Cartesian plan is a method created by the French philosopher and mathematician, René Descartes. These are two perpendicular axes that belong to a common plane.
Descartes created this coordinate system to demonstrate the location of some points in space.
This graphic method is used in several areas, especially in mathematics and cartography.
How to make?
To locate points on a Cartesian plane, we must take into account some important indications.
The vertical line is called the ordinate (y) axis. The horizontal line is called the abscissa (x) axis. With the intersection of these lines we have the formation of 4 quadrants:
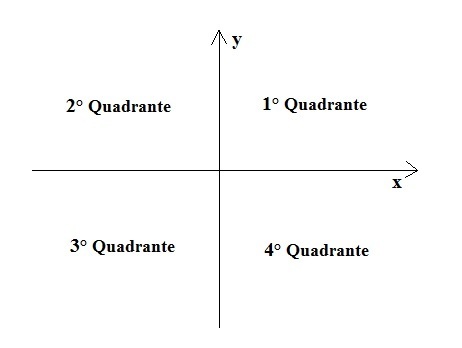 Representation of the Cartesian Plan
Representation of the Cartesian Plan
It is important to note that on the Cartesian plane, numbers can be positive or negative.
That is, positive numbers go up or to the right depending on the axis (x or y). Negative numbers, on the other hand, go to the left or down.
- 1st quadrant: numbers will always be positive: x > 0 and y > 0
- 2nd quadrant: numbers are negative or positive: x 0
- 3rd quadrant: numbers are always negative: x
- 4th quadrant: numbers can be positive or negative: x > 0 and y
Examples
Cartesian coordinates are represented by two rational numbers in parentheses, which are called elements:
A: (4, 7)
B: (8, -9)
C: (-2, 2)
D: (-5, -4)
E: (5, 3)
 Example
Example
These elements form an “ordered pair”. The first element corresponds to the abscissa (x) axis. The second element corresponds to the ordinate (y) axis.
Note that the point where the axes meet is called the “origin” and corresponds to the ordered pair (0, 0).
Cartesian product
The Cartesian product is used in set theory. It is applied to distinct sets and corresponds to the multiplication between ordered pairs. This method was also created by René Descartes.
Solved Exercises
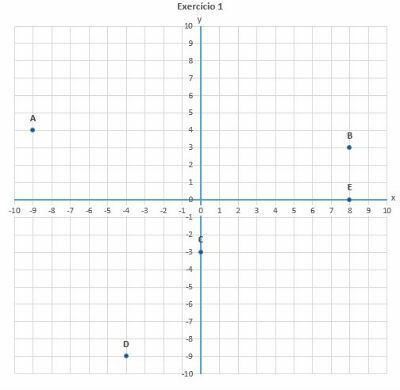
1. Find the pairs ordered in the Cartesian plane:
a) (-9, 4)
b) (8, 3)
c) (0, -3)
d) (-4, -9)
e) (8.0)
2. In which quadrants are the points located:
a) (-2, -4)
b) (3, 1)
c) (0, 6)
d) (8, -7)
e) (9, -3)
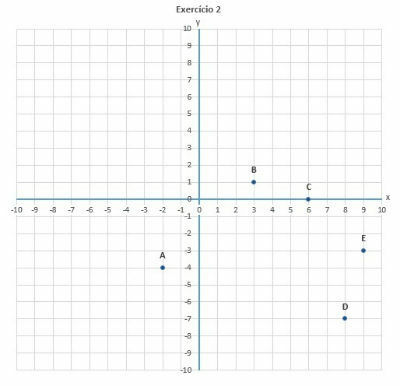
a) 3rd quadrant
b) 1st quadrant
c) 1st quadrant
d) 4th quadrant
e) 4th quadrant
3. Which ordered pair is not represented in the Cartesian plane?
a) (3, -4)
b) (4, -3)
c) (-8, -9)
d) (8, 9)
e) (9, -8)
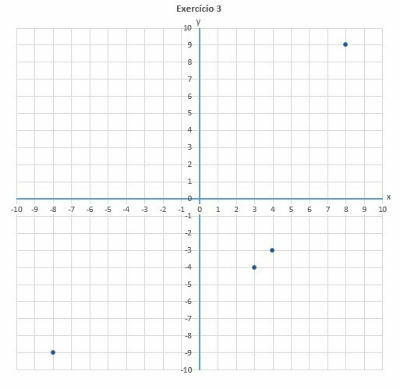
Answer: letter E.
See too:
- discards
- conical
- Line Equation
- Distance between two points
- Exercises on distance between two points