Human evolution is a theory that indicates that the evolutionary process started with the first forms of life until reaching the current stage of human development, the homo sapiens sapiens.
Biology estimates that life on Earth arose 3.8 billion years ago in the form of single-celled organisms called prokaryotes. Millions of years later, with the changes related to oxygen and the evolution of photosynthesis, the first eukaryotic beings (with complex cells containing organelles) appeared.
The mutations continued over time and about 530 million years ago, the first fish appeared, which then gave rise to amphibians (340 million years ago), reptiles (310 million years ago) and eventually to mammals (about 100 million years ago) back). Finally, the first primate mammals on Earth gave rise to hominids.
It is important to clarify that the meaning of “hominid” has been revised several times over time. For this reason, it is still very common that the term is used to refer exclusively to humans (genus homo), although it also includes chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans.
These four species, also known as Great Primates, had a common ancestor 14 million years ago. and, over time, they subdivided into different species as physical attributes diverged with new mutations. Eventually, primates gave rise to the first human life forms, about 3.5 million years ago.
Stages of human evolution
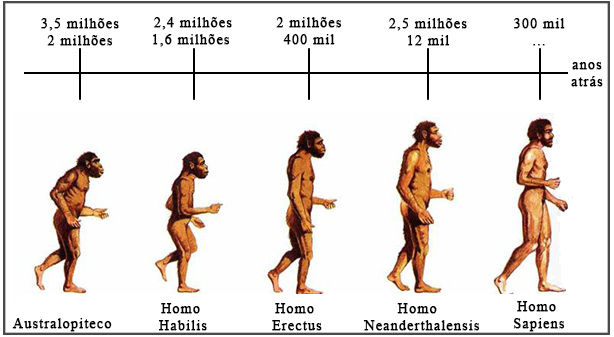
Timeline of human evolution with the estimate of the first and last appearance of each species.
In the study of human evolution, it is important to pay attention to the fact that the appearance of a new species does not imply the immediate extinction of another. The timeline above shows that less evolved species cohabited with their successors for thousands of years, until their eventual extinction.
Australopithecines

Science believed that this species was actually a close ancestor of humans. This classification came to be questioned after the discovery of older australopithecine fossils with characteristics very similar to members of the genus homo. Nowadays, although there is no consensus, the similarities with humans keep the Australopithecine species closely related to the beginning of human life on Earth.
Australopithecines were bipedal beings of short stature (no more than 1.4 meters) and their bodies were covered with hair. The species lived in tropical parts of Africa, feeding on fruits and leaves, and was the first to use the opposable thumb to hold and handle instruments.
The term australopithecus comes from the Latin "australis", which means southern and from the Greek "pithekos", which means primate.
Homo Skills
From the Latin “skillful man”, the species lived on Earth about 2.4 and 1.6 million years ago. In physical terms it is the member of the genus homo more different from today's humans. You homo habilis they got their name because they were the first hominids to use their hands to make rudimentary tools made of stone. Their brains were 50% larger than those of australopithecines and had an average height of 1.3 meters.
homo erectus

With the hands intended for handling instruments, the homo habilis learned to balance on both legs and, over time, gave rise to the homo erectus. The species is estimated to have lived between 2 million years and 400,000 years ago.
You homo erectus were the first to control fire. In addition to contributing to nightlife survival, the discovery brought drastic changes to the food and customs of the species, especially enabling migration to more cold. For this reason, the homo erectus they were the first to leave Africa and spread across the world, some 1.8 million years ago.
Homo Neanderthalensis

Better known as Neanderthal Man, it is considered the closest ancestor to modern humans. They lived in Europe and Asia between 2.5 million and 12,000 years ago. Despite being smaller in stature than today's humans, Neanderthals had the constitution much stronger and more resistant physics that, added to the mastery of weapons and fire, made them excellent hunters.
Living in colder regions, Neanderthals learned to make clothes to stay warm. Furthermore, it is believed that the cold has a direct connection with the feeling of socialization developed by Neanderthals, who spent a lot of time gathered around campfires or in caves.
Neanderthals are considered the most carnivorous members of the family. homo. This characteristic was decisive, considering that when climate change eliminates the greatest part of the animals hunted by them, the Neanderthals were unable to feed themselves, being eventually extinct.
homo sapiens

From the Latin "wise man", it is the member of the family homo with the most developed brain. It is estimated that the first homo sapiens have emerged about 300,000 years ago.
With keen reasoning ability, the homo sapiens they were able to interpret the environment around them, solve problems and thus continue the adaptation process to the present day. Science classifies the modern human being as homo sapiens sapiens which means "man who knows he knows". This means that today's human beings have developed an awareness of their knowledge and learned to use them in the search for new ones.
Theories of human evolution
In opposition to Creationism, a theory that explains the human origin through a divine entity, the evolutionary theory is strongly based on the studies developed by Chales Darwin.
Darwinism, as evolutionary theory is also known, believes that the human being, like other species, evolved gradually over time, as they underwent small changes as a way to adapt to the environment.
know more about creationism and evolutionism.


