At optical fibers are flexible filaments made of transparent materials such as glass or plastic fibers and which are used as a means of propagation of the light. Optical fibers are generally very thin, with only a few micrometersof thickness (10-6 m), but can be several kilometers long. Optical fibers have several applications, with data transmission being one of the most common.
Fiber Optic Physics
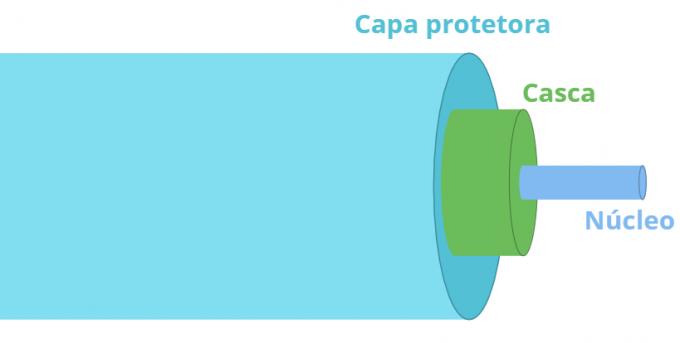
Optical fibers consist of core, shell and protective cover.
Optical fibers are formed by a high transparent core. refractive index coated with transparent plastic layers whose refractive indices are lower than those of the core. The physical phenomenon that allows the use of optical fibers is the reflectioninternaltotal from light.
For your total internal reflection, light is emitted into the fiber optic core in a minimum angle of incidence, called limit angle (also called critical angle), measured in relation to the interface between the core and its casing. Such an angle allows the light to undergo successive internal reflections inside the optical fiber without it escaping from there.
In this way, light can be propagated over long distances, with minimal losses in its intensity, in addition to monitoring the format in which the fiber optic cables are arranged.
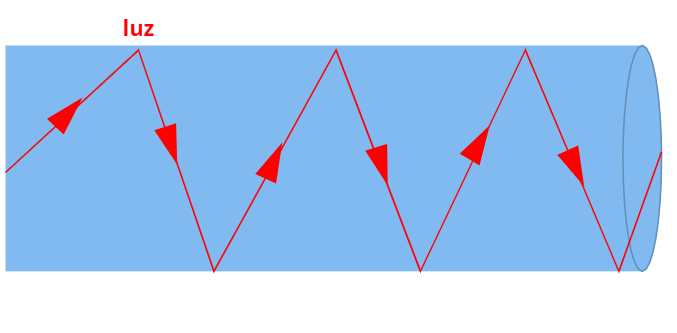
Simply put, fiber optic cable works like a mirrored tunnel that reflects light.
Optical fibers can also propagate more than one color, or wave-length, inside. This process, called multiplexing, allows more information to be transmitted simultaneously over a single optical fiber, such as internet, telephone and television, something that cannot be done with conventional cables, such as those made of copper, widely used for transferring Dice.
When different wavelengths are emitted inside an optical fiber, the colors tend to mix, thus forming a beamWhite, because of the synthesisadditive of colors. Thus, at the terminals of this type of optical cable, a kind of prism capable of scattering light is used, separating the different colors and thus displaying its spectrum discrete, characteristic of each wavelength.
Lookalso:What is refraction?
what is it for
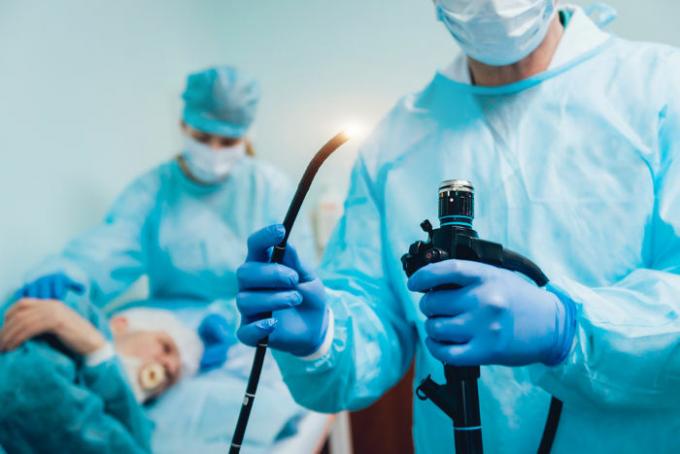
The endoscope is used to take images of the inside of the throat.
Check out some of the main uses of optical fibers:
StreaminginDice: Optical fibers can be used to transmit data from internet, telephone, television, networks, radio etc.
obtaininginimages: Optical fibers can be used to obtain images from hard-to-reach places, since light can be reflected in their interior over great distances.
Sensors: Through optical fibers, it is possible to build a wide variety of sensors capable of sensitive temperature variations, small deformations in solids, light frequencies, polarization of light etc.
Advantages and disadvantages

Light is able to propagate inside optical fibers thanks to the optical properties of its core.
→ Advantages
Speedinstreaming: Most fiber optic cables used in the world are capable of transmitting 40 Gbit/s (Gigabits per second – 109 bits/s), however, currently there are technologies that are capable of transferring up to 1 Pbit/s (Petabit per second – 1015 bits/sec).
Resistance to electromagnetic interference: Fiber optic cables are made of dielectric materials, and light propagation inside these materials is not interfered with by external electromagnetic waves.
Lowmitigationinsignal: Unlike conductive cables, optical fibers can transmit information with small losses: about 0.2 dB/km (0.2 decibels - unit of intensity of the energy carried by the wave).
Cost: Fiber optic cables are cheaper than copper conductor cables.
Lifeuseful: This type of cables has a very long service life, estimated at over 100 years of continuous use.
Space: Due to their data transfer rate, fiber optic cables take up much smaller space than conventional cables.
→ Disadvantages
Application: Fiber optic cables are either underground or always connected to the ground.
Fragility: Fiber optic cables are sensitive and can break more easily than copper cables, and they are not as malleable as metallic cables.
Distances: Although they absorb little light, fiber optic cables that cover large distances like those that are submarines, they need many signal repeaters to reinforce the losses of intensity of the light.
fiber optic speed
Most fiber optic cables used today have transmission capabilities between 10 and 40 Gbits/s. However, there are a number of applications where higher transfer rates are required, so some transfer companies telecommunications have already developed cables over 7000 km in length, capable of transmitting up to 15.5 Tbits/s (Terabits/s - 1015 bits/sec). Fiber optic cables of this type are estimated to be capable of supporting up to 3,000,000 simultaneous telephone calls or up to 90,000 television channels.

Optical fibers can be used for internet transmission.
How is fiber optics made?
The most common material for the construction of optical fibers is silica, the popular name for oxideinsilicon (SiO2). However, depending on the desired application, other materials can be used in its construction, such as fluorine-derived glasses and some elements of the chalcogen family, such as sulfur.
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock
