Frequency and period are two interlinked concepts in physics. Both deal with phenomena that recur regularly. While period is the time for a repetition to occur, frequency is the number of times a phenomenon occurs in each unit of time.
Frequency (f)
The frequency is called f as the number of times an event occurs per unit of time. if n is this number of repetitions:
An example of frequency is the number of complete turns the Earth rotates around its axis in a week. If the unit of time is a week and the complete loop is a day, the frequency will be:
That is, seven laps in a week.
In the International System of Units (SI), the number of repetitions per second is considered, with the default unit being Hertz (Hz).
1 Hz = 1 cycle per second
Example
An engine that completes 120 cycles per minute works at what frequency?
Period (T)
The period T is the time interval required for a phenomenon to complete one cycle. As an example, we have the period of 365.25 days for the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun.
In the International System of Units (SI), the period is measured in seconds.
Relationship between frequency and period
As the frequency f is the number of repetitions per second, there is a relationship between these magnitudes.
In this way, knowing the period T we can determine the frequency f. It is also possible to determine the period once you have the frequency.
Since T is measured in seconds, the frequency is determined by . This unit is called Hertz.
Frequency and period in circular motion
As circular motion studies movements that are repeated regularly, frequency and period are widely used to characterize it.
The period is the time it takes a body in circular motion to complete one turn, and the frequency is the number of repetitions per second.
In various equipment and rotating machines it is common to check the frequency in terms of revolutions per minute RPM.
Converting RPM to Hz
We can associate the number of revolutions that occur each minute (RPM) with the number of revolutions each second (Hz).
60 rotations every minute equals 60 rotations every 60 seconds.
To determine how many Hz equals a value in RPM, we divide by 60.
For example, if a machine works at 1 380 RPM, the frequency, in Hz, will be:
Frequency, Period, and Angular Velocity
the angular velocity is determined by the angular displacement
that occurs in the time interval
.
Considering the angular displacement of a complete turn , and time as the period T, the angular velocity can be written as:
As , we can also write the speed:
The default unit of angular velocity is the radian per second (rad/s).
Waveform, frequency and period
In the study of waves, the concepts of frequency and period are widely used, whether electromagnetic or mechanical waves.
It is considered as period the time necessary for a wave to leave a height, such as a peak or a valley, for example, and return to this initial position.
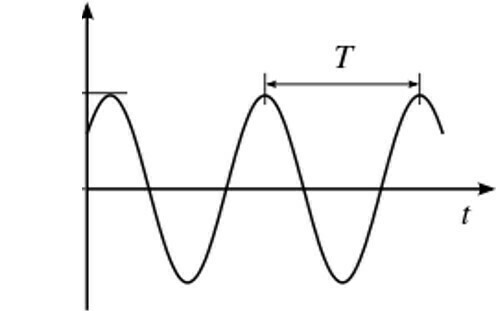
Frequency is the number of times a wave repeats this movement each second.
See too:
- waves
- Circular motion
- simple harmonic motion
- Angular Velocity
ASTH, Rafael. Frequency and period: what it is and how to calculate it.All Matter, [n.d.]. Available in: https://www.todamateria.com.br/frequencia-e-periodo/. Access at:
See too
- waves
- Angular Velocity
- Circular motion
- Simple pendulum: period, potential energy and restoring force
- simple harmonic motion
- Sound waves
- Mechanical Waves
- Exercises on uniform circular motion

