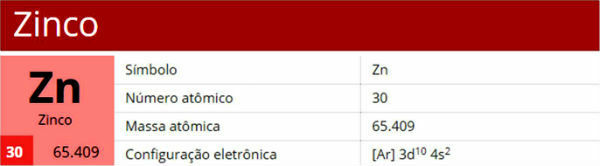
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn, atomic number 30, atomic mass 65.4 and located in group 12 of the periodic table.
At room temperature, zinc is found in a solid state. Corresponds to a bluish-white metal.
It is relatively easily found in nature, and its association with oxygen and sulfur is common, forming oxides and sulfides. It is usually found with lead, silver and gold.
The countries with the largest reserves of zinc are: Peru, China, Australia, the United States and Canada. Brazil does not have a large concentration of the mineral.
applications
Zinc is widely used in the galvanizing of steel or iron, protecting these metals against corrosion. This is because zinc is a metal that does not corrode.
Another use is in the manufacture of metal alloys. It is used as a sacrificial metal, meaning it corrodes in place of another metal that is of interest.
Zinc oxide is used in the paint industries, in addition to the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and textile sectors. Some examples of products are: face powder, sunscreen, rubbers and plastics.
Zinc is still widely used in the manufacture of tiles, batteries and dry batteries.
Also read about:
- Periodic table
- Chemical elements
Zinc is also important inside the human body, it plays roles that contribute to the correct functioning of metabolism, especially of proteins and nucleic acids.
It is also important to regulate the activity of several enzymes, in addition to acting on the immune system.
Despite such importance, our body does not synthesize zinc. Therefore, the element must be acquired through food.
Foods rich in zinc are red meat, poultry, shellfish, nuts, cereals, beans and eggs.
Some benefits of the presence of zinc in the diet include:
- Assistance in the healing process
- Protection against colds and flu
- Fertility of men and women
- muscle mass gain
- Strengthening the immune system
- Fights aging
- Aids in weight loss
On the other hand, lack of zinc in the diet causes hair loss, diarrhea, tiredness, depression, difficulty in healing and sexual impotence.
Learn more, read also:
- Nutrients
- mineral salts
- Foods of mineral origin