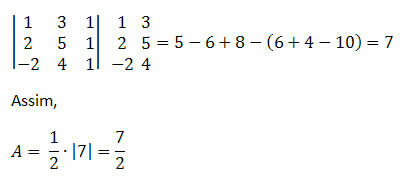The three-point alignment can be determined by applying the determinant calculation of a 3x3 order matrix. When calculating the determinant of the constructed matrix using the coordinates of the points in question and finding a value equal to zero, we can say that there is collinearity of the three points. Note the points on the Cartesian plane below:

The coordinates of points A, B and C are:
Point A (x1,y1)
Point B (x2,y2)
Point C (x3,y3)
Through these coordinates we will assemble the 3x3 matrix, the abscissa of the points will constitute the 1st column; the ordinates, the 2nd column and the third column will be complemented with the number one.
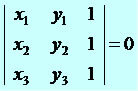
Applying Sarrus we have:
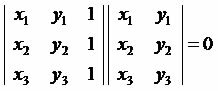
x1*y2*1 + y1*1*x3 + 1*x2*x3 – (y1*x2*1 + x1*1*y3 + 1*y2*x3) = 0
x1y2 + y1x3 + x2*x3 – y1x2 – x1y3 – y2x3 = 0
Example 1
Let's check if the points P(2,1), Q(0,-3) and R(-2,-7) are aligned.
Resolution:
Let's build the matrix using the coordinates of points P, Q and R and apply Sarrus.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
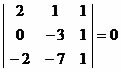
2*(–3)*1 + 1*1*(–2) + 1*(–7)*0 – [1*(–3)*( –2) + 1*0*1 + 2*(–7)*1] = 0
– 6 – 2 – 0 – [6 + 0 – 14] = 0
– 8 – 6 +14 = 0
–14 + 14 = 0
0 = 0
We can verify that the points are aligned, since the determinant of the matrix of the coordinates of the points is null.
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Analytical Geometry - Math - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Marcos Noé Pedro da. "Three-point alignment condition"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/condicao-alinhamento-tres-pontos-2.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.