The carbon atom is considered special for its ability to form bonds with other atoms and give rise to long carbon chains. Everything is due to the tetravalence of carbon, it can join forming four bonds, and the participating atoms can be carbon or other elements. The latter, when present in the carbon chain, are called heteroatoms.
The most common heteroatoms are: Nitrogen (N), Oxygen, Sulfur (S) and Phosphorus (P).
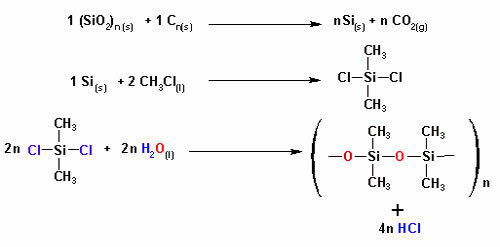
Example:
The oxygen atom present in the chain above is a heteroatom, as it is between carbons.
But beware! Do not confuse branching with heteroatom carbon, see:
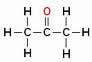
The Oxygen atom (in red) is not located between carbons but above them, forming a branch, so it cannot be considered as a heteroatom.
Classification of atoms in a carbon chain:
In a chain, each carbon is classified according to the number of other carbon atoms attached to it.
primary carbon: Directly attached to only 1 other carbon.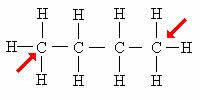
The arrow indicates the primary carbons. Note that because they are located at the ends of the carbon chain, these atoms bind to only 1 carbon.
secondary carbon: Directly linked to 2 other carbons.

The indicated carbons are located between two carbons.
tertiary carbon: Directly linked to 3 other carbons.
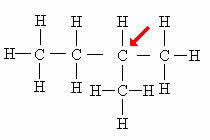
Note that the presence of the branch (CH3) attached to the indicated atom causes it to receive the tertiary carbon classification.
Quaternary carbon: Directly linked to 4 other carbons.
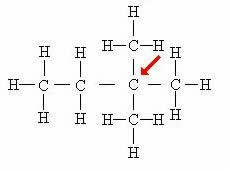
In this case, the four atoms attached to the central carbon (indicated by the arrow) form a kind of “square”, which further evidences the presence of the quaternary carbon.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
See more!
Classification of carbon chains: types of bond
Properties of organic compounds
Organic chemistry - Chemistry - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUZA, Líria Alves de. "Ability of organic compounds to form chains"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/capacidade-compostos-organicos-formar-cadeias.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
d) Carbon atoms form ionic bonds easily.