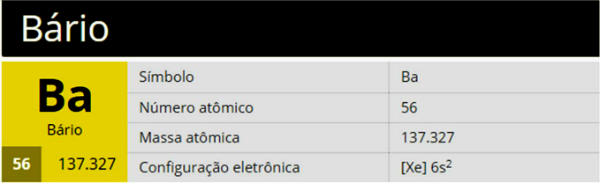
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba, atomic number 56 and atomic mass 137,327, belonging to group 2 (Family 2A) of the periodic table, being an alkaline earth metal.
Its name derives from the Greek barys and it means heavy.
Features
At room temperature, it is found in a solid state, with a soft consistency and a silvery color. However, in nature it is not found in its pure form, as it is easily oxidized in contact with air.
Barium is found in barite ores (BaSO4) and witherite (BaCO3). The main mining areas for these ores occur in the UK, Italy, Czech Republic, USA and Germany.
Barium has high melting points (1000 K - 727 °C) and boiling (2170 K - 1897 °C). It's still a good conductor of electricity.
It is very reactive in contact with water and alcohol. Its reaction with water produces hydroxide and releases hydrogen.
Soluble barium compounds are toxic to the body. Despite being found in water and food, the amount of barium present is not enough to cause health problems.
Due to its high oxidizing power, barium must be preserved in mineral oil.
Learn more, read also:
- Chemical elements
- Periodic table
applications
Among the main applications of barium are included:
- In its pure form it is used for oxygen removal from electronic valves;
- Rat poison, in the form of barium carbonate;
- Used as a white pigment in paints;
- Glass production;
- Barium sulfate is used as a fluid for drilling oil and gas wells;
- Barium chlorate and nitrate are used in the production of green flames in pyrotechnic flares;
- Barium sulfide enhances contrast for x-ray examinations of the digestive system and is given orally to patients. Ingestion does not cause health problems, as the substance is insoluble, does not accumulate and is quickly eliminated from the body;
While barium sulfide is harmless, barium carbonate is extremely toxic and can be fatal. The person with intoxication has breathing difficulties, vomiting, tremors, tachycardia, increased blood pressure and salivation.
You may also be interested in:
- Metal links
- Copper
- Lithium


