Ethanol or ethyl alcohol is an organic compound of the alcohol family, whose molecular formula is CH3 – CH2 – OH (same as C2H6O).
A colorless liquid, ethanol easily dissolves in water because it is a polar molecule. It has a very peculiar smell and its boiling point is reached at 78ºC, while its melting point is reached at -114ºC.
Brazil is the second largest ethanol producer in the world, just behind the United States of America (USA). Together, both are responsible for 70% of the production of this compound.
Structural Formula
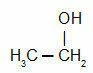
Ethanol is made up of two carbon atoms bonded to five hydrogen atoms. In addition to these, it has an oxygen atom linked to a hydrogen atom, the so-called hydroxyl (OH).
Its carbon makes only single bonds, which is why it is saturated.
Production
In Brazil, the main raw material is sugarcane. In addition to sugarcane, ethanol can be obtained through the fermentation of sugars contained in sugar beet, castor beans, corn and soybeans, among others.
After the sugarcane is harvested and washed to remove impurities, production follows these steps:
- crushing, after which the bagasse appears.
- Concentration and Crystallization, after which the dark sugar and molasses are obtained.
- Fermentation of molasses, the fermented wine being obtained.
- Distillation of the fermented wine, from which ethanol is obtained.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the advantages of ethanol, we can mention the fact that it does not pollute like gasoline. This is because ethanol does not produce sulfur dioxide (SO2).
In addition to being less polluting, there is also the fact that its price is lower than that of gasoline. These two reasons lead to the choice between the two fuels.
The downside is that ethanol production requires the existence of large tracts of land for planting. One of the consequences is the environmental damage from deforestation.
Another effect is hunger, because much of the land that could be used to grow food that would satisfy people's hunger is used for planting the raw material for ethanol.
properties
- highly flammable
- Toxic
- Soluble in water
- neutral pH
- polar molecule
- boiling at 78°C
- Melting at -114°C
applications
In Brazil, most ethanol is used as fuel, but also as raw material for paints and solvents.
There is also hydrous ethanol, which is 5% water. It is used in the manufacture of food and beverages, cleaning products, medicines, perfumes and fuel.
Read too:
- alcohols
- Alcohol Characteristics
- Methanol
- Biofuels
- Prohibition