THE evapotranspiration it is a process that can be defined as the evaporation of water from the soil plus the transpiration of plants. Through this process, water is returned to the atmosphere, so it is directly related to the water cycle.
The term evapotranspiration was used for the first time in 1944, by Thornthwaite & Wilm, in reference to the simultaneous occurrence of water present in the soil and the transpiration of plants.
Read too:Water — everything you need to know about this essential resource for life
What is evaporation?
Before we can better understand what evapotranspiration is, we need to define evaporation. Evaporation is a process by which water slowly changes from liquid to gas and gradual, at a temperature below the boiling point. For evaporation to occur, factors such as temperature, radiation, wind and air humidity must be considered.
Evapotranspiration process
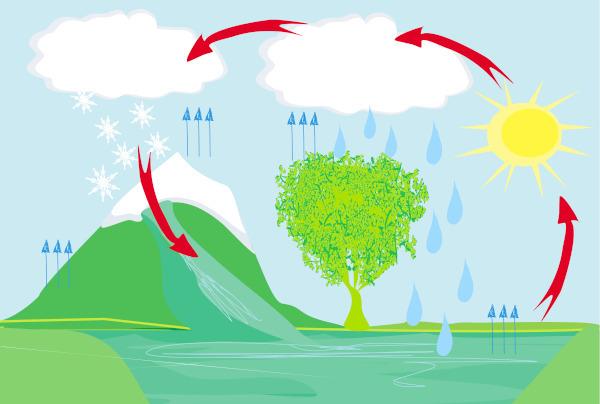
Evapotranspiration can be defined as the loss of water through soil evaporation and plant transpiration. This process occurs in greater quantity in areas with higher temperature and abundant precipitation. For evapotranspiration to occur, factors such as soil water availability and the stage of vegetation development must be considered.
In a region of woods and forests with trees, the transpiration of the plant can vary according to the amount of leaves of the plant, the state of its leaves and also the seasons. In the case of agricultural crops, the transpiration rate varies during sowing, plant growth, maturity and harvest phases.
Importance of evapotranspiration
evapotranspiration is essential for the water cycle, since it is through this process that a large amount of water returns to the atmosphere. When returning to the atmosphere, the water vapor can help in the formation of clouds, thus contributing to the regulation of the rainfall regime. In addition, evapotranspiration affects atmospheric moisture, water balance of microbasins and crop development and yield.
Read too: Watersheds - drainage area of a main river and its tributaries
Evapotranspiration in the Amazon Forest
THE Amazon rainforest it is the largest tropical forest on the planet and occupies a large part of the Brazilian territory. It is responsible for the formation of air masses laden with water vapor, known as “flying rivers”.the water of Atlantic Ocean it evaporates, thanks to the heat of the sun, and the vapor formed enters the continent due to the action of the trade winds. Upon reaching the Amazon region, the column of humid air coming from the ocean receives the moisture released by the forest trees through the process of transpiration.
The "flying rivers" ensure that rain from the Amazon is taken to the regionscentral and Southeastern regions of the country. O logging of the Amazon Forest, however, puts the route of these “rivers” at risk, directly affecting the rainfall regime in various parts of Brazil. To learn more, read: Flying rivers of the AmazonThe.
Basic concepts related to the evapotranspiration process
potential evapotranspiration
Potential evapotranspiration can be defined as the total water transferred by evaporation and transpiration to the atmosphere, in an area with extensive natural surface, totally covered by low-sized vegetation and well supplied with Water. In other words, we can say that potential evapotranspiration is the maximum evapotranspiration what would happen if the ground had a sufficient supply of water.
Reference Evapotranspiration
Reference evapotranspiration is a concept used to refer to the loss of water from a surface cultivated with grass, which it has a height of 0.08 to 0.15 m, in an active development phase, covering the entire ground and not showing deficiency of Water.
Actual or current evapotranspiration
Actual or current evapotranspiration refers to amount of water transferred to the atmosphere by evaporation and transpiration, considering the actual conditions of soil moisture and atmospheric factors. We can define real evapotranspiration also as the evapotranspiration that actually occurs due to the limited availability of water in the soil and the variability of the plant cycle. This evapotranspiration must always be equal to or less than the potential evapotranspiration.
Perspiration in the vegetable
Perspiration is a process that consists of loss of water by the vegetable in the form of steam. It can occur in any part of the vegetable, but the main organ related to the process is the leaves. In leaves, the presence of cuticle serves as an effective barrier against water loss, however a small fraction of water is lost by this coating. The biggest loss, however, occurs through the stomata.

The opening and closing of stomata directly affects a plant's transpiration rate. When closed, the stomata prevent the loss of water through perspiration, but they also keep out carbon dioxide. Therefore, the sweating process is directly linked to the absorption of carbon dioxide by the leaf, a process that is fundamental for the realization of photosynthesis. Thus, sweating is considered an unavoidable evil. It is worth noting that excessive transpiration is harmful to the plant, and can even kill the plant by dehydration.
Another point that deserves attention in relation to transpiration in vegetables is the theory of tension-cohesion. According to this theory, water moves from the roots towards the aerial parts of the plant, due to a tension generated by the transpiration and/or water use in leaves and the cohesion of water molecules, which allow this tension to be transmitted along all the xylem. To learn more, read: Water transport through the vegetable body.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/evapotranspiracao.htm

