.
Answer: c) 1 - lipid bilayer; 2 - peripheral protein; 3 - whole protein; 4 - channel protein and 5 - carbohydrates.
1 - Lipid bilayer: basic structure of the membrane formed by phospholipids, cholesterol and glycolipids.
2 - Peripheral protein: located on only one side of the membrane.
3 - Integral protein: crosses the membrane side by side.
4 - Channel protein: allows the diffusion of certain molecules or ions.
5 - carbohydrates: components of glycoproteins that project to the outside of the cell.
question 4
One of the main functions of the plasma membrane is to control the entry and exit of substances from the cell. Through its selective permeability, the cell envelope performs __________ and transports materials from the most concentrated region to the less concentrated one without wasting energy. When ATP is used to move substances from the less concentrated to the more concentrated medium, __________ occurs.
Blank spaces are correctly filled in by:
a) simple diffusion and active diffusion.
b) simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion.
c) bulk transport and passive transport.
d) passive transport and active transport.
e) bulk transport and active transport.
Answer: d) passive transport and active transport.
One of the main functions of the plasma membrane is to control the entry and exit of substances from the cell. Through its selective permeability, the cell envelope performs the passive transport and transports materials from the most concentrated to the least concentrated region without wasting energy. When ATP is used to displace substances from the less concentrated to the more concentrated medium, the active transport.
Active transport and passive transport are mechanisms for transporting substances across the membrane.
Materials enter and leave the cell by passive transport, such as simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion, without wasting energy as the displacement occurs naturally from the most concentrated medium to the least focused.
In active transport, as in bulk transport, the transfer of substance from one region to another takes place against a concentration gradient. Because the transport takes place from the less concentrated region to the most concentrated, it is necessary to expend energy (ATP) to carry out the displacement.
question 5
In some organisms there is a cell wall, an envelope that is located externally after the plasma membrane. The main difference in the composition of the prokaryotic cell wall and cell membrane is:
a) The prokaryotic cell wall is formed by the association of carbohydrates with proteins, while the cell membrane is made up of lipids and proteins.
b) The prokaryotic cell wall is formed by the association of amino acid with protein, while the cell membrane is made up of lipids and carbohydrates.
c) The prokaryotic cell wall is formed by the association of lipid with protein, while the cell membrane is made up of carbohydrates and proteins.
d) The prokaryotic cell wall is formed by the association of carbohydrate with amino acid, while the cell membrane is made up of lipids and proteins.
e) The prokaryotic cell wall is formed by the association of carbohydrate with lipid, while the cell membrane is made up of lipids and amino acids.
Answer: a) the prokaryotic cell wall is formed by the association of carbohydrate with protein, while the cell membrane is made up of lipids and proteins.
In prokaryotic beings, cells have a cell wall, whose main substance in the composition is peptidoglycan, which is formed by the association of carbohydrate with protein.
Unlike the cell wall, the plasma membrane is of lipoprotein composition, that is, the junction of lipids with proteins occurs.
question 6
The plasma membrane, also called the lipoprotein membrane, is one of the basic structures of the cell. Identify which of the components below DOES NOT make up the plasma membrane.
a) Antigens
b) Phospholipids
c) Cytosol
d) Enzymes
e) Cholesterol
Answer: c) Cytosol.
Antigens and enzymes are proteins that occupy the plasma membrane. Phospholipids and cholesterol are lipids that are part of its composition.
Therefore, the only component of the alternatives that is not part of the plasma membrane is the cytosol. This material, also called hyaloplasm, is present in the cell cytoplasm, being a viscous and semi-transparent matrix where molecules and cell organelles are dispersed.
question 7
The lipid bilayer is the basic structure of the plasma membrane, formed by phospholipids, cholesterol and glycolipids. As they are amphipathic molecules, lipids have polar and non-polar portions.
In phospholipids, the hydrophilic and hydrophobic portions correspond, respectively, to:
a) hydrophilic, part polar, with phosphorus and hydrophobic, part non-polar, with lipids.
b) hydrophilic, part polar, with the phosphite group and hydrophobic, part non-polar, with amino acids.
c) hydrophilic, part non-polar, with the hydroxyl radical and hydrophobic, part polar, with incorporated carbohydrates.
d) hydrophilic, part non-polar, with the phosphate group and hydrophobic, part polar, with the hydrocarbon chains.
e) hydrophilic, part polar, with the phosphate group and hydrophobic, part non-polar, with the long “tails” of fatty acids.
Answer: e) hydrophilic, part polar, with the phosphate group and hydrophobic, part non-polar, with the long “tails” of fatty acids.
Phospholipids are made up of “polar heads” and their “tails”.
The phosphate groups are located in the polar part and, therefore, these ends are hydrophilic, that is, capable of interacting with water. The tails are long chains of hydrocarbons that, being hydrophobic, do not interact with water.
question 8
In the lipid bilayer, the polar “head” of phospholipids are on each face of the membrane, in contact with the cytosol and extracellular fluid. The “tails” of fatty acids are oriented inside the membrane.
One of the main properties of the plasma membrane is selective permeability. Materials, such as water, nutrients and oxygen, enter the cell and others, such as carbon dioxide, leave the cell structure through the membrane.
The transport of substances through the plasma membrane can be carried out with or without energy expenditure. Tick the alternative that presents a transport in favor of the concentration gradient.
a) Sodium pump
b) Potassium pump
c) Coupled transport
d) Diffusion facilitated
e) Bulk transport
Answer: d) Diffusion facilitated.
Passive transport is characterized by the passage of substances without energy expenditure, as the material flow follows a concentration gradient, from the more concentrated to the less concentrated region.
Among the alternatives, only facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport. In it, the proteins existing in the plasma membrane help the passage through the lipid bilayer.
