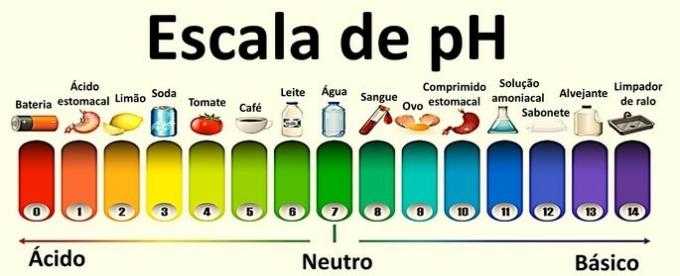
pH represents the hydrogen ionic potential and pOH is the hydroxy ionic potential of the solutions.
These are logarithmic scales used to measure the acidic and basic character of a sample.
The values that compose them range from 0 to 14 and were obtained from the ionic balance of water.
A neutral solution has a pH of 7. Values below 7 classify the solutions as acidic, while after 7 the solutions are basic.
With the pH value, it is possible to find the corresponding one on the pOH scale, just by making a subtraction.
Ionic water balance
A water molecule has the ability to ionize according to the equation:
Here we have an ionic balance, because the process is reversible and the ions can also come together and form a water molecule again.
Another way to demonstrate the balance that occurs is through the autoionization.
A water molecule generated hydronium ions (H3O+) and hydroxyl (OH-) through the disruption of a second molecule.
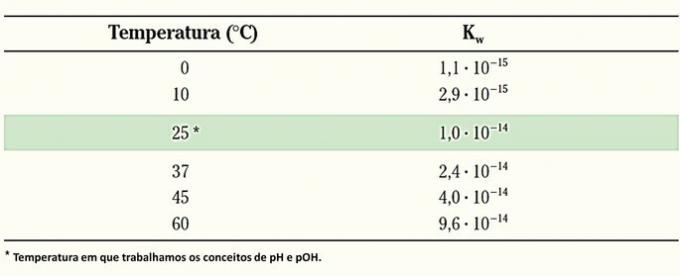
Ionic product of water (Kw)
The constant for the ionic balance of water is:
As water is a pure liquid, its concentration is taken as 1 and does not interfere with the constant value. Therefore, the expression becomes:
O ionic product of Water é .
This expression receives the symbol Kw (W comes from the English word water - water) and like the equilibrium constant, it varies with temperature.
Determination of pH and pOH
At a temperature of 25°C, the ionic product of water is:
In the ionization of pure water, 1 mol of H3O+ is formed with 1 mol of OH- .
Soon,
As these values are extremely low, it was decided to use the values of cologarithms, which correspond to the logarithm with a swapped sign.
Applying the cologarithm to the ionic product of water, we have to:
We can observe that: if we know the pH of a solution, the pOH value can be found by subtracting the first value from 14.
Acidity and basicity of solutions
Neutral solution: the concentration of hydronium ions is equal to that of hydroxyls.
| [H3O+] = 1,0. 10-7 mol/L | pH = 7 |
| [oh-] = 1,0. 10-7 mol/L | pOH = 7 |
Example: pure water.
acid solution: the concentration of hydronium ions is greater than that of hydroxyls.
| [H3O+] |
pH |
| [oh-] |
pOH |
Example: soda, lemon and tomato.
basic solution: the concentration of hydroxyls is greater than that of hydronium ions.
| [H3O+] |
pH |
| [oh-] |
pOH |
Example: egg, soap and bleach.
pH calculation
The concept of hydrogenic potential was created by the Danish chemist Peter Lauritz Sorensen (1868-1939) to express the acidity of a solution through the concentration of H+.
See the table below demonstrating the ionization of a acid:
| Initial Molarity | 0,020 | 0 | 0 |
| ionization | 0,001 | 0,001 | 0,001 |
| Molarity in balance | 0,019 | 0,001 | 0,001 |
In the example we have that the concentration of H ions+ é 0,001. Therefore, the pH of the solution is:
[H+] = 0,001 = 10-3
pH = - log 10-3 = 3
As the pH of the solution is less than 7, this solution is acidic.
Summary on pH and pOH
| Definitions | pH: hydrogen ionic potential of the solution. | |
|---|---|---|
| pOH: hydroxylionic potential of the solution. | ||
| general formula | pH + pOH = 14 | |
| Solutions | Neutral | pH = pOH = 7 |
| acidic |
pH pOH > 7 |
|
| basics |
pOH pH > 7 |
|
| pH calculation | pH = - log [H+] | |
| Calculation of pOH | pOH = -log[OH-] |
Exercises on pH and pOH
1. (FMTM) The pH of gastric juice, an aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid (HCℓ), is approximately 2. Therefore, the mass, in grams, of HCℓ existing in each liter of gastric juice, is
Data: Molar masses (g/mol) H = 1, Cℓ = 35.5
a) 7.3 · 10-2
b) 3.65 · 10-1
c) 10-2
d) 2
e) 10
Correct alternative: b) 3.65 · 10-1.
1st step: calculate the concentration of H ions+.
2nd step: calculate the molar mass of HCl.
3rd step: calculate the mass of hydrochloric acid in each liter of gastric juice.
2. (UEMG) Several cleaning products have ammonia in their constitution. The label of one of these products indicates pH = 11. This means that the concentration of hydroxonium cations and hydroxyl anions in this product are, respectively:
to 1. 10-3 and 1. 10-11
b) 1. 10-11 and 1. 10-7
c) 1. 10-11 and 1. 10-3
d) 1. 10-11 and 1. 10-11
Correct alternative: c) 1. 10-11 and 1. 10-3.
a) WRONG. These concentrations correspond to a solution of pH = 3.
b) WRONG. Although the concentration of H+ indicate that the pH of the solution is 11, the concentration of OH ions- is wrong, as it should be 3, since: pOH = 14 - pH.
c) CORRECT. pH = 11 and pOH = 3, since pH + pOH = 14.
d) WRONG. Although the concentration of H+ indicate that the pH of the solution is 11, the concentration of OH ions- is wrong, as it should be 3, since: pOH = 14 - pH.
a) 0.1 mol/L NaOH
b) NaCl 0.5 mol/L
c) H2ONLY4 1.0 mol/L
d) 1.0 mol/L HCl
e) 0.2 mol/L KOH
Correct alternative: e) KOH 0.2 mol/L.
a) WRONG. The solution is basic as its pH is greater than 7, but it does not have the higher pH of the alternatives.
b) WRONG. NaCl is a salt as it is the product of a strong acid and base reaction. Therefore, its pH is neutral.
c) WRONG. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid, so its pH is low.
d) WRONG. Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, so its pH is low.
e) CORRECT. The solution is basic as its pH is greater than 7.