Organic reactions are reactions that take place between organic compounds. There are several types of reactions, which occur by breaking molecules giving rise to new bonds.
Widely used in industry, it is from them that medicines and cosmetic products, plastics, among many other things, can be produced.
the main types of organic reactions they are:
- addition reaction
- replacement reaction
- elimination reaction
- Oxidation reaction
Addition Reaction
The addition reaction takes place when the bonds of the organic molecule break and a reagent is added to it.
It happens mainly in compounds whose chains are open and which have unsaturations, such as alkenes () and alkynes (
).
Examples of addition reactions
Example 1: hydrogenation (addition of hydrogen)
Hydrogenation of an alkene produces an alkane.
Example 2: halogenation (addition of halogens)
Halogenation of an alkene produces a halide.
Example 3: hydration (addition of water)
Hydration of an alkene produces an alcohol.
Read too: Organic compounds
Replacement Reaction
The substitution reaction happens when there are bonding atoms (or a group) that are replaced by others.
It happens mainly among alkanes, cyclans and aromatics.
Examples of substitution reactions
Example 1: halogenation (substitution with halogen)
Halogenation of an alkane produces a halide.
Example 2: nitration (substitution by nitro)
Nitration of an alkane produces a nitro compound.
Example 3: sulfonation (substitution by sulfonics)
Sulphonation of an alkane produces an acid.
Read too: Organic Functions
Elimination Reaction
The elimination reaction takes place when a carbon ligand is removed from the organic molecule.
This reaction is contrary to the addition reaction.
Examples of elimination reactions
Example 1: hydrogen elimination (dehydrogenation)
Removing hydrogen from an alkane produces an alkene.
Example 2: elimination of halogens (de-halogenation)
The elimination of halogens from a dihalide produces an alkene.
Example 3: halide elimination
Removal of halide from a halide produces an alkene.
Example 4: water elimination (alcohol dehydration)
Removing water from an alcohol produces an alkene.
See too: esterification
Oxidation Reaction
The oxidation reaction, also called redox, takes place when there is a gain or loss of electrons.
Examples of Oxidation Reactions
Example 1: energetic oxidation of alkenes
The energetic oxidation of an alkene produces carboxylic acids.
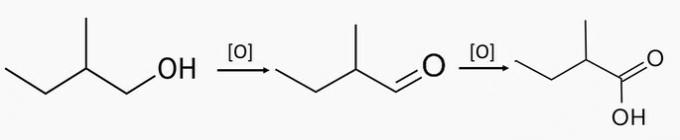
Example 2: primary alcohol oxidation
The energetic oxidation of a primary alcohol produces carboxylic acid and water.
Example 3: secondary alcohol oxidation
Oxidation of a secondary alcohol produces ketone and water.
Read too: Carboxylic Acids
Exercises on organic reactions
question 1
(Unifesp/2002) Many alcohols can be obtained by acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes.
In this addition reaction, the H in water is added to the carbon that has more hydrogens attached to it and the hydroxyl group is attached to the less hydrogenated carbon (Markovnikov's rule).
Knowing that the alcohols formed in the hydration of two alkenes are respectively 2-methyl-2-pentanol and 1-ethylcyclopentanol, what are the names of the corresponding alkenes that gave rise to them?
a) 2-methyl-2-pentene and 2-ethylcyclopentene.
b) 2-methyl-2-pentene and 1-ethylcyclopentene.
c) 2-methyl-3-pentene and 1-ethylcyclopentene.
d) 2-methyl-1-pentene and 2-ethylcyclopentene.
e) 3-methyl-2-pentene and 2-ethylcyclopentene.
Correct alternative: b) 2-methyl-2-pentene and 1-ethylcyclopentene.
2-Methyl-2-pentanol alcohol is produced by hydrating 2-methyl-2-pentene alkene.
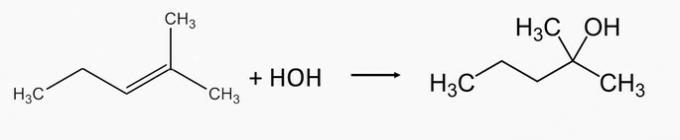
1-ethylcyclopentanol alcohol is generated by the hydration of 1-ethylcyclopentene alkene.
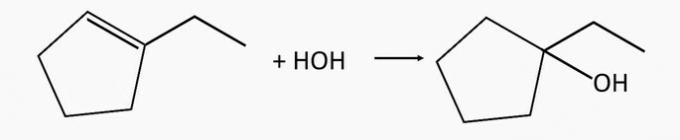
question 2
(Ufal/2000) In the study of the chemistry of carbon compounds, it is learned that BENZENE:
( ) It is hydrocarbon.
( ) Can be obtained from acetylene.
( ) In oil, it is a component of greater mass proportion.
( ) May undergo substitution reaction.
( ) It is an example of a molecular structure that presents resonance.
(TRUE) Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon. This compound is formed only by carbon and hydrogen atoms, whose formula is C6H6.
