You constitutional isomers, better known as flat isomers, are those compounds with static structures that have the same molecular formula, but differ by structural formulas.
There are five types of constitutional isomerism, one of which is tautomerism or dynamic isomerism. Tautos means “two of himself”, which is exactly what happens with isomers in tautomery, they are present in the same liquid phase, coexisting in dynamic equilibrium.
This type of isomerism only occurs with compounds that have highly negative elements, such as oxygen and nitrogen, bonded to a carbon that makes a double bond and to a hydrogen. The electronegative element attracts the electrons from the double bond, displacing it, forming another compound belonging to another function.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Therefore, tautomery is a special type of constitutional isomerism of function.. The two most important cases are of tautomerism between a ketone and an enol (ketoenol) and between an aldehyde and an enol (aldoenolic).
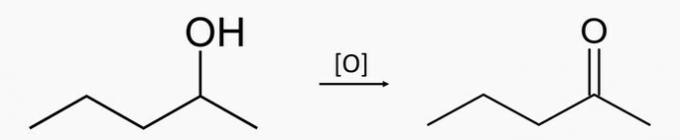
See below an example of aldoenol tautomeria, in which we have in balance the propanal (aldehyde) and propenol (enol), whose molecular formulas are: C3H6O.

By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Dynamic Constitutional Isomerism or Tautomery"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/isomeria-constitucional-dinamica-ou-tautomeria.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry
Know what the various types of plane and spatial isomers are all about, such as function, position, chain, tautomerism, metamerism, cis-trans geometric and optical isomerism.