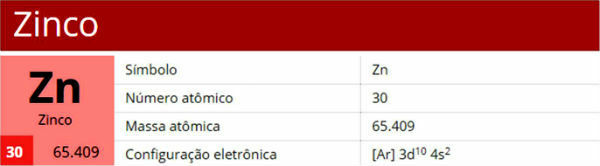
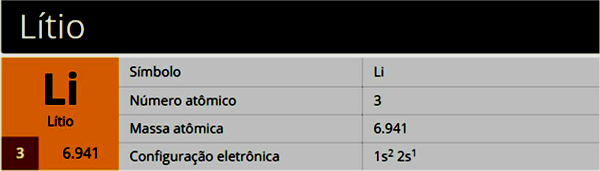
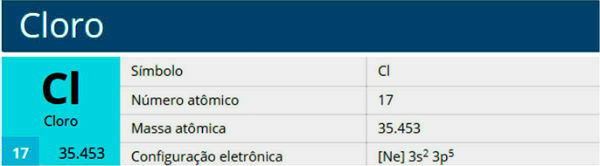
Alcohols are compounds formed by hydroxyls attached to saturated carbon atoms. The main alcohols are ethanol and methanol.

Ethanol structural formula
The presence of the hydroxyl functional group (-OH) is also a characteristic of other organic compounds, the phenols.
Nomenclature
The nomenclature of alcohols follows the rule of the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, in Portuguese).
Alcohol names are formed by prefix, an intermediate word and a suffix, as follows:
- prefix - indicates the number of carbons: 1 met, 2 et, 3 prop, 4 but, 5 pemt, 6 hex, 7 hept, 8 oct, 9 non, 10 dec.
- intermediate - indicates the type of chemical bond: an for single bonds, dien for 2 doubles, in for 1 triple, diin for 2 triples, enin for 1 double and 1 triple.
- suffix - indicates the organic function. In this case, l is the suffix for alcohols.
Examples of Alcohols and Applications
The main alcohols are ethanol and methanol.
O ethanol or ethyl alcohol (molecular formula C2H6O) is the type of alcohol used in alcoholic beverages and fuels.
It tends to replace the gasoline place. This is because it is more economical and does not produce sulfur dioxide (SO2), that is, it is less polluting.
After the United States, Brazil leads the world in ethanol production. In our country, its main raw material is sugar cane.
O methanol or methyl alcohol (molecular formula is CH3OH) is used as a solvent in the pharmaceutical industry and also as a fuel for racing cars.
It is highly toxic, which is why its ingestion can cause serious damage and even death.
There is also iodized alcohol, which is used as an antiseptic, and isopropyl alcohol, which is used to clean electronic devices.
Glycerin or glycerol, in turn, is used in cosmetic products. While xiliton is a polyalcohol used as a natural sweetener.
Classification
Depending on the hydroxyl position, alcohols can be:
- Primers when attached to just one carbon atom.
- Secondaries when attached to two carbon atoms.
- tertiary when attached to three carbon atoms.
From the oxidation of primary alcohols, aldehydes are obtained, which can be found in flowers and fruits, for example.
Alcohols can also be classified by the number of hydroxyls:
- Monoalcohol when they have only one hydroxyl.
- alcohol when they have two hydroxyls.
- Trialcohol when attached to three hydroxyls.
properties
- Acid
- characteristic smell
- Density lower than water
- Colorless
- Flammable
- Liquid, when it has up to 11 carbons. Solid, above 11 carbons
- polar molecule
- high boiling point
- Toxic
Also read about: Prohibition.