An organic reaction can occur in different ways, in this context you check the Addition, Substitution and Elimination Reaction.
Addition Reaction
In the addition reaction, the joining of two or more molecules produces only one product.
Examples:
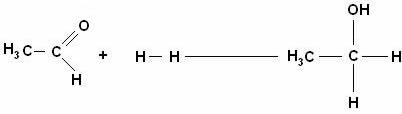
Two molecules (cetaldehyde and H2) come together to form ethanol (CH3CH2OH).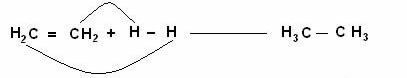
The ethylene molecule (C2H4) joins the H2 (hydrogen gas) and gives rise to the product ethane (C2H6).
Replacement Reaction
In this case, an atom or group of atoms is replaced by a radical of the other reactant, that is, the exchange of a ligand occurs in the molecule.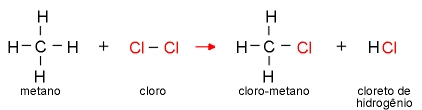
Note that a hydrogen in the Methane molecule has been replaced by a chlorine atom, giving rise to the products chloromethane and hydrogen chloride.
Elimination Reaction
In this type of reaction, the exit of ligands from a molecule occurs without replacing these ligands by others.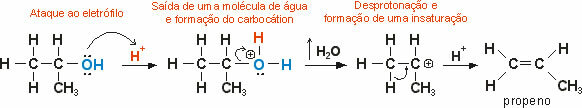
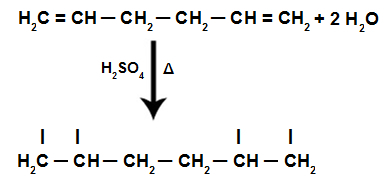
The intramolecular dehydration of alcohols is an Elimination reaction, where the atoms in the molecule of the organic reagent (propanol) decrease due to the exit of the water molecule.
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
See more!
saponification reaction
Organic chemistry - Chemistry - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUZA, Líria Alves de. "Types of organic reactions"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/tipos-reacoes-organicas.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.