Despite being a widely used term, the word "fruit" is actually an unofficial designation given to sweet-tasting fruits. In other words, "fruit" does not exist in the botanical vocabulary.
The fruit (or fruit) is an integral part of some plants. As a general rule, we can say that it is responsible for protecting and carrying the seeds and that it can sometimes be used as food.
Difference between fruit and fruit
Although they are often considered the same thing, fruit and fruit have different concepts.
Every fruit, for example, is a fruit, but not every fruit is a fruit.
The fruit, considered a botanical structure, has a more general concept. It is developed through fertilization of the ovary of a flower.
Fruits are often called vegetables precisely because they do not have a sweet taste.
The word fruit, on the other hand, is a designation that does not officially exist in the botanical vocabulary.
It is just a more generic way of referring to fruits that have a sweet taste and that can, in general, be consumed.
Fruit formation
The fruit formation process only occurs in plants classified as angiosperms, that is, plants that produce flowers and whose seeds are inside the pericarp.
Fruits are developed from the flower's fertilized ovary. Fertilization takes place through a process called pollination.
Pollination is the transfer of pollen (located in the anthers of a flower) to the stigma (female recipient) of a flower of the same species or to the stigma itself.

The bee is one of the insects that most helps the process of pollination of flowers.
When landing on a flower, the pollen is attached to the body of the bee that, when flying to the next flower, has the pollen detached from its body and pollinates the flower where it lands.
Types of pollination
See below for the main types of pollination:
| anemophilia | Pollination that occurs through the wind. |
|---|---|
| Entomophilia | General nomenclature used to refer to any type of pollination carried out by insects. The term is used primarily to refer to pollination by bees, wasps and flies. |
| Cantarophilia | Performed by beetles. |
| psychophilia | Pollination performed by butterflies. |
| Phalenophilia | Name given to the pollination process carried out by moths. |
| Ornithophilia | Pollination that occurs through the birds. |
| hydrophilicity | Occurs when the transfer of pollen occurs through the Water. |
| Artificial | Pollination by men |
| chiropterophilia | Pollination by bats. |
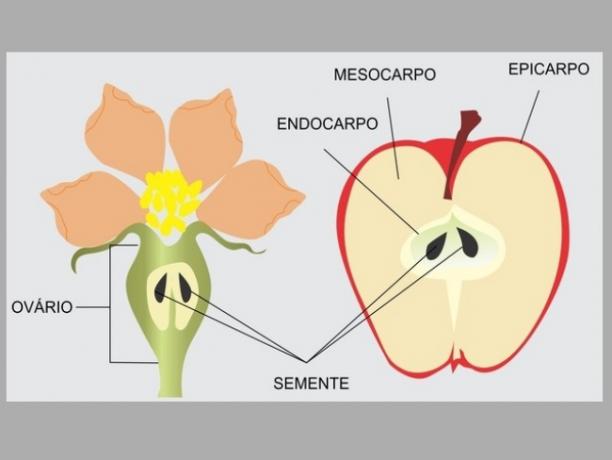
After fertilization, the flower undergoes a very significant change and of all its components, only two remain: o peduncle it's the ovary.
The flower's ovary undergoes a process of development and becomes the fruit (or fruit). The eggs, on the other hand, start to constitute the seeds.
know more about flower and flower parts.
fruit parts
The fruit (or fruit) is made up of two main parts: pericarp and seed.
The pericarp results from the development of the ovary wall. It is subdivided into epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp.

The epicarp is the outermost layer of the fruit.
The mesocarp, as its name suggests, is the middle layer, the most intermediate. It usually consists of the most developed layer of the fruit and its composition can vary a lot.
The endocarp is the innermost layer.
The seeds, in turn, are the result of the fertilized egg.
Learn more about the main differences between fruits, fruits and pseudo fruits.
Types of Fruits
Fruits can be classified into two main types: fleshy and dry.
fleshy fruits
The fleshy fruits are those that, when ripe, have a soft consistency.

This group of fruits is further subdivided into three types: berries, drupes and we put.
Examples of fleshy fruits: orange, apple and watermelon.
Dry fruits
The main characteristic of dried fruit is that it does not have a soft pulp.