(TRUE) Benzene can be produced from acetylene through the following reaction:
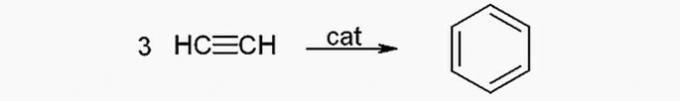
(FALSE) Petroleum is a mixture of hydrocarbons and the mass of the components is related to the size of the chain. Thus, larger carbon chains have greater mass. The heavier fractions of petroleum, such as asphalt, have chains with more than 36 carbon atoms.
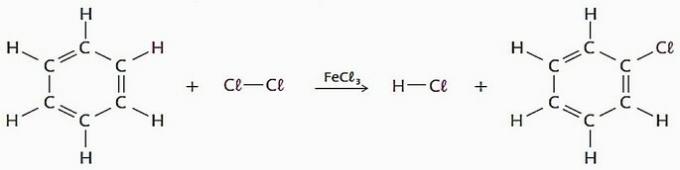
(TRUE) Substitution reactions using benzene as a reagent have many industrial applications, mainly for the production of drugs and solvents.
In this process a hydrogen atom can be replaced by halogens, nitro group (-NO2), sulfonic group (—SO3H), among others.
See an example of this type of reaction.
(TRUE) Due to resonance, benzene can be represented by two structural formulas.
However, in practice it has been observed that the length and energy of the bonds established between carbon atoms are equal. Therefore, the resonance hybrid is the closest to the real structure.
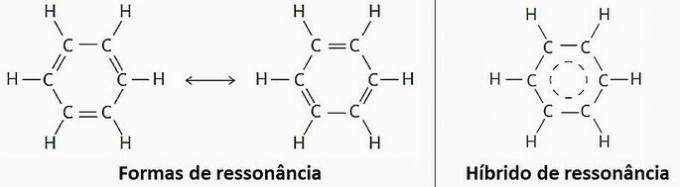
question 3
(UFV/2002) The oxidation reaction of an alcohol with molecular formula C5H12O‚ with KMnO4 provided a compound of molecular formula C5H10O.
Check the option that shows the CORRECT correlation between the name of the alcohol and the name of the product formed.
a) 3-methylbutan-2-ol, 3-methylbutanal
b) pentan-3-ol, pentan-3-one
c) pentan-1-ol, pentan-1-one
d) pentan-2-ol, pentanal
e) 2-methylbutan-1-ol, 2-methylbutan-1-one
Correct alternative: b) pentan-3-ol, pentan-3-one.
a) WRONG. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol produces a ketone. Therefore, the correct product for the oxidation of 3-methylbutan-2-ol is 3-methylbutan-2-one.
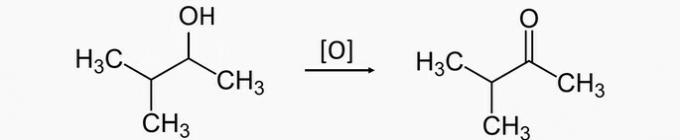
b) CORRECT. Oxidation of the pentan-3-ol secondary alcohol produces the pentan-3-one ketone.

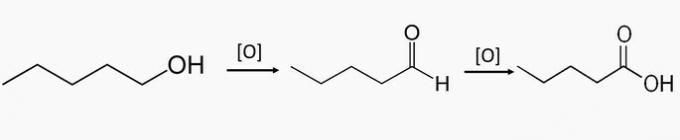
c) WRONG. These compounds are part of the oxidation of primary alcohols, which produces an aldehyde or a carboxylic acid.
Pentan-1-ol is a primary alcohol and by partial oxidation of the compound pentanal can be formed and by total oxidation pentanoic acid is formed.
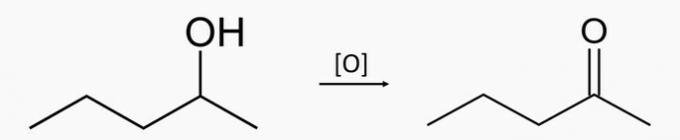
d) WRONG. Oxidation of the secondary alcohol pentan-2-ol produces the pentan-2-one ketone.
e) WRONG. The primary alcohol 2-methylbutan-1-ol produces the aldehyde 2-methylbutanal in partial oxidation and 2-methylbutanoic acid in total oxidation.
question 4
(Mackenzie/97) In the elimination reaction, which occurs in 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide in an alcoholic medium, a mixture of two organic compounds that are position isomers is obtained.
One of them, which forms lesser amounts, is 1-butene. The other is the:
a) methylpropene.
b) 1-butanol.
c) butane.
d) cyclobutane.
e) 2-butene.
Correct alternative: e) 2-butene.
Alkenes are produced by the reaction of the organic halide HBr with potassium hydroxide KOH, in the presence of ethyl alcohol as a solvent.

Different compounds were formed due to the halogen atom being in the middle of the carbon chain, generating more than one possibility of elimination.
However, although there are two possibilities of products they will not have the same quantities formed.
The 2-butene, for this reaction, will be formed in greater quantity, as it comes from the elimination of a tertiary carbon. 1-butene was formed from the elimination of a primary carbon and, therefore, a smaller amount was formed.



