THE salt hydrolysis between strong acids and bases it occurs when the cation in a salt does not interact with the anion in water, and the anion in the salt does not interact with the cation in water. Hydrolysis between cations and anions of a salt and water occurs only when the product formed is a weak acid, a weak base, or both. Understand the salt hydrolysis between strong acids and strong bases step by step:
a) Step 1: water ionization
Water is a substance that has the ability to suffer autoionization, that is, it produces hydronium cation (H+) and hydroxide anion (OH-) from its structure.
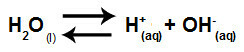
Equation representing the self-ionization of water
b) Step 2: Dissociation of salt
When a salt is added to water, it goes through the process of dissociation. As salt is an ionic compound, in water, its cations and anions are released into the medium, as in the equation shown below:
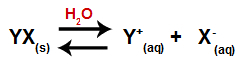
Equation representing the dissociation of any salt
c) Step 3: Salt hydrolysis of strong acids and bases
For strong acid: when the anion of the salt combined with the H
+ of water to form HCl, HBr, HI or another acid in which the subtraction of the number of oxygens by the number of hydrogens is equal to or greater than 2, we will have a strong acid. Therefore, the combination between the mentioned ions does not occur.For strong foundation: when the cation of the salt belonging to the IA (alkali metals) or IIA (alkaline earth metals other than magnesium) families is combined with the OH- of water, it will form a strong foundation. Therefore, the combination between the mentioned ions does not occur.
When salt ions do not interact with water ions, we have the following equation:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
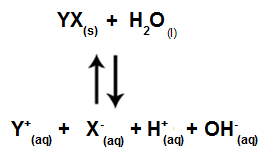
Equation showing all ions present in the solution
In summary, as the salt ions do not interact with the water ions, the salt ions do not promote any change in the final solution. Thus, we can write the equation of a salt hydrolysis between strong acids and strong bases just with the water ionization equation.
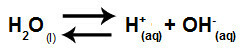
Equation representing the hydrolysis of strong acids and bases
d) Example of salt hydrolysis between strong acids and bases
When we add the potassium chlorate salt to water (KClO3), the salt dissociates and releases the potassium cation (K+) and the chlorate anion (ClO3-) in the middle.
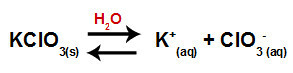
Dissociation equation for potassium chlorate
It is important to remember that water undergoes self-ionization and provides the medium with hydronium cation (H+) and hydroxide anion (OH-). We must now assess the interaction between salt and water ions.
When the H+ interacts with ClO3-, it forms perchloric acid (HclO3). Since the subtraction of the number of oxygens by the number of ionizable hydrogens in perchloric acid is 2, it is strong. Therefore, the interaction between the ions does not occur.
When the K cation+ interacts with the OH anion-,we have the formation of a strong base, as potassium is an alkali metal. Therefore, the interaction between the ions does not occur.
The equation that represents the salt hydrolysis between strong acids and bases from the dissolution of potassium chlorate in water is:
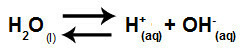
Chemical equation of potassium chlorate hydrolysis
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "Saline hydrolysis between strong acids and strong bases"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/hidrolise-salina-entre-acidos-bases-fortes.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Test your knowledge and learn more with this list of solved exercises on chemical balances. Through this material, you will be able to better understand how to work equilibrium constants (Kp, Kc and Ki), equilibrium shift, pH and pOH, as well as equilibrium in so-called buffer solutions.