Atom is the name given to the shaper of matter (everything that occupies space and has mass). This name was proposed by the Greek philosophers Democritus and Leucippus. Chemical elements, molecules, substances and organic or inorganic materials are formed by atoms.
In its constitution, the atom has particles (protons, neutrons and electrons), not being the smallest part of the matter. Still, your visualization is not possible. What is known about the atom is related to scientifically proven physical, chemical and mathematical aspects.
The evolution of knowledge about the atom has caused several technologies to be developed and improved.
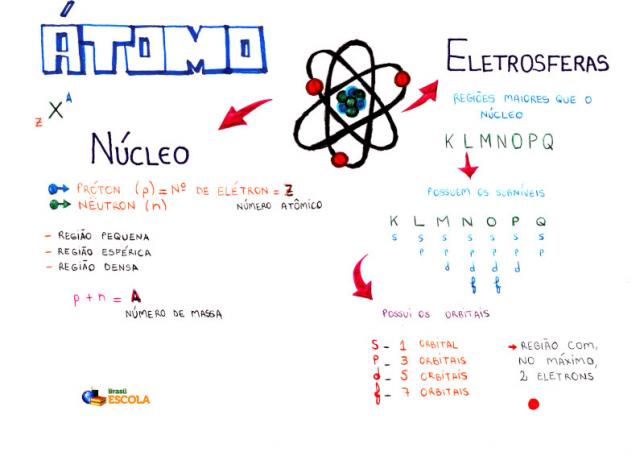
Basic composition of an atom
Core: denser region of the atom and holds protons and neutrons;
Energy Levels: regions that surround the nucleus and that house sublevels, orbitals and electrons. There are seven energy levels, which are represented by the letters K, L, M, N, O, P and Q;
Energy sublevels: are regions that house the orbitals. They are present at all levels and are represented by letters (s, p, d f). Its quantity depends on each level: K (has s sublevels), L (has s and p sublevels), M (has s, p and d sublevels), N (has sublevels s, p, d and f), O (has sublevels s, p, d and f), P (has sublevels s, p and d) and Q (has sublevels s and P);
Atomic orbitals: regions most likely to find an electron. Each sublevel has a different number of orbitals: s (one orbital), p (three orbitals), d (five orbitals), and f (seven orbitals);
protons: positive particles (represented by p);
electrons: negative particles that also have wave behavior (represented by e);
neutrons: uncharged particles that decrease the repulsion between protons in the nucleus (represented by n).
Mind Map: Atom
* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
representation of an atom
The simplest way to represent an atom is to use the abbreviation of the chemical element it forms. The acronym Se, for example, represents all the atoms that form the chemical element selenium.
The acronym that represents the atom can still provide two important pieces of information: the atomic number (represented by the letter Z and always on the left side bottom of the atom's acronym) and the mass number (represented by the letter A, which can be positioned on the left or right side at the top of the acronym of the atom).
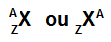
Acronym of an atom with mass number and atomic number
atomic number (Z): indicates the number of protons present in the nucleus of the atom and the number of electrons (e) present in the energy levels.
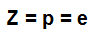
Formula that indicates the representativeness of the atomic number
-
Mass number (A): indicates the mass present in the nucleus of the atom, which results from the sum of the number of protons (p) and the number of neutrons (n).
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

Formula that indicates the representativeness of the mass number
Atomic Similarities
Atoms of the same chemical element or different chemical elements can be compared in terms of the number of protons, electrons, neutrons and mass, being classified as follows:
a) Isotopes
They are atoms that have:
same atomic number;
same number of protons;
different mass number;
different number of neutrons;
Example:
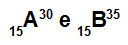
Atoms A and B are isotopes
Atoms A and B are isotopes because:
Atom A has 15 protons, atomic number equal to 15, 15 electrons, 15 neutrons and mass number equal to 30.
Atom B has 15 protons, atomic number equal to 15, 15 electrons, 20 neutrons and mass number equal to 35.
b) Isobars
They are atoms that have:
different atomic numbers;
different numbers of protons;
different numbers of electrons;
same mass numbers;
different numbers of neutrons.
Example:
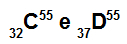
Atoms C and D are isobars
Atoms C and D are isobaric because:
Atom C has 32 protons, atomic number equal to 32, 32 electrons, 23 neutrons and mass number equal to 55.
Atom D has 37 protons, atomic number equal to 37, 37 electrons, 18 neutrons and mass number equal to 55.
c) Isotones
They are atoms that have:
different atomic numbers;
different numbers of protons;
different numbers of electrons;
different mass numbers;
same number of neutrons.
Example:
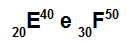
Atoms E and F are isotopes
Atoms E and F are isotopes because:
Atom E has 20 protons, atomic number equal to 20, 20 electrons, 20 neutrons and mass number equal to 40.
Atom F has 30 protons, atomic number equal to 30, 30 electrons, 20 neutrons and mass number equal to 50.
d) Isoelectronics
They are atoms that have:
same number of electrons.
NOTE: isoelectronic atoms can also have the same mass number (isobars), the same number of neutrons (isotones) or the same number of protons (isotopes).
Example:
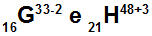
Atoms G and H are isoelectronic
Atoms G and H are isoelectronic because:
Atom G has 16 protons, atomic number equal to 16, 18 electrons (the sign -2 indicates that it has two more electrons than the number of protons), 17 neutrons and mass number equal to 33.
Atom H has 21 protons, atomic number equal to 21, 18 electrons (the +3 sign indicates it has three fewer electrons than the number of protons), 27 neutrons, and mass number equal to 48.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is an atom?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-atomo.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry
Atoms and the construction of the Universe, atomic theory, that everything is made, matter is made up of atoms, Theory of the four elements, ancient alchemists, atomic theory, fundamental particle.
Chemistry

Niels Bohr, Bohr's atom, atomic physics, stable atom, atomic model, planetary system, layers of the electrosphere, energy levels, electron shells, electron energy, Rutherford atomic model, excited state atom.