O blood is a special kind of fabric conjunctive that guarantees the transport of nutrients, oxygenand metabolic waste by the body, in addition to ensuring the processes of Blood coagulation and defense of the organism. The blood is formed by a liquid extracellular matrix, in which they are found cells and suspended cell fragments. It is contained within the Cardiovascular system, which guarantees its movement in a unidirectional flow.
Read too:Heart
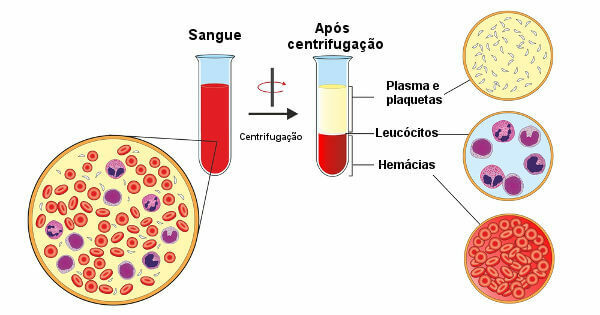
After centrifuging the blood, it is possible to observe the separation of its liquid part from the blood cells.
→ Components
Blood is composed of blood plasma, two cell types (erythrocytes and leukocytes) and named cell fragments platelets. You erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets are called the figured elements of the blood. These elements constitute 45% of volume of blood, while plasma constitutes 55% of its volume.
A healthy person has a total blood volume of approximately 7% of their body weight. |
- Blood plasma
O blood plasma and the liquid part of the blood
and presents itself with a color light yellow. This represents more than half of our body's total blood volume and is 90% consisting of water.In the plasma are still found mineral salts, proteins, hormones, among other substances, such as nutrients and waste from metabolism. It is in the plasma that the figurative elements are suspended.
- Figured elements
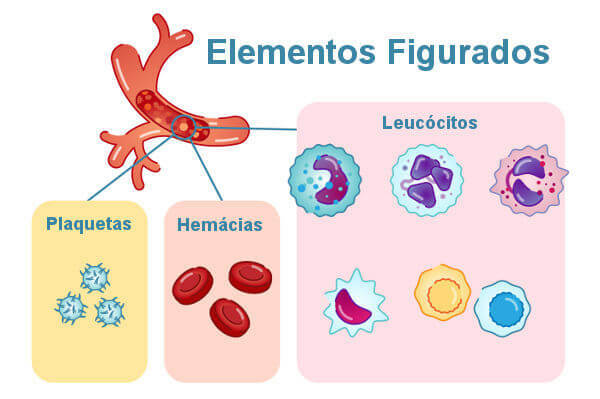
The elements figured are red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets.
Red blood cells, red blood cells or erythrocytes
At Red Cells, also known as red blood cells and erythrocytes, are the cells responsible for oxygen transport in the body.they are cells anucleate, that is, they do not have core and are shaped like a biconcave disc. These cells are small, showing about seven to eight micrometers in diameter.
Red blood cells have a life spanI enjoy, which lasts about 120 days, being later destroyed, mainly in the spleen. Under normal conditions, these cells do not leave the interior of the blood vessels.
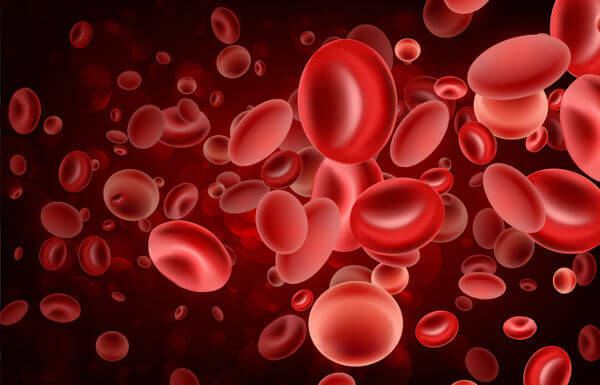
Red blood cells have a biconcave disc shape.
The red coloration of these cells is due to the presence of a protein named hemoglobin, which, in addition to guaranteeing the color, is responsible for the transport of oxygen in the body.
