One 2nd degree function is defined by the following formation law f (x) = ax² + bx + c or y = ax² + bx + c, where a, b and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. Its representation on the Cartesian plane is a parable which, according to the value of the coefficient a, has concavity facing up or down. The 2nd degree function assumes three possibilities of results or roots, which are determined when we do f (x) or y equal to zero, transforming the function into a 2nd degree equation, which can be solved by Bhaskara.
2nd degree function graph
Coefficient a > 0, parabola with concavity facing up
Coefficient a < 0, parabola with the concavity facing downwards
? > 0 – The 2nd degree equation has two distinct solutions, that is, the 2nd degree function will have two real and distinct roots. The parabola intersects the abscissa (x) axis at two points.

? = 0 – The 2nd degree equation has a single solution, that is, the 2nd degree function will have only one real root. The parabola will intersect the abscissa (x) axis at just one point.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

? < 0 – The 2nd degree equation has no real solutions, so the 2nd degree function will not intersect the abscissa (x) axis.

Notable Points of the Graph of a 2nd Degree Function
The vertex of the parabola is an important point on the graph, as it indicates the maximum value point and the minimum value point. According to the value of the coefficient The, the points will be defined, note:
When the coefficient value The is less than zero, the parabola will have maximum value.

When the coefficient value The is greater than zero, the parabola will have a minimum value.
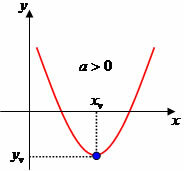
Another important relationship in the 2nd degree function is the point where the parabola cuts the y axis. It is verified that the value of the coefficient c in the law of formation of the function corresponds to the value of the y axis where the parabola intersects it.

by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
High School Function - Roles - Math - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
OLIVEIRA, Gabriel Alessandro de. "Graph of 2nd degree function"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/grafico-funcao.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Math

Second Degree Function, Function, Function Graph, Parabola, Concavity, Parabola Down, Concavity Up, Graphing, Coefficient a Positive, Coefficient a Negative.