O formic acid gets its name because its first obtainment was through the distillation of red ants (from the Latin formica = ant), which inject this carboxylic acid through their bite, causing severe pain, swelling and itching.
However, its official nomenclature is methaneic acid, whose structural formula is represented below:

In addition to ants, methanoic acid is also found in bees, nettles, pine trees and some fruits.
At room temperature it is colorless, liquid, caustic, strong smelling and irritating. This acid is used as a mordant, in the production of carbon monoxide, in the treatment against rheumatism, in the production of oxalic acid, as a germicide, as a disinfectant, and in the production of other products Organic.
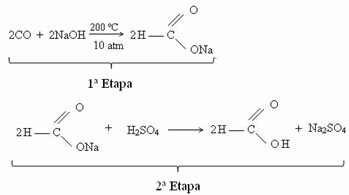
Currently, formic acid is obtained through the reaction between carbon monoxide and caustic soda. This reaction is a technique similar to that developed in 1855 by the French chemist Marcellin Berthelot (1827-1907). Next we have this reaction, in which sodium methanoate is first obtained, which, after reacting with sulfuric acid, produces methaneic acid as one of the products:
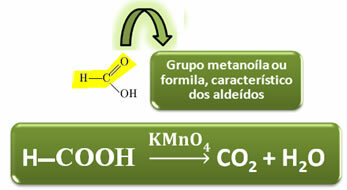
Unlike other carboxylic acids, formic acid has the functional group of aldehydes, which gives it the property of acting as a reducer. Reduces Fehling and Tollens reactives, being oxidized to carbon dioxide and water.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
