Kps is the acronym used to represent the solubility product constant, which refers to the product (multiplication) of the concentrations in quantity of matter of the ions present in a solution.
Whenever a poorly soluble solute is added to a solvent such as barium sulfate, a small amount of part of this salt dissolves in the water, and the rest accumulates in the bottom of the container, forming the body of background. The salt that dissolves suffers dissociation, releasing cations and anions into the water.

Precipitate present in a solution with water and barium sulfate
Besides the salt does not present good solubility, the amount of dissolved solute does not change over time because there is a dissolution equilibrium between the salt ions (present in the solution) and the background body.

BaSO Dissolution Balance4 in water
Kps of a solute
O Kps of a solute is the product of the molar concentrations of the participating ions. It is always necessary to raise the ion concentration to its respective stoichiometric coefficient (used to balance the equation).
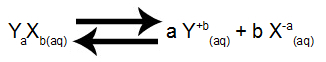
Dissolution equilibrium of electrolyte YTheXB
O Kps of the proposed equilibrium for salt YTheXB it will have the concentration of reagent Y (raised to its stoichiometric coefficient (a) and the concentration of product X (raised to its stoichiometric coefficient (b)).
Kps = [Y+b]The.[X-The]B
Example
Suppose we are preparing a solution with water and aluminum cyanide [Al(CN)3], which is a practically insoluble salt in water. When this salt is added to water, it ends up suffering the phenomenon of dissociation.

Al (CN) electrolyte dissolution equilibrium3
So, through the equation of the equilibrium of salt dissolution, we have that its Kps will have the multiplication of the concentration of the aluminum cation (Al+3) raised to exponent 1 by the concentration of cyanide anion (CN-1) raised to exponent 3.
Kps = [Al+3]1.[CN-1]3
Kps meanings of a solute
When we find the Kps of a particular salt mixed with water, we also know the concentration of each of the ions in the solution. With this data, we can determine the ranking of a solution or the behavior of the solute in the solution. Consider the following balance:
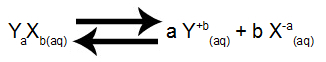
Dissolution equilibrium of electrolyte YTheXB
We can make the following relationships:
If Kps = [Y+b]The.[X-The]B = 0, we have a saturated solution without the presence of precipitate;
If Kps > [Y+b]The.[X-The]B = 0, we have an unsaturated solution, that is, a low amount of solute dissolved in the solvent (in relation to solubility coefficient);
If Kps < [Y+b]The.[X-The]B = 0, we have a saturated solution with a bottom body, that is, there will be a precipitation of the electrolyte (solute);
If the Kps value of the electrolyte is too low, it is a poorly soluble material in the solvent.
Example of Kps calculation of a solute
(UERN): The solubility of calcium nitrate [Ca (NO3)2] in water is 2.0. 10–3 mol/liter at a certain temperature. The Kps of this salt at the same temperature is:
a) 8.10–8.
b) 8.10–10.
c) 3.2.10–10
d) 3.2.10–8
Exercise data:
Formula of salt: Ca (NO3)2;
Molar salt concentration (solubility): 2.0. 10–3 mol/L.
To solve and calculate Kps, you need to do the following:
Step 1: Set up the salt dissolution balance.
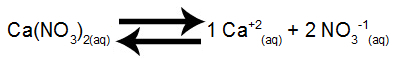
Calcium nitrate dissolution equilibrium in water
Calcium nitrate, when undergoing dissociation in water, releases 1 mol of calcium cations (Ca+2) and 2 mol of nitrate anions (NO3-1).
Step 2: Assemble the expression of the Kps of the salt
The Kps of this salt will be the product of the calcium cation concentration raised to exponent 1 by the concentration of the nitrate anion raised to exponent 2, as shown below:
Kps = [Ca+2]1.[AT THE3-1]2
Step 3: Determine the values of ion concentrations in the solution
To calculate the Kps, we need the values of the ion concentrations, however, the exercise provided the molarity of the salt in the solution. To determine the concentration of each ion, simply multiply the molarity of the salt by the stoichiometric coefficient of the participant in the reaction:
For calcium cation:
[Here+2] = 1. 2,0. 10–3
[Here+2] = 2,0. 10–3 mol/L
For the nitrate anion:
[AT THE3-1] = 2. 2,0. 10–3
[AT THE3-1] = 4,0. 10–3 mol/L
Step 4: Use the concentration values found in step 3 in the Kps expression (determined in step 2).
Kps = [Ca+2]1.[AT THE3-1]2
Kps = [2.10-3]1.[4.10-3]2
Kps = 2.10-3.16.10-6
Kps = 32.10-9
or
Kps = 3.2.10-9 (mo/L)
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-kps.htm
