THE hydrolysis constant (Kh) refers to a chemical balance established from the hydrolysis of a salt (chemical reaction involving a soluble salt and water).
As the constant of any other equilibrium, the expression of hydrolysis constant is constructed from the product of product concentrations divided by the product of reagent concentrations, as follows:
Kh = [products]
[reagents]
Working with the hydrolysis constant involves knowledge of three important phenomena:
- Dissociation of salts;
- Water ionization;
- Salt hydrolysis.
Dissociation of salts
When a soluble salt is added to water, it dissociates and releases a cation other than hydronium (H+) and anion other than hydroxyl (OH-).

To remind you when a salt is or is not soluble in water, Click here and study the salt solubility table.
water ionization
Water is a substance that naturally undergoes the phenomenon of self-ionization, that is, it produces a hydronium cation and a hydroxyl anion.
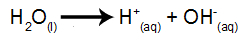
water ionization equation
hydrolysis of a salt
As a soluble salt it releases ions into the water and the water undergoes ionization, producing
ions in the middle, the reaction (hydrolysis) between the salt ions and the water ions can take place. When this reaction occurs, the possible interactions are:- Cation of the salt with the anion of water (formation of a base);
- Anion of salt with the cation of water (formation of a salt);
The above interactions will only occur if the base or acid formed is weak.
See an example of the hydrolysis of a salt:
→ Hydrolysis of ammonium hypochlorite (NH4ClO)
When ammonium hypochlorite is added to water, it dissolves and dissociates, releasing the ammonium cation ions (NH4+) and the hypochlorite anion (ClO-):

Equation showing the ions released in the dissociation of ammonium hypochlorite
As water, when undergoing ionization, produces H+ and OH-, we have in the solution two cations and two anions, which can react. The NH4+ cation only reacts with the OH- anion because it forms a weak base (NH4OH). The ClO- anion only reacts with the H+ cation because it forms a weak acid (HClO).

Ammonium hypochlorite hydrolysis equilibrium equation
Construction of the expression of the hydrolysis constant
The construction of the hydrolysis constant of a salt depends exclusively on the hydrolysis equation for that salt. The hydrolysis of ammonium hypochlorite, for example, worked on in the previous item, generated the following equation:

Ammonium hypochlorite hydrolysis equilibrium equation
How to build the expression of hydrolysis constant takes into account products and reagents, the expression of the constant would be:
Kh = [HClO].[NH4OH]
[ClO-].[NH4+]
NOTE: Water does not participate in the equation because it is a liquid reagent and also because it is the fundamental means for the occurrence of hydrolysis, that is, it is constant.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-constante-hidrolise.htm