Examples of dried fruit: almonds, chestnuts, walnuts and hazelnuts
Dried fruits are subdivided into two groups: dehiscent dried fruits and indehiscent dried fruits.
dehiscent dried fruit
They are those that have a dry and woody consistency and that tend to open, when ripe, to release the seeds.
Examples of dehiscent fruits: chestnuts
NOTE: chestnut is one of the few examples of fruits dehiscent. It is more common the existence of fruits dehiscents such as beans and peas.
Indehiscent dried fruit
Indehiscent dried fruits, as well as dehiscent, have a dry and woody consistency. The difference between these two types of fruit is that the indehiscent ones do not open to release the seeds.
Fruits can also have different classifications according to their place of origin (such as the exotic fruits and the tropical fruits) or with its flavor (as with citrus fruits).
Examples of indehiscent fruits: walnuts and hazelnuts
exotic fruits
Exotic fruits are those whose original environment is different from the place where they are sold.
As they are not usually produced in large scales, exotic fruits tend to have a higher cost in relation to the more common fruits.
The concept of exotic applies to species that are outside their natural range. However, popularly, exotic fruits are also recognized as those that have particular shapes and colors.
See some exotic fruits rich in health benefits that are available for sale in Brazil.
Lychee

Lychee is an original fruit from southern China, with a sweet pulp and a slight touch of acidity.
See below its main benefits:
- Rich in vitamin C.
- It has anti-inflammatory effects.
- It is rich in fiber, which benefits bowel function.
- Helps control blood pressure.
- Improves the immune system.
mangosteen

Mangosteen is a fruit original from the tropical region of Southeast Asia. Its pulp has a sweet and spicy flavor.
Some of its benefits:
- It has anti-inflammatory action.
- Rich in an antioxidant nutrient called xanthone.
- Strengthens the immune system.
- regulates menstruation
- treat diarrhea
Pomegranate

Pomegranate is a fruit of Mediterranean origin.
Its pulp is formed by several seeds covered by a transparent fleshy layer and its flavor is slightly sour.
Its main benefits are:
- Prevents cardiovascular problems.
- It is rich in vitamins A and C.
- It has folic acid.
- Prevents and improves throat infections.
- Prevents Alzheimer's.
Pitaya
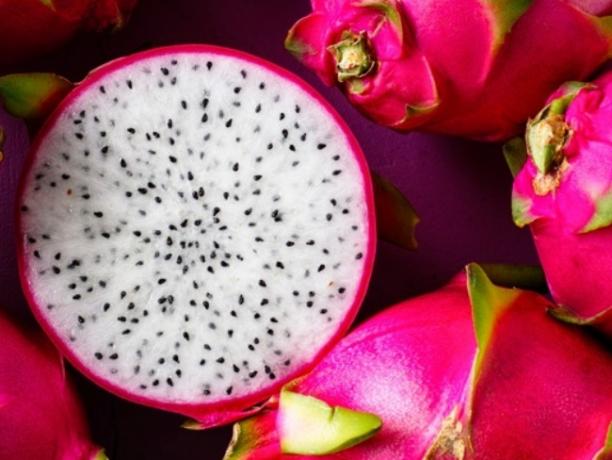

The pitaya is a fruit native to Central America and Mexico, whose pulp has a very sweet taste.
The main benefits of pitaya are:
- Fights cholesterol.
- Helps you lose weight.
- Helps the digestive process.
- Assists metabolism.
- Helps eliminate free radicals.
physalis

Physalis is a fruit that comes from regions with temperate, hot and subtropical climates.
Its shape is similar to that of a tomato and its flavor is slightly acidic.
Its main benefits are:
- Strengthens the immune system.
- Purifies the blood.
- Lowers cholesterol levels.
- Helps you lose weight.
- Prevents anemia.
Tropical fruits
Tropical fruits can be grown by plants from different types of habitat.
They have as a common characteristic the fact that they are fruits intolerant to low temperatures and frost.
In Brazil, they can be found practically all over the country.
See below some tropical fruits easily found in Brazil.
Pineapple

Pineapple is a fruit native to South America.
Its main properties are:
- It's a diuretic.
- Accelerates tissue healing.
- Lowers blood pressure.
- Helps in the treatment of kidney stones.
- Fights anemia.
Banana

