The flower is the structure responsible for the reproduction of angiosperm plants.
It is through reproduction that new plants are originated, ensuring the maintenance of ecosystems.
Functions of flowers
The primordial function of flowers is the production of seeds for the formation of new plants, ensuring the survival of the species.
Thus, the flower is responsible for the reproduction of plants. For this, they are formed by modified leaves, usually with attractive colors and different formats to attract their pollinators.
parts of flowers

A complete flower has the following structures:
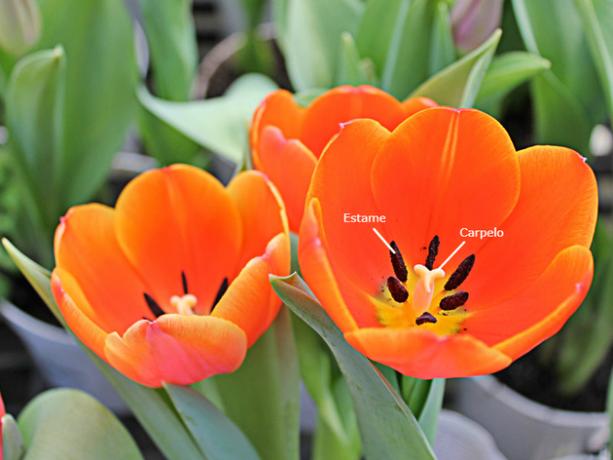
- Stamen: male structure of the flower where the fillet and anther are located.
- Carpel: female structure of the flower, formed by the stigma, style and ovary.
- petals: modified and colored leaves with the function of attracting pollinators. The set of petals is called a corolla.
- sepals: located below the petals, usually green in color. The set of sepals is called the chalice.
This entire structure is supported by the peduncle, stem responsible for connecting the flower to the plant.
The peduncle has a dilated portion connected to the flower called the receptacle floral, where the floral elements are inserted.
Gyneceus and Androceu

Depending on the structure of the flower, it can be female or male. This definition depends on the presence of the gynoecium and the androecium.
gynoecium
The set of carpels is called the gynoecium, the female part of the flower.
The gynoecium is formed by carpels, pistil, stigma, style and ovary. Inside the ovary are the plant's female gametes.
The stigma is the portion that receives the pollen grain and through the stylet connects to the ovary. The ovary is the part that will turn into fruit.
The fruit is the result of the development of the ovary, while the seed represents the development of the egg after fertilization.
androce
The set of stamens is called the androceus, the male part of the flower. The androceu is formed by stamens, anther and fillet.
Stamens are formed by anther and fillet. The fillet corresponds to a long and thin rod, where at its end is the anther, responsible for the production of pollen.
Read too:
- Plant Parts
- plant kingdom
- Botany: the study of plants
types of flowers

Flowers have different classifications, which can be in terms of sex or number of flowers.
Classification by sex
- Hermaphrodites or monoecious: are the flowers that have the male and female reproductive organs in the same flower. most angiosperms they are hermaphrodites, as an example we can mention the tulip.
- Dioic: are the flowers that present the male or female reproductive organs in separate ways. As an example we can mention the papaya tree.
Presence of floral elements
- full flowers: these are the flowers that have all the floral elements: chalice, corolla, androceu and gynoecium. The rose is an example of a full bloom.
- incomplete flowers: are flowers with the absence of any of the floral elements. The begonia is an example of an incomplete flower, as it has either a stamen or a pistil, but not both.
Flower pollination

THE pollination it is the act of reproduction of plants that consists in the transfer of pollen from the male part of the flower to the female part.
Pollination can occur as follows:
- direct pollination: when it happens in the same flower, it is self-pollination.
- Indirect pollination: represents the pollination between flowers of the same plant.
- Cross pollination: is when pollination takes place between flowers of different plants.
Curiosity
The presence of flower and fruit that protects the seed is one of the main characteristics of angiosperms, which in turn are vascular, as they have roots, stems and leaves.
already the gymnosperms they are plants that produce flowers and seeds, but their seeds are bare and are not surrounded by the developed ovary (which are the fruits).
To know more:
- All about plant leaves
- Types of fruits
- Stem Types
- Root types