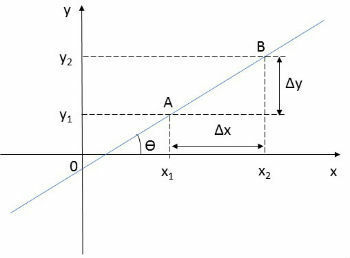
We determine a straight line in the Cartesian plane knowing two distinct points, but it is also possible to be determined knowing only a point and an angle, since a line s intersects the Ox axis at a point M forming an angle α.
Angle α is formed by the line r and a point on the Ox axis located to the right of point M. Its measurement will vary between 0°≤ α < 180°.
This angle is the slope of the line and its tangent is the value of its slope. Since it will only be possible to find its angular coefficient when the line is not vertical, that is, the value of α must be different from 90°.
Example 1:
Inclination of line s equal to 60º.
Angular coefficient equal to m = tg 60° = √3.
Example 2:
Inclination of the line s equal to 0°, as it is parallel to the Ox axis.
Angular coefficient equal to m = tg0º = 0.
Inclination of the line equals 90°.
It will not be able to find the value of the slope of the line s when the inclination is equal to 90°, as it is not possible to find the value of the tangent of 90°.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
by Danielle de Miranda
Graduated in Mathematics
Basil School Team
Analytical Geometry - Math - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
RAMOS, Danielle de Miranda. "Inclination of the straight line and its angular coefficient"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/inclinacao-reta-seu-coeficiente-angular.htm. Accessed on June 29, 2021.