Amazon Forest is the biggest rainforest in the world and represents 30% of the remaining tropical forests.
Extending more than 5.5 million km2, most of it is located in Brazilian territory and about 40% is distributed among 8 other countries in South America.
The Amazon Forest, one of the areas of greatest biodiversity on the planet, is part of the Amazon biome, one of the six Brazilian biomes.
There are about 45,000 species of plants and vertebrates in it and it is believed that many species have yet to be discovered.
 Aerial photo of the Amazon River.
Aerial photo of the Amazon River.
Characteristics of the Amazon Forest
Location
In Brazil, the Amazon Forest is located in the northern region and covers the following states: Amazonas, Roraima, Acre, Amapá, Pará, Maranhão, Tocantins, Mato Grosso and Rondônia.
Its territory also extends to other countries: Colombia, Peru, Venezuela, Bolivia, Ecuador, Guyana, French Guiana and Suriname.
 Map of the Amazon Forest.
Map of the Amazon Forest.
The Amazon Forest is located in the Amazon basin, the largest hydrographic basin in the world, with 6 million km
2 and 1100 tributaries. Its main river is the Amazon, the largest river in extension and volume of water in the world.Vegetation
They exist seven types of vegetation in the Amazon rainforestAttractions: dense rainforest, campinarana, stationary deciduous forest, open rainforest, pioneer formation with fluvial and/or marine influence, mountain refuges and savannas.
THE dense rainforest is the predominant vegetation and corresponds to 41.67% of the territory.
The vegetation of the Amazon Forest can also be divided into three plant formations: firm forest, floodplain forest and igapó forest.
These formations are classified according to the amount of water they receive. The amount of water, in turn, will determine the type of vegetation in each one of them.
THE dry land forest it covers 96% of the territory and the floodplain forest and the igapó forest together cover only 4%.
The terra firme forest is never flooded, but it has high levels of humidity. In this region there is a great diversity of tree species, such as mahogany and angelim.
THE floodplain forest it is flooded during periods of flooding of the rivers and the igapó forest remains flooded all the time. At igapó forest this is where the water lily is found, one of the most famous plants in the biome.
Fauna and Flora
The Amazon is one of the richest areas in biodiversity in the world, it is estimated that 10% of all plants and animals in the world can be found in this region.
Some animals found in the Amazon Forest are: toucan, monkey, alligator, jaguar, boa constrictor, anaconda, ocelot, tortoise, macaw, piracuru.
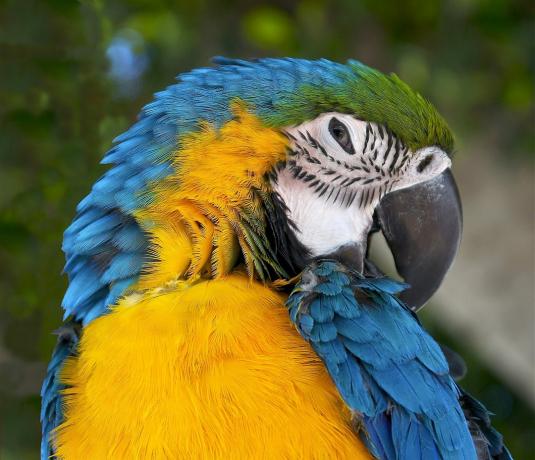 Macaw Canindé.
Macaw Canindé.
 Piracuru.
Piracuru.
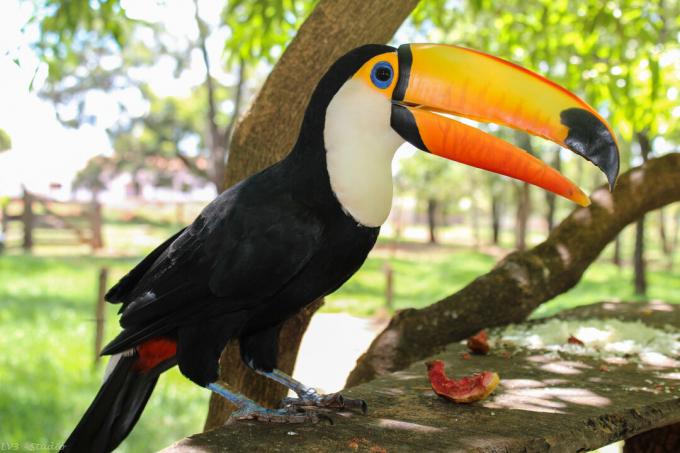 Toucan.
