Impulse is a quantity in Physics that measures the effects of a force on a body over a period of time. Just like force, impulse is a vector quantity, requiring, in addition to its value, also the direction in which it acts.
Since impulse is the result of the multiplication of a force and time, the direction and direction of the impulse are the same as that of the force.
Formula for the impulse of a constant force
Considering the constant acting force, the impulse can be calculated by:
Where, in the International System of Measurements we have:
I is the impulse module, measured in N. s;
F is the force, measured in Newtons; is the time interval, measured in seconds.
Impulse Theorem
The Impulse Theorem is used to determine the impulse of a body or material point that is under the action of more than one force. As there are situations in which calculating the resultant force is a difficult task, we use another quantity in this task: the quantity of movement.
In this way, it is possible to determine the impulse of the resultant force that acts in a time interval, even without knowing the resultant of the forces, but rather the variation in the momentum.
The quantity of movement is the product between the mass and the speed of the body.
Where,
Q is the intensity of the momentum,
m is the mass in kilograms,
v is the speed in meters per second.
The Impulse Theorem says that the resulting impulse is equal to the variation in the momentum of a body in the same range of action of the force.
Considering the constant mass in the time interval, we can highlight m.
Where, is the speed at the final instant;
is the speed at the initial instant.
See too Quantity of Movement.
Impulse calculation using the force x time graph
As the impulse is the result of the product between the force and the time in which it acts, the intensity of the impulse is numerically equal to the area of the graph.
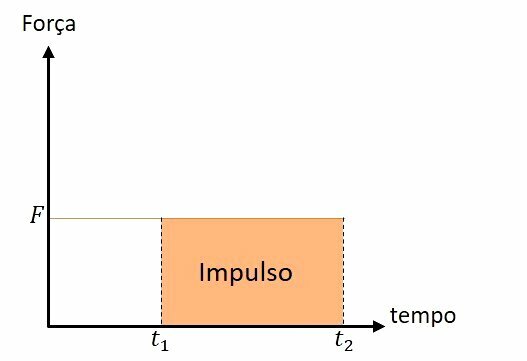
The area of the rectangle is the product of the base (t2 - t1) and the force F.
Impulse Exercises Solved
Exercise 1
A constant force of intensity 9 N acts on a material point for 5 s. Determine the magnitude of the impulse obtained.
Answer: 45 N. s
The impulse is the product between the force modulus and the actuation time.
Exercise 2
A body with a mass of 3 kg moves with a constant direction under the action of forces and accelerates, increasing its speed from 2 to 4 m/s. Determine the resulting impulse during the acceleration process.
Answer: 6 N.s
As we do not know the intensity of the resulting force that determines the movement, but we do know its mass and the variation in speed, we can determine the impulse using the Impulse Theorem.
Exercise 3
The intensity of the resulting force acting on a body with a mass of 5 kg varies with time, as shown in the graph. Determine the intensity of the force F impulse, in the interval from 0 to 15 s.

Answer: 125 N. s.
The impulse modulus is numerically equal to the area determined between the graph line and the time axis.
The intensity of the force increases from 0 to 10 N, between 0 and 5 s. Calculating the area of the triangle we have:
Where b is the base, and h, the height.
After 5 s, the force remains constant for 10 s, forming a rectangle.
The total area is 25 + 100 = 125.
The impulse intensity is 125 N. s.
ASTH, Rafael. Impulse: how to calculate, formulas and exercises.All Matter, [n.d.]. Available in: https://www.todamateria.com.br/impulso/. Access at:
See too
- Quantity of Movement
- Work in Physics
- Hydrostatic
- Mechanical Energy
- Gravitational Force
- Frictional force
- Atmospheric pressure
- Mechanical power and performance