Although many people think that banana is a Brazilian fruit, it is actually of Asian origin.
Its main benefits are:
- It is beneficial for the heart.
- Decreases PMS symptoms.
- Prevents cramps.
- Good for the skin.
- Aids digestion.
Papaya
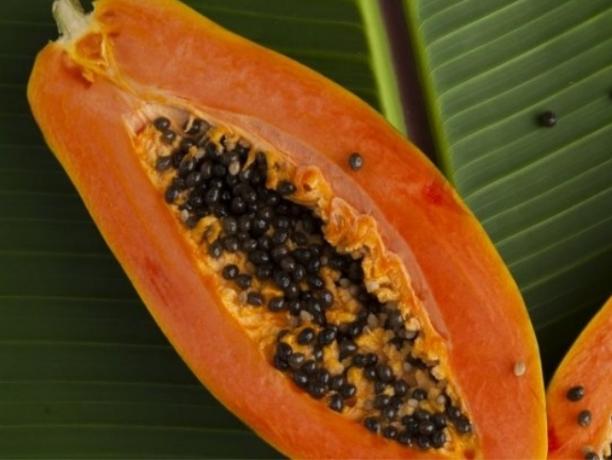

Papaya, a fruit of Mexican origin, can be found in Brazil throughout the year.
Its main properties are:
- Improves intestinal flow.
- Aids healing.
- Good for the skin.
- Helps to normalize cholesterol levels.
- Strengthens bones.
Mango

Mango is a fruit of Asian origin, native to India and can be found in over 100 varieties.
Its main benefits are:
- It is rich in B vitamins.
- It's good for the vision.
- Helps control diabetes.
- Improves the immune system.
- Helps control cholesterol.
Avocado

Avocado is a fruit of Central American origin, which is used both in the preparation of sweet and savory meals.
Its main properties are:
- Helps lower cholesterol levels.
- It's rich in protein.
- Strengthens the immune system.
- Improves memory capacity.
- It is rich in fiber.
know more about tropical weather.
citrus fruits
Citrus fruits, also called citrus fruits, have as main characteristic their acidity, which results in a slightly sour flavor.
For this reason, consumption of citrus fruit is not recommended for those who are suffering from heartburn.
They are very rich in vitamin C and also have a substance called synephrine, which helps with weight loss.
Synephrine intensifies the breakdown of fat molecules, however, it does not replace physical activity.
The main benefits of citrus fruits are:
- They are rich in vitamin C.
- Reduce constipation.
- They help the body absorb iron.
- Strengthen the immune system.
- Help to lose weight.
- Good for the skin.
- They hydrate the body.
- Fight cell aging.

Orange, lemon, lime, kiwi and grapefruit are examples of citrus fruits.
Benefits of Fruits
Fruits are a rich source of vitamins, fiber and other substances that are beneficial to the body, especially with regard to combating certain diseases and maintaining the proper functioning of the body.
According to the WHO (World Health Organization), each person should consume 3 to 5 servings of fruit per day, depending on their needs.
5 reasons to include fruit in your daily diet
- They are rich in fiber and for this reason they benefit the functioning of the digestive system.
- Intake of fruits has a direct impact on the mood and thus helps to fight depression.
- Stimulate memory.
- They are usually low in fat, sodium and calories.
- They help lower blood cholesterol levels, thus reducing the risk of heart disease.
Check out a table below with a list of fruits and their respective nutritional information.
| FRUIT | NUTRITIONAL VALUE | THERAPEUTIC ACTION | ORIGIN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passion fruit | Rich in vitamin C. | It has calming properties and acts against diarrhea, coughing and ulcers. | tropical america |
| Mango | Rich in vitamins A and C, and in the B complex. | It aids digestion and is used to fight bronchitis. | Asia |
| Orange | High content of vitamin A, C, B complex, iron and carbohydrates. | Prevents colds and flu. Detoxifies the body and helps the intestines work. | South China |
| Banana | Rich in carbohydrates. | Beneficial for the treatment of diarrhea and erysipelas. Its pulp helps to treat inflammation. | Southeast Asia |
| Papaya | It has vitamins A and C, proteins and minerals. | Aids digestion. | tropical america |
| Apple | Rich in vitamins and minerals. | Fights diarrhea and rheumatism. | Europe and Asia |
| Lemon | Rich in Vitamin C | Anti-flu. Fights acidity, acne, cold sore and migraine. | India |
The colors of the fruits
By observing the colors of the fruit, we can get an idea of which nutrients it has, as each hue is the result of an element present in its composition.
Check below the properties of the fruits according to their colors.
Yellow and orange fruits
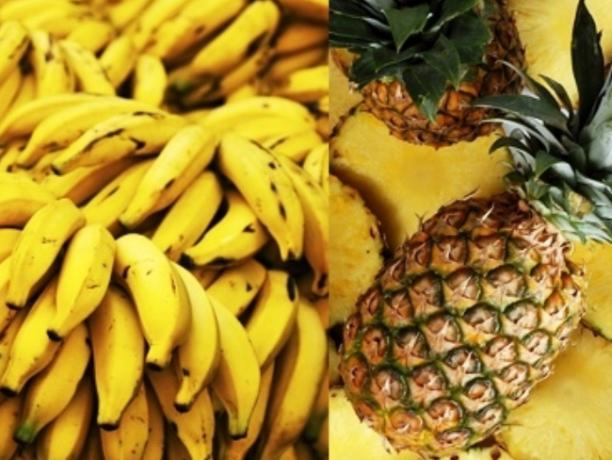

