Fermentation it is a chemical process, with the absence of oxygen gas (O2), in which fungi and bacteria transform organic matter into other products and energy. It is the way that these beings find to produce energy for the performance of their biological functions.
Regardless of the living being who is performing the fermentation, it always occurs in the cytoplasm (or cytosol) of the cell and with the aid of enzymes, which act as catalysts.
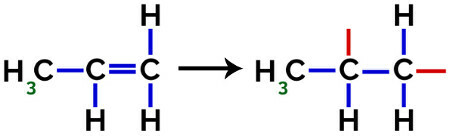
Therefore, we can say that the fermentation it is a way of energy production that uses organic matter, such as glucose. Before fermentation takes place, a process called glycolysis is carried out.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a chemical process in which phosphates (P) are incorporated into the glucose molecule, favoring its breakdown into two pyruvic acid molecules, as in the equation shown below.

Alcoholic fermentation
It is a fermentation performed by some types of bacteria and some fungi (such as yeast Sacharomyces cerevisiae). In this reaction, pyruvic acid (whose formula is C
3) is decarboxylated (loses its hydroxyl), generating acetaldehyde through the action of the enzyme pyruvate decarboxylase (absent in animals).
As a result of this fermentation, NADH produces the reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol molecules (C2H6O), still producing carbon dioxide (CO2).
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
That fermentation it is very common in the production of bread, wine, beer and ethanol.

Carbon dioxide production during a fermentation
Lactic fermentation
THE lactic fermentation, performed exclusively by bacterial action (the lactobacilli), occurs when glycolysis has as carbohydrates to glucose or galactose, obtained from the breakdown of a lactose molecule (sugar present in milk). In glycolysis with lactose derivatives, we have the formation of pyruvic acid, ATP and NADH2, instead of NADH.

Through the action of the enzyme lactic dehydrogenase, pyruvic acid is converted (through a reduction reaction) to lactic acid (C3H6O3), when the carbonyl becomes a hydroxyl.
This fermentation is very common in the production of yogurts and cheeses.
acetic fermentation
Acetic fermentation occurs when ethanol, obtained from alcoholic fermentation, comes into contact with bacteria of the family Pseudomonaceae, such as Acetobacter or gluconobacter.

These bacteria transform ethanol into acetic acid molecules (C2H4O2) through an oxidation process. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is fermentation?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-fermentacao.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Production of ethanol, organic compound, alcohol, hydroxyl functional group, sugar cane, sucrose, garapa, molasses, brown sugar, sulfur dioxide, Saccharomyces, fuel, alcohol content, Gay-Lussac.