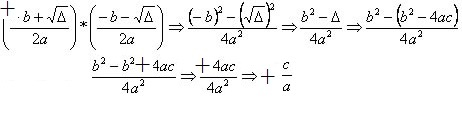Answer: The sum of the real roots is zero.
We factor the how
and we rewrite the equation as:
We do and we substitute in the equation.
We fall back on a quadratic equation with parameters:
a = 1
b = -2
c = -3
The discriminant of the equation is:
The roots are:
y1 and y2 are the roots of the quadratic equation, but we're finding the roots of the 4th-degree bisquare equation.
We use the relation to find the roots of the bisquare equation for each y value found.
For y1 = 3
are real roots.
For y2 = -1
Since there is no solution in the set of real numbers for the square root of a negative number, the roots are complex.
So the sum of the real roots is:
Right answer:
First we must manipulate the equation in order to position on the same member of the equality.
Making the distributive and passing the 81 to the left side:
We have a bisquare equation, that is, twice squared. To solve, we use an auxiliary variable, doing:
We factor the in equation I and rewrite it as
. So, equation I becomes:
We use the device of equation II, substituting in equation I, per
.
Once we have a quadratic equation, let's solve it using Bhaskara.
The parameters are:
a = 1
b = -18
c = 81
The delta is:
The two roots will be equal to:
Once the roots y1 and y2 are determined, we substitute them in equation II:
Thus, the solution set of the equation is:
Response:
Moving the 15 to the left side:
factoring how
:
Doing and substituting in the equation:
In the polynomial equation of the second degree of variable y, the parameters are:
a = 1
b = -8
c = 15
Using Bhaskara to determine the roots:
The equation we are solving is the bisquare, with variable y, so we have to come back with the values for y.
Substituting in the relation :
For the root x1=5
For the root x2 = 3
So, the solution set is: .
Answer: The product of the real roots of the equation is -4.
factoring for
and rewriting the biquadratic equation:
Doing and substituting in the equation, we have an equation of the second degree of parameters:
a = 1
b = 2
c = -24
The delta is:
The roots are:
The biquadratic equation is in the variable x, so we must go back through the relation .
For y1 = 4
For y2 = -6
Since there is no real solution to the square root of a negative number, the roots will be complex.
The product of the real roots will be:
Answer: The roots of the equation are: -3, -1, 1 and 3.
Doing the distributive and bringing the -81 to the left side:
For simplicity, we can divide both sides by 9:
Since we get a bisquare equation, let's reduce it to a quadratic equation, doing .
The equation is:
The parameters are:
a = 1
b = -10
c = 9
The delta will be:
The roots are:
Returning to x, we do:
For the root y1 = 9
For the root y2 = 1
So the roots of the equation are: -3, -1, 1 and 3.
Correct answer: d) 6
factoring the for
and rewriting the inequality:
Doing and substituting in the previous inequality:
Solving the parameter inequality:
a = 1
b = -20
c = 64
Calculating the delta:
The roots will be:
Substituting the roots y1 and y2 in the relationship between x and y:
For the root y1 = 16
For the root y2 = 4
Analyzing the intervals that satisfy the condition:
[ -4; -2] and [2; 4]
Therefore, considering only the integers that make up the intervals:
-4, -3, -2 and 2, 3, 4
Six integers satisfy the inequality.
Correct answer: a) .
factoring for
and rewriting the equation:
Doing and substituting in the above equation:
We fall back on an equation of the second degree of parameters:
a = 2
b = -8
c = 6
Calculating the delta:
The roots are:
Substituting the roots of the quadratic equation x1 and x2 into the equation relating x and y:
For x = 3, we have:
For x = 1, we have:
So, the solution set is:
Right answer: .
factoring equal to
and rewriting the equation:
Doing and rewriting the equation:
In the quadratic equation the parameters are;
a= 1
b= -11
c = 18
The delta is:
Now we must substitute the values of the roots of the quadratic equation y1 and y2 in the relation .
For y1 = 9
For y2 = 2
Therefore, the product of the positive roots will be: