Light refraction is defined as the change in propagation speed as a consequence of the change in the propagation medium. That is, when a light ray changes from one medium to another, with different refractive indices, it suffers a deviation, approaching or moving away from the normal.
1st Law of Refraction
The incident ray I, the normal N and the refracted ray R, belong to the same plane, called the plane of incidence of light, that is, the incident ray, the normal straight line and the refracted ray are coplanar.

Rays of light on the same plane
2nd Law of Refraction
For each pair of media and for each monochromatic light that is refracted, the product of the sine of the angle that the ray forms with the normal and the refractive index of the medium in which the ray is located is constant.
This law is known as the Snell-Descartes law.
The second law of refraction is expressed mathematically by the equation:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
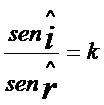
As the angle of incidence (i) forms in the middle (1) and the angle of refraction (r) forms in the middle (2), we verify that the product of the absolute refractive index of the medium by the sine of the angle formed with that medium is always constant.
no1. sin i = n2. feel
For small angles of incidence (imax. = 5º), we have that the sine of the angle of incidence is equal to the sine of the angle of refraction.
sen i sen r
By Kléber Cavalcante
Graduated in Physics
Brazil School Team
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
CAVALCANTE, Kleber G. "The Laws of Refraction of Light"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/as-leis-refracao-luz.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.