Toucan. Cururu frog.
Cururu frog.
Regarding flora, it is estimated that there are about 30 thousand species of plants in the Amazon Forest. Among these species, there are edible plants, medicinal plants and also plants that provide important raw materials, such as latex.
Some of the species of the Amazon flora are: açaí, rubber, peach palm, chestnut, andiroba, water lily, guaraná and Jatobá.
 Jatobá pulp is edible and its bark has medicinal properties.
Jatobá pulp is edible and its bark has medicinal properties.
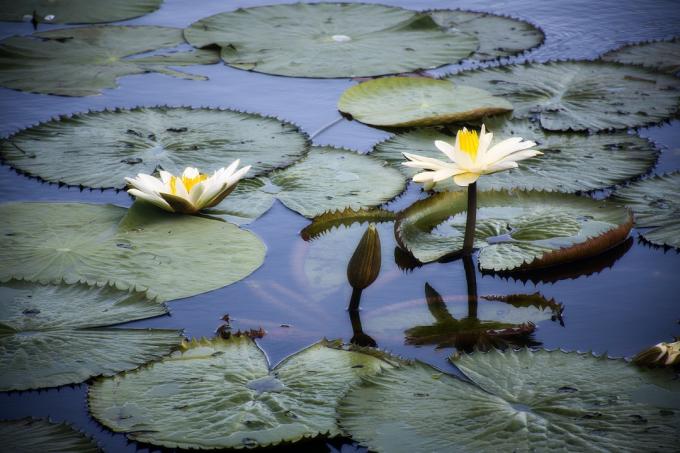 The lily pad can reach 2.5 meters in diameter.
The lily pad can reach 2.5 meters in diameter.
 It is from the rubber tree that latex, the raw material for rubber, is extracted.
It is from the rubber tree that latex, the raw material for rubber, is extracted.
Approximate number of species of Amazonian flora and fauna:
| plants | Mammals | birds | reptiles | amphibians |
| 30.000 | 311 | 1.300 | 273 | 232 |
The diverse species of plants and animals provide sustenance to local populations. Hunting and fishing provide food and several products have great economic importance for the region, as is the case of latex, which is extracted from rubber trees and is the raw material for the production of rubber.
know more about biodiversity.
Climate
The Amazon Forest has equatorial climate, with high air temperature and humidity. The temperature in the region varies, on average, from 22º C to 28º C and has a rainfall index that varies from 1,400 mm to 3,500 mm per year. Air humidity can exceed 80%.
Over the course of a year, there are two seasons in the region: dry and rainy.
Learn more about the Brazilian biomes.
Ground
The Amazon Forest soil is poor, with only a thin layer of nutrients called humus, which is produced from the decomposition of organic matter. This layer, however, is fundamental for the development of forest species.
Importance of the Amazon Forest
In addition to the enormous biodiversity and sources of livelihood for local communities, the Amazon Forest plays an important role in climate balance of the planet.
Trees, when carrying out the photosynthesis process, absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) and release oxygen (O2) and so do the air filtration. Carbon dioxide is emitted by burning fossil fuels and is the main greenhouse gas.
This means that the Amazon Forest helps to reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and, consequently, helps to contain global warming.
Another very important function of the Amazon Forest is evapotranspiration, a phenomenon that contributes to climate balance in several regions of South America.
know more about greenhouse effect and global warming and logging.
Flying rivers and their importance for environmental balance
Flying rivers originating in the Amazon Forest region are also phenomena of great importance for the environmental balance in several regions in South America.
