Gluten is a mixture of different types of protein commonly found in farinaceous obtained from some cereals, such as wheat, barley, rye and oats. This mixture has the following main characteristics:
Elasticity: physical property of the material to undergo deformation and return to its original shape;
Viscosity: physical property of the material to resist movement or shear (cut).
gluten can be found in a multitude of foods industrialized, such as:
Breads
Pasta in general
Cakes and Cookies
Crackers
Ice cream
Candy
corn chips
Soft drinks
chocolate milk
breaded meats
Cold cuts in general (ham, mortadella, sausage)
The main proteins that can form gluten are gliadin, glutenin, avenin, secalin and hordein. However, its composition depends on the cereal used to obtain the farinaceous:
Oat: presents avenin
Wheat: has gliadin and glutenin
Rye and Barley: have secalin and hordein
The elasticity property of gluten comes from glutenin, and the viscosity is provided by gliadin. Below, we will learn about the main chemical characteristics of these proteins:
Gliadin: has molecular formula C29H47N7O9 and it has a long, linear chain (no branches). Its main feature is its extensibility, which is very evident when it is mixed with water.
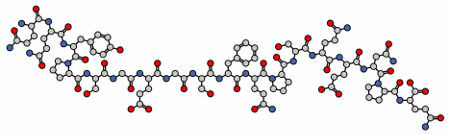
Gliadin structural formula
Their molecular units unite through intramolecular bonds, such as Van der Waals forces, forming globules, as in the image below:
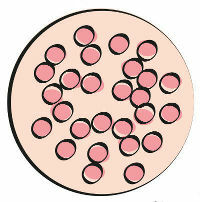
Schematic representation of Gliadin units
NOTE: Extensibility is visible when we handle the bread dough, for example, and we notice its cohesiveness or viscosity (a material well adhered to each other).
Glutenin:is a protein that has a long chain,branched and a high molecular mass. The presence of branches favors elasticity. Their molecular units are joined by means of disulfide bonds (between sulfur atoms).

Schematic representation of glutenin molecule
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
THE gluten formation only occurs if we mix water with the proteins of the aforementioned cereals, subjecting them to a mechanical force. With this, intermolecular bonds are created between the Gliadin and Glutenin units, as shown below:
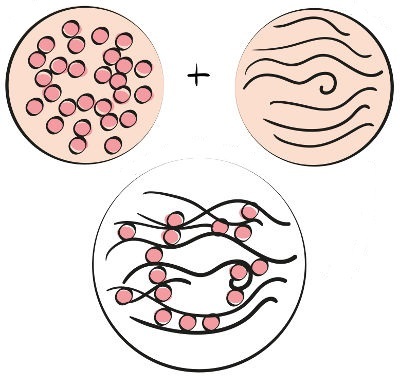
Schematic representation of gluten formation
The presence of gluten in wheat flour can be easily noticed during the preparation of a bread, for example. When we put the dough in the oven, it is one size; but when you take it out after a while, the size practically doubles. This is because the gluten, for being a network formed by the interaction of different protein molecules, manages to trap the carbon dioxide produced during cooking, which causes the dough to grow.
at the moment, a very common discussion about gluten is whether its ingestion is harmful to health or not. In reality, there are people who have gluten intolerance, which may present a pathology called celiac disease, a chronic inflammation in the intestinal mucosa that causes the following symptoms:
Diarrhea
Abdominal pain
malnutrition
Anemia
Fatigue
Small bowel damage
To avoid these inconveniences, a diet with gluten-free foods, that can be:
Cereals: rice, corn, millet;
Pseudocereals: quinoa, amaranth, buckwheat;
Flour and Starch: rice flour, corn starch, cornmeal, cassava flour, potato starch, soy flour, flour, arrowroot, rice flakes and corn;
Pastas: made with the permitted flours.
Vegetables, fruits and vegetables: all, raw or cooked;
Dairy: milk, butter, cheese and dairy products;
Fats: oils and oils;
Meat: beef, pork, chicken, fish, eggs and seafood;
Grains: beans, lentils, peas, chickpeas and soybeans;
Oil seeds: walnuts, almonds, peanuts, Brazil nuts, cashews, hazelnuts, macadamia nuts, flaxseed, sesame, pumpkin.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is gluten?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-gluten.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

See the definition of basic Chemistry concepts such as matter, energy, substance, mixture, body, object, mass, volume and system.