carboxylic acids are organic compounds that have a carboxyl functional group, that is, a carbon that makes a double bond with oxygen and a single bond with an OH group.
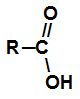
Carboxyl is the functional group of every carboxylic acid
The term carboxylic acid is used to designate an oxygenated organic function, that is, one that has an oxygen atom in its structure. The compounds belonging to this group have a corrosive capacity and a sour taste, as they are acidic.
Characteristics of carboxylic acids
Generally speaking, they are soluble in organic solvents;
The only carboxylic acids that are soluble in water are those that have up to four carbon atoms in their structure;
In general, carboxylic acids are denser than water, with the exception of acids with one or two carbon atoms;
Carboxylic acids that have up to nine carbons are liquid at room temperature;
In solid state, they are whitish and have a waxy (wax) appearance;
In the liquid state, they are colorless;
As they have the carboxyl, they are able to establish hydrogen bonds;
Its compounds are polar;
In general, they are odorless, with the exception of acids with up to three carbons, which have an irritating smell, and those with up to six carbons, which have a disgusting smell;
rule of nomenclature for carboxylic acids
To perform the nomenclature of a carboxylic acid, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) determines the following rule:
Acid
+
prefix (referring to the number of carbons in the chain)
+
infix (referring to the type of bonds between carbon atoms)
+
Hi co
See some examples:
Carboxylic acid with six carbon atoms
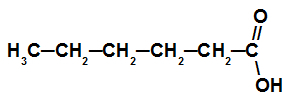
This acid has a chain with six carbon atoms (prefix hex), only single bonds (infix an) and a carboxyl (oic), so its name is hexanoic acid.
-
Carboxylic acid with seven carbon atoms
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
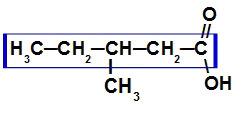
As this acid is branched, the main chain is the one with the greatest number of carbons and the carboxyl. In this compound, the main chain has five carbon atoms (prefix pent), only single bonds between carbon atoms (infix an) and a carboxyl (oic), so its name is acid 3-methyl-pentanoic.
NOTE: The numbering of the main chain must always start from the carboxyl carbon.
Carboxylic acid with two carboxyls
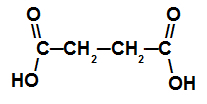
This acid has a chain with four carbon atoms (prefix but), only single bonds between carbon atoms (infix an) and two carboxyl atoms (dioic), hence its name is acid butanedioic acid.
NOTE: Between the infix and the “dioic”, a connecting vowel was added.
Chemical reactions with carboxylic acids
The) esterification reaction
It is a chemical reaction in which a carboxylic acid reacts with a alcohol and form one ester and water, as shown in the following equation:

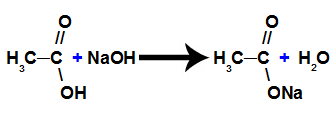
b) Salification reaction
It is a chemical reaction in which a carboxylic acid reacts with an inorganic base and forms a salt of the carboxylic acid and water, as shown in the following equation:
ç) elimination reaction
In this reaction, two carboxylic acid molecules are dehydrated, resulting in a anhydride and water, as shown in the following equation:

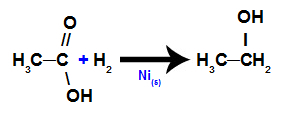
d) Reduction of carboxylic acids
In this reaction, a carboxylic acid is subjected to a medium that contains hydrogen gas (H2) and solid nickel, which results in the formation of an alcohol, as shown in the following equation:
Applications of carboxylic acids
Production of organic esters;
Production of carboxylic acid salts;
Preparation of perfumes;
Vinegar production;
Production of artificial silk;
production of disinfectants;
Dyeing of fabrics.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What are carboxylic acids?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-sao-acidos-carboxilicos.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Carboxyl functional group, carboxylic acids, ethanoic acid, acetic acid, vinegar, methanoic acid, formic acid, benzoic acid, fungicide, low molecular weight carboxylic acids.