These rivers are formed by the process of evapotranspiration, which is the absorption of soil water by trees and the release of this water in the form of water vapor.
Part of this vapor is precipitated causing rain in the forest region itself, another part is carried by air currents. This air current takes the flying rivers to the region of the Andes Mountains, when the rivers meet this barrier, part of it precipitates, part follows with the air currents.
These currents go towards the mid-west, southeast and south of Brazil and also to the region of the La Plata Basin, being very important for the maintenance of humidity in these locations.
know more about moisture and water cycle.
Deforestation of the Amazon Forest
Despite the great importance of the Amazon Forest for the environment, deforestation and the destruction of the biome are growing at alarming levels.
Deforestation in the region began in the 1970s with the commercial exploitation of available natural resources. According to the National Institute for Space Research (INPE), about 700,000 km2 of the forest have already been deforested, that is, 17% of the original cover.
The main causes of deforestation in the Amazon Forest are illegal logging, the expansion of agriculture, lack of land use planning and inefficient inspection.
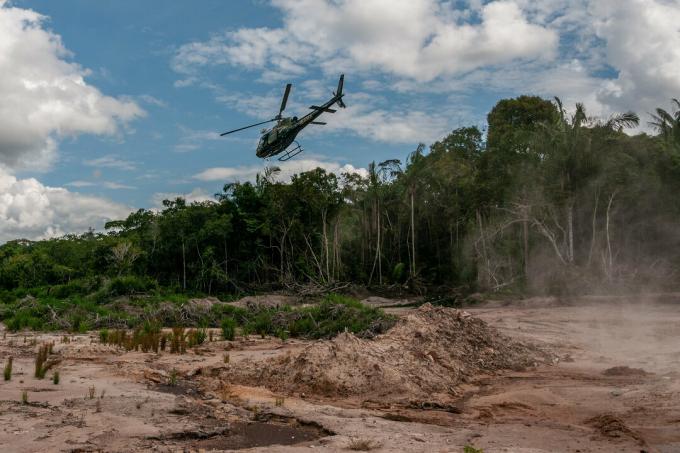 Deforestation in the Tenharim do Igarapé Preto Indigenous Land, in Amazonas.
Deforestation in the Tenharim do Igarapé Preto Indigenous Land, in Amazonas.
 Illegal logging in the Pirititi Indigenous Land, in Roraima.
Illegal logging in the Pirititi Indigenous Land, in Roraima.
know more about logging.
Legal Amazon and International Amazon
There are two known classifications for the Amazon, the international and the legal. The legal Amazon is the Brazilian part, present in 9 states and representing 60% of the total extension of the Amazon Forest.
This classification was created in 1953, during the government of Getúlio Vargas, with the objective of creating strategies for the economic development of the region.
The international Amazon is represented by the entire territory of the forest, comprising 9 countries and 50% of the South American territory.
Understand more about the cool amazon and international amazon.
Amazon Biome
The Amazon is one of the six biomes that exist in Brazil. In addition to the Amazon, the country is made up of the following biomes: Cerrado, Atlantic Forest, Caatinga, Pampa and Pantanal.
A biome is a set of ecosystems of animal and plant organisms, with their own characteristics of climate, vegetation, flora and fauna.
Learn more about Amazon biome and meet the others Brazilian biomes.
Data on the Amazon Forest
- 40% of the territory of South America is the Amazon;
- 40,000 plant species have already been identified in the Amazon;
- 39 million people live in the Amazon;
- 175 indigenous peoples live in the region;
- 75% of the Amazon population lives in Brazil;
- More than 2,000 species have already been identified for use as food and medicine;
- The Amazon Forest has about 10% of all plant species on the planet;
- Indigenous peoples use about 1,600 species of plants to cure diseases;
- Flying rivers release 17 trillion liters of water into the Atlantic Ocean a day.
 Indigenous children of the Amazon.
Indigenous children of the Amazon.
See also the meaning of equatorial climate, ecosystem and fauna.