THE light reflection it is an optical phenomenon in which a beam of light, when incident on a surface, returns to its original medium. Thanks to this phenomenon we are able to see objects around us, as the light falls on the bodies, which, by in turn, they reflect it, causing light rays to reach our eyes, thus enabling our eyesight.
According to the light incidence surface, the reflection can be classified in two ways:
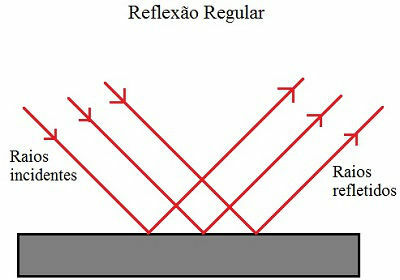
diffuse reflection: occurs when light rays fall on an irregular or rough surface and are reflected in different directions. Look at the picture:

Representation of diffuse reflection
The figure above shows how diffuse reflection, also known as light scattering, occurs. Light rays fall parallel to each other on an irregular surface and are reflected in various directions. This is what makes it possible to view objects from different angles, because as the light rays spread out, they reach our eyes, regardless of our position. That's why we can see everything that goes on around us.
Regular or specular reflection: When light rays fall on a smooth or regular surface and are reflected in the same direction, parallel to each other, as shown in the following figure:
Representation of regular reflection
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Note in the figure that, in this type of reflection, the reflected light rays are parallel and propagate in the same direction. An example of regular reflection is that which occurs in flat mirrors, where the image formed is quite sharp.
The fact that light rays propagate in only one direction makes it impossible to observe the image from different positions. This can be seen in the mirrors, depending on your position in relation to it, it is not possible to see your reflected image.
the laws of reflection
Like all physical phenomena, light reflection also obeys certain rules. To understand them, look at the following figure:
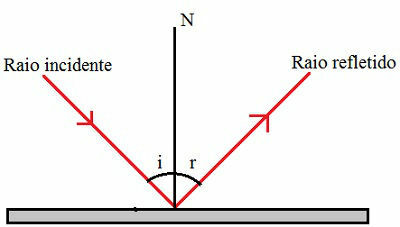
Diagram showing the behavior of a ray of light when falling on a surface
Consider the ray of light represented in the figure, where:
i – is the angle of incidence;
r – is the angle of reflection;
N - is the Normal line perpendicular to the reflecting surface.
From these definitions, we can enunciate the following laws of reflection:
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, i = r;
The incident light ray, the reflected one and the normal line always belong to the same plane.
By Mariane Mendes
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
TEIXEIRA, Mariane Mendes. "What is light reflection?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-reflexao-luz.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.