THE leafis a plant organ responsible for most of the photosynthesis that plants do. However, some species may have leaves that are specialized in other functions such as protection and support.
The main foliar modifications are bracts, cataphylls, cotyledons, thorns, phyllodes and tendrils.
We prepare a list of exercises on foliar adaptations so you can test your botanical knowledge about the different specializations of the leaves.
You can consult the template and save this exercise list in PDF at the end of the post. Enjoy!
Exercises on foliar adaptations
1) (UFSC) In most plants, the leaf is the main photosynthetic organ. The histological structures of a plant leaf are shown schematically in the figure below.
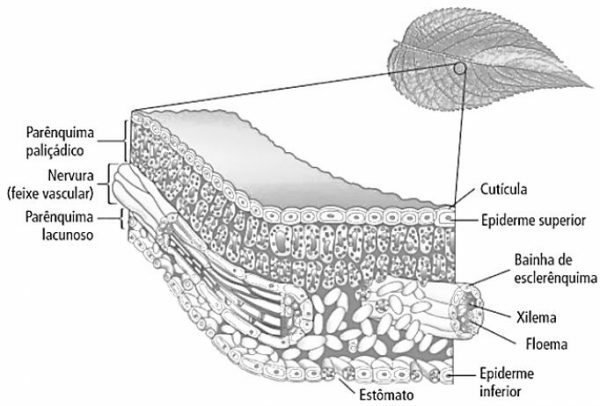
About leaf structures, it is correct to state that:
01) xerophytic plants can present the epidermis with several layers of cells.
02) the cuticle facilitates gas exchange between the epidermis and atmospheric air.
04) the upper epidermis, as it receives direct sunlight, has a greater amount of chloroplast compared to other tissues.
08) photosynthesis occurs in all histological structures of a leaf.
16) the stomata select the CO2, which is used in photosynthesis, and the N2, which is used in the formation of proteins and nucleic acids.
32) the leaf is an organ formed by various plant tissues.
64) leaves like the one represented in the diagram are found in Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
2) Leaves are extremely important structures for plant survival, being mainly related to photosynthesis. Some leaves, however, are modified to perform other functions, such as attracting pollinators. Among the alternatives below, mark the one that does not represent a foliar adaptation.
a) Bract.
b) Tendril.
c) Aculeus.
d) Cotyledon.
e) Cataphyll.
3) (UDESC) There are epidermal structures composed of chlorophyll cells that delimit an opening and that are capable of controlling the gas exchange between the plant and the environment. These leaf structures of dry climate plants (xerophytes) generally appear in greater numbers, possibly as an adaptation to save water.
Check the alternative that indicates the name of this leaf structure.
a) Trichomas.
b) Chlorophyllian parenchyma.
c) Xylem.
d) Stomata.
e) Phloem.
4) Leaf adaptations allow the leaf to perform several other functions, in addition to photosynthesis and respiration. The ___________, for example, are structures that allow the plant to fix itself in the substrate. Among the structures below, mark the one that correctly completes the space.
a) tendrils
b) aculeus
c) bracts
d) cotyledons
e) cataphiles
- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Math Games Course in Early Childhood Education
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course
5) (FUVEST) Many plants adapted to dry terrestrial environments and with high light intensity have leaves:
a) small with stomata concentrated in the lower part, many light trichomes, impermeable cuticle and aquifer parenchyma.
b) large with stomata concentrated in the lower part, few clear trichomes, impermeable cuticle and airy parenchyma.
c) small with concentrated stomata on the upper part, absence of trichomes, wax on the leaf epidermis and aquifer parenchyma.
d) large with stomata equally distributed on both parts, absence of trichomes, absence of wax on the leaf epidermis and air parenchyma.
e) small with concentrated stomata on the upper part, many light trichomes, wax on the leaf epidermis and air parenchyma.
6) Certain leaves are modified to perform important activities on the plant. Some leaves, for example, have the function of protecting gemstones. These structures are called:
a) bracts.
b) tendrils.
c) cataphiles.
d) spines.
e) cotyledons.
7) Among the structures described below, mark the one that does not have a leaf origin.
a) Tendrils.
b) Bracts.
c) Trichomas.
d) Cataphiles.
e) Filodium.
8) You may have noticed that the onion is made up of several structures in the shape of scales. These scales are actually modified leaves that help to protect the buds and are called:
a) bracts.
b) cotyledons.
c) filodion.
d) cataphiles.
e) tendril.
9) The spines are leaf structures that have the function of decreasing herbivory and also:
a) protect the gems.
b) fix the plant in the substrate.
c) nourish the embryo inside the seed.
d) avoid excessive water loss.
e) attract pollinators.
10) We often hear people say that they got pierced with the thorns of the roses. Despite being a common statement, the rose does not have thorns, but aculeum. The spines differ from the pinles by:
a) being a pointed structure.
b) have vascular tissue.
c) because they are modifications of the epidermis.
d) because they are easy to detach.
e) for acting only in defense of the plant.
Template
1 - 01 and 32
2 — c
3 — d
4 — the
5 — the
6 — c
7 — c
8 — d
9 — d
10 — b
Click here to save this exercise list in PDF!
See too:
- List of exercises on leaf morphology
- List of flower exercises
- List of exercises on Botany
The password has been sent to your email.