The absence of a nucleus in red blood cells favors the increase in the space for hemoglobin in these cells. It is noteworthy that, in addition to the absence of a nucleus, the red blood cells also Do not have mitochondria.
When we observe a reduction in the number of red blood cells, we have a condition known as anemia. |
Blood is red because of the large amount of red blood cells found in it. This cell is found in the greatest quantity, being observed, in each microliter of blood, about five to six million erythrocytes.
Mind Map: Blood

* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
Leukocytes or white blood cells
Leukocytes, also called white blood cells, are the cells responsible for defense of our body. They are colorless, present spherical shape and are able to perform diapedesis, which is their active output from blood vessels, to act as a defense in injured tissues or attacked by pathogens. On average, for each microliter of blood, there are five to ten thousand leukocytes.
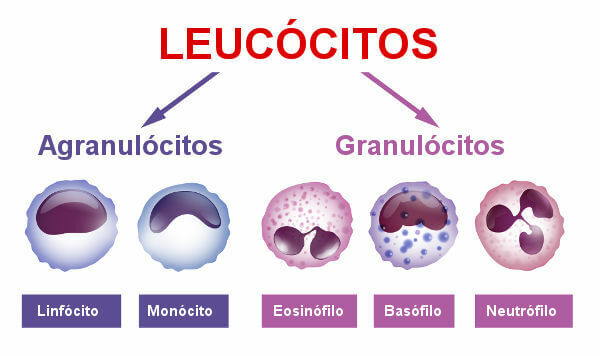
There are different types of white blood cells.
They exist different types of leukocytes, each performing a certain function related to the protection of the body. Some of them, for example, carry out the process of phagocytosis, others are responsible for the production of antibodies, which are defense proteins. Neutrophils, basophils, monocytes, eosinophils and lymphocytes are types of leukocytes.
Read too:What is Phagocytosis?
On a blood count, increased white blood cell counts may represent an infection. |
You leukocytes are divided into two groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes.
Granulocytes are characterized by presenting irregularly shaped core and specific granules in your cytoplasm. Neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils are granulocyte-type leukocytes.
You agranulocytes, unlike the group previously mentioned, they have a nucleus with a more regular shape and in their cytoplasm there is no presence of specific granules. Lymphocytes and monocytes are examples of agranulocytes.
platelets
At platelets they are fragments of bone marrow megakaryocytes, i.e, are not cells themselves. These structures have about two to three micrometers in diameter and they also have no core.
They act in the clotting process and also help repair blood vessels that have suffered some kind of damage. In each microliter of blood, there are about 150,000 to 450,000 platelets.
In patients with dengue, there is a drop in the number of platelets. In classic dengue, it is observed that this count is below 100,000 in each microliter of blood. |
→ where is produced
Blood is produced in what is called bone marrow. This is located at cavities of bones spongy and also in the medullary canal of long bones.
Read too:bone marrow donation
→ Diseases that affect the blood
Some diseases directly affect blood cells, triggering a series of unpleasant and even fatal consequences. Let's look at some of these diseases below:
Anemia: when there is a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Anemia can be triggered, for example, by lack of iron in the diet and bleeding. Anemic individual presents, among other symptoms, weakness, tiredness, shortness of breath and dizziness.
sickle cell anemia: when there is an alteration in the red blood cells, which have a sickle shape. This change can trigger the formation of clots that lead to obstruction of blood vessels, which can cause damage to certain organs. In sickle cell anemia, the person may experience pain and fatigue.
Hemophilia: it is a genetic problem, linked to the X chromosome, that causes changes in blood clotting. This means that people with this problem can bleed excessively in the face of an injury. The treatment of hemophilia is usually based on replacement of the clotting factor that is not present in the patient.
Leukemia: is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells and is characterized by the production of abnormal cells. There are, according to the National Cancer Institute (Inca), more than 12 different types of leukemia. Treatment for anemia is varied and may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy and also bone marrow transplantation.
Read too: Blood donation
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
