Apolar is the quality of what has no polarity, usually related to organic molecules.
In chemistry, the polarity of organic molecules is related to the intensity of electronegativity of the atoms that make up these molecules. When there is no difference between the electronegativity of atoms, this molecule is considered non-polar.
In a nonpolar molecule, the difference in electronegativity of the binding of atoms must always be zero, as they are nullifying.
Normally, non-polar connections are made up of Hydrocarbons, that is, compounds formed by carbon atoms or / and hydrogen.
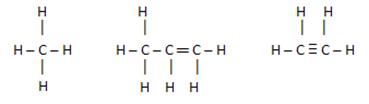
These compounds have similar electron charges, so there is no charge shift between them, but the nullification of these charges.
See also the meaning of molecule.
When there are different organic compounds in a hydrocarbon bond, for example, it is already considered polar.
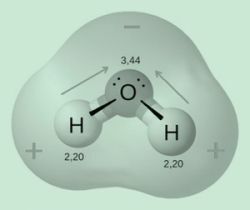 Example: the molecular geometry of water (H2O) is formed by two atoms of hydrogen and one of oxygen, being that the electrons in this compound are more concentrated in the oxygen, causing there to be a displacement of loads. Thus, oxygen becomes more electronegative than hydrogen, characterizing this molecule as polar.
Example: the molecular geometry of water (H2O) is formed by two atoms of hydrogen and one of oxygen, being that the electrons in this compound are more concentrated in the oxygen, causing there to be a displacement of loads. Thus, oxygen becomes more electronegative than hydrogen, characterizing this molecule as polar.
In other words, water is a polar compound.
know more about Hydrocarbons.
non-polar and polar
Unlike non-polar connections, polar molecules are those that have nonzero electronegativity between atoms.
Due to different electron densities, some atoms accumulate more electrons than others, making the attraction force more intense.
Some of the main non-polar compounds are: gasoline, methane and ethane.
Some of the main polar compounds are: water, sugar and alcohol.