They represent the main source of vitamin C. Rich in carotenoids and bioflavonoids, they help to strengthen the immune system and circulation.
Examples: orange, melon, mango, tangerine, pineapple.
Red fruits

Rich in lycopene, they help prevent diseases such as prostate and breast cancer.
They have antioxidant properties, fight stress and strengthen memory, eyes and skin.
Examples: watermelon, blackberry, house, cherry.
purple fruits
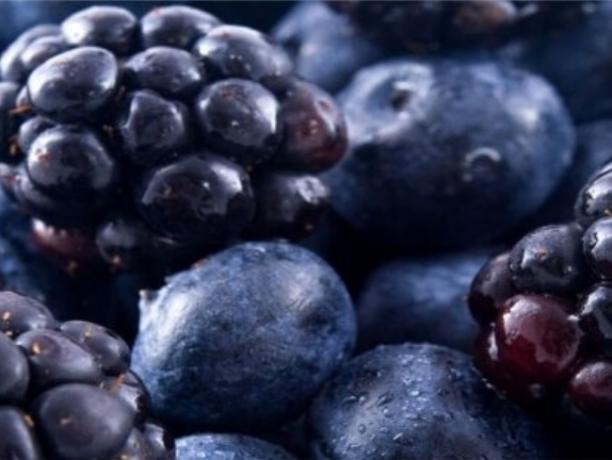

Purple fruits are rich in anthocyanin, which in addition to helping to prevent liver and heart disease, helps to slow aging and strengthen memory.
Examples: jabuticaba, plum, grape.
white fruits

They have a high concentration of flavonoids and B-complex vitamins.
They are beneficial for the heart as they help control blood cholesterol. They also help to strengthen teeth and bones as they are high in calcium and potassium.
Examples: banana, pear, earl fruit, melon.
green fruits

Green fruits are usually rich in iron, potassium, beta-carotene and vitamins C and E. They assist in the production of red blood cells and blood clotting and have a healing and antibacterial action.
Examples: kiwi, green grape, green apple, avocado.
Brazilian fruits
Although fruits such as apples, oranges and watermelons are easily found in supermarkets and fairs throughout the Brazilian territory, these fruits are not original to Brazil.
Check out the only six Brazilian fruits that, according to agronomist Harri Lorenzi, are produced on a large scale.

Pineapple Benefits: helps to lose weight, aids digestion, improves skin and hair, strengthens the immune system, has antioxidant action.
Cocoa Benefits: lowers cholesterol, prevents anemia, reduces the risk of diabetes, helps regulate the bowel, improves blood circulation.

Cashew Benefits: helps to lose weight, strengthens the immune system, blood and bones, gives freshness to the skin and hair, cashew nuts prevent cardiovascular disease.
Coconut Benefits: It has antimicrobial properties, fights carcinogens, strengthens the immune system, coconut water helps to keep the body hydrated, coconut oil helps to burn fat.

Guava Benefits: it is rich in vitamin C, contains antioxidants, protects against cardiovascular diseases, prevents anemia, reduces stress, fights aging, promotes eye health.
Passion fruit benefits: helps in the treatment of insomnia, anxiety and depression, improves digestion, regulates blood pressure, improves bone density, improves circulation.
See too: Difference of fruit and fruit.