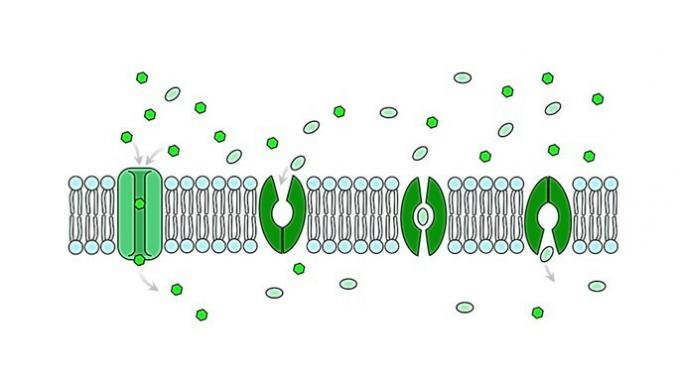
The other alternatives are active cell transports, which take place with energy expenditure.
question 9
The proteins that make up the plasma membrane are basically classified as integral and peripheral. The main difference between them is that:
a) while the integral proteins are intercalated in the lipid bilayer, the peripheral proteins cross the membrane side by side.
b) while integral proteins have the ability to cross the membrane, peripheral proteins are located on only one face of the membrane.
c) while integral proteins do not attach directly to the lipid bilayer, peripheral proteins are strongly bound to membrane lipids.
d) while integral proteins are located on the inner face of the plasma membrane, peripheral proteins are part of the cell's exterior.
e) while integral proteins project to the cell cytosol, peripheral proteins are intercalated in the lipid bilayer.
Answer: b) while integral proteins have the ability to cross the membrane, peripheral proteins are located on only one face of the membrane.
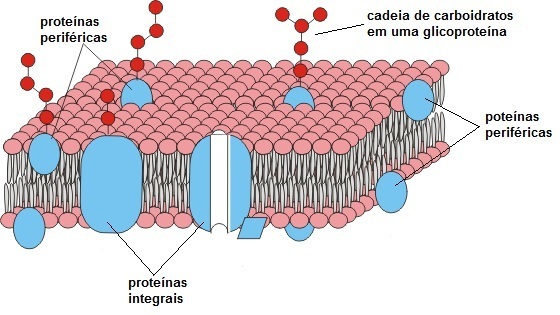
Integral proteins, also called transmembrane proteins, have the ability to cross the membrane side by side, projecting both to the cytosol, inside the cell, and to the region extracellular.
Peripheral proteins are located on only one side of the membrane, on the inner or outer surface.
question 10
The cell membrane is a dynamic and fluid structure, consisting of a lipid bilayer, which is part of all cells in living beings.
It has specializations in some cells, which are important modifications to perform their functions, such as:
a) microvilli, desmosomes and interdigitations.
b) microcavities, mesosomes and interconnections.
c) microvilli, mesosomes and interdigitations.
d) microcavities, mesosomes and interdigitations.
e) microvilli, desmosomes and interconnections.
Answer: a) microvilli, desmosomes and interdigitations.
Microvilli can be found in cells to facilitate the absorption of substances, such as in the small intestine, as it increases the area of absorption by the projections created.
Desmosomes are dense plaques, a coating that makes it possible for two adjacent cells to adhere.
Interdigitations are protrusions that allow cells to fit with their neighboring cells to facilitate the exchange of substances.
question 11
(UFESC) One of the fundamental properties of the plasma membrane is its selective permeability. Various processes for passing substances through the membrane are known. It can be said, about them, that:
01. Osmosis is the passage of solvent from the more concentrated medium to the less concentrated medium.
02. All transport of substances across the membrane involves energy expenditure.
04. Diffusion is facilitated when it involves the presence of specific carrier molecules.
08. Active transport is characterized by the passage of solute against a concentration gradient and in the presence of carrier molecules.
Answer: 12 (04 + 08).
01. WRONG. Osmosis is the passage of solvent from a medium with a lower concentration to another with a higher concentration.
02. WRONG. Transport can be active with energy expenditure and passive transport without energy expenditure.
04. CORRECT The proteins that permeate the lipid bilayer, called permeases, help transport substances through facilitated diffusion.
08. CORRECT The transport of substances occurs from the region with the lowest concentration to the one with the highest concentration. In coupled transport, a type of active transport, transport proteins are essential for the passage of substances.
question 12
(Enem/2019) The fluidity of the cell membrane is characterized by the ability of the molecules that make up this structure to move. Living beings maintain this property in two ways: by controlling temperature and/or by changing the lipid composition of the membrane. In this last aspect, the size and degree of unsaturation of the hydrocarbon tails of phospholipids, as represented in the figure, significantly influence fluidity. This is because the greater the magnitude of the interactions between the phospholipids, the less fluid the membrane will be.
Thus, there are lipid bilayers with different phospholipid compositions, such as those shown in I to V.
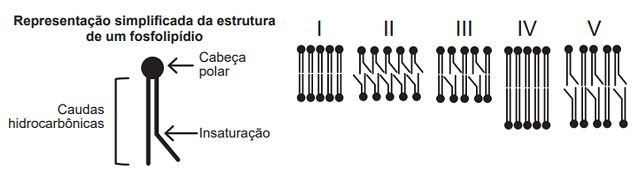
Which of the lipid bilayers presented has greater fluidity?
there
b) II
c) III
d) IV
e) V
Answer: b) II.
The intermolecular force between the components of the lipid bilayer is related to the fluidity of the plasma membrane.
Therefore, the lower the intermolecular force, the greater the fluidity of the membrane, as it reduces the interaction between phospholipids.
To gain more knowledge, the following texts will help you:
- Plasma membrane
- Active transport
- passive transport