Ideas about the constitution of matter (the atom) emerged in ancient Greece, around 450 BC. a., from, mainly, of Democrito and Leucipo. However, the atom actually only received a scientific character after the so-called Dalton's atomic theory.
THE Dalton's atomic theory it was fundamental for the development of atomic knowledge, as it served as a basis for other scientists to know the atom and its characteristics.
Who was John Dalton?
John Dalton, a chemist by training, was born in Cumbria, England, in 1766 and died in Manchester in 1844. His life was destined from an early age to scientific research and teaching, so much so that he taught or contributed to the development of several areas of knowledge.
His greatest legacy as a scientist, however, was the development of the first atomic theory. It was through several experiments related to the mixture of gases and knowledge of the works proposed by Lavoisier that Dalton's atomic theory emerged in 1808.
Postulates of Dalton's Atomic Theory
Dalton's atomic theory was based on experiments, but none of these experiments could reveal the atom clearly. Hence, Dalton called the atom the smallest part of matter.
Dalton's theory presents far more postulates than proofs. See some of them:
Atoms are massive and spherical in shape (similar to a billiard ball);
Atoms are indivisible;
Atoms are indestructible;
One chemical element it is a set of atoms with the same properties (size and mass);
Atoms of different chemical elements have different properties from each other;
The relative weight of two atoms can be used to differentiate them;
A compound chemical is formed by the same combination of different types of atoms;
Different chemical substances are formed by combining different atoms.
Representations of the Dalton Atomic Model
Dalton named his atomic model the billiard ball and, therefore, started to represent the atoms of the elements known in his day by means of spherical symbols.
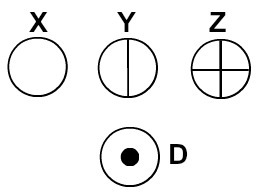
Atoms represented according to Dalton's atomic theory
Each atomic representation that has a specific detail indicates a different chemical element. Didactically the elementary and middle level books and exercises represent the atoms only by spheres with different colors.
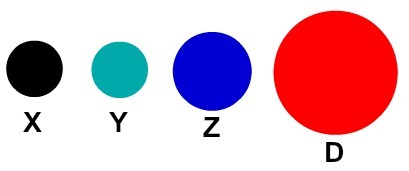
Didactic representation of atoms
Contributions of Dalton's Atomic Theory
understanding of Lavoisier's Law of Conservation of Mass
The French chemist Lavoisier claimed in 1785 that “in a chemical reaction, mass is conserved because there is neither creation nor destruction of atoms ”. Dalton's atomic theory proved this fact, as one of his postulates states that the atom is indestructible.
Therefore, if we carry out the combustion of coal (C) in the presence of oxygen gas (O2), we will have a chemical reaction between one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. This reaction will form carbon dioxide (CO2), which has exactly the same atoms that made up the substances before the reaction.
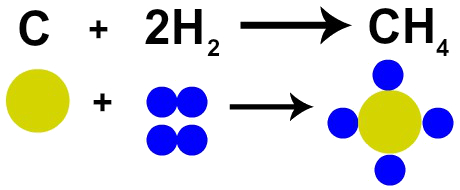
Representation of Lavoisier's Law by Dalton's Atomic Model
understanding of simple substances
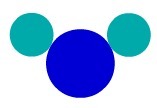
Using the Dalton's atomic model, we can understand a simple substance, that is, one that has atoms of the same characteristic forming a molecule. Therefore, we have atoms belonging to the same chemical element.
In substance F2, for example, we have two fluorine atoms, so we must use two types of equal atoms in the representation according to Dalton's atomic theory.

Simple substance representation according to Dalton's atomic model
understanding of compound substances
In a compound substance, we have atoms of different characteristics forming the molecule. Therefore, we have different chemical elements forming the substance.
Substance H2O, for example, has three atoms: two hydrogen and one oxygen. See its representation according to the atomic model of Dalton:
Representation of a compound substance according to the skinDalton's atomic model
Understanding the mixtures
The understanding of a mixture (union of two or more different substances) through Dalton's atomic theory is simple: just put two different molecules in the same container.
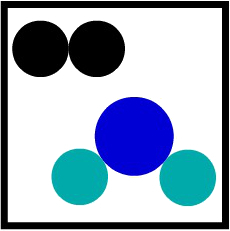
Representation of a second mixture Dalton's atomic model
Other Scientific Contributions by John Dalton
introduced the concept of atomic mass;
Formulated the law of partial pressures of gases (Dalton's Law);
He discovered the visual impairment called color blindness;
He studied the behavior of vapors and gases at different temperatures;
He found that all gases expand (they try to occupy a certain place) in space in the same way.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/teoria-atomica-dalton.htm
