Electrostatic shielding is the physical phenomenon that makes the electric field always null inside the materials conductors. This is due to the way in which the electrical charges are distributed along the surface of the conductors in equilibrium electrostatic.
Result of an experiment named faraday's cage, electrostatic shielding was discovered by Michael Faraday in 1936 and is still used in different contexts in order to protect electronic circuits.
See too: Capacitors - dielectric means used to store electrical charges
Who Discovered Electrostatic Shielding?
Electrostatic shielding was discovered byMichael Faraday (1821-1867), in the year 1936, through an experiment that became known as cageinFaraday. The experiment consisted of a large closed metal cage that received intense electrical discharges, while Faraday remained seated in a chair, unaffected by the electric current.

How does electrostatic shielding work?
Electrostatic shielding is also the phenomenon that causes cell phone signals, for example, to lose intensity or even be canceled when we are in the elevator. Thanks to this phenomenon, we are safe in cars during a storm. rays: the car body, which is closed and made of conductive material, ensures that we are not exposed to the harmful effects of lightning. This is because, inside any closed conductor, the electric field is null, But why this happen? Look at the picture:
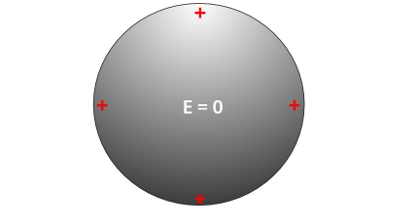
In the figure shown, we have a objectconductor, with excess positive charges. Note that the charges are spaced as far apart as possible from each other, due to electrostatic repulsion, but also the mobility of electrical charges in conductors. Due to these two factors, in conductive materials, all excess electrical charges always occupy the surface of the material, so that there is no imbalance of electrical charges inside the conductor.
When we place the object leading the figure in the presence of a fieldelectricexternal, something interesting happens: the electric charges move according to the direction of the electric field, in this way, the electric field produced by the charges is canceled out by the external electric field, watch:

Since the electric field inside the conductor is null, There is not potential difference between any points of the conductor, so there is no movement of loads. In this way, when we find ourselves inside a closed conductor, we are protected from electrical interference from the external environment and from waveselectromagnetic.
The situation described above allows us to understand why the electrostatic shielding affects the signal of telecommunications inside the elevator, as mentioned at the beginning of the text: o electric field of the radio waves, which transmit the cell signal, becomes null inside a perfectly closed conductor.
See too: Electrostatics - study of electrical charges at rest
Electrostatic shielding applications
Electrostatic shielding is used in a large number of technological applications. Its main purpose is to protect sensitive components electronic circuits, which can be damaged if exposed to external electrical fields.
Some appliances, such as microwaves, radios, televisions, storage devices, DVD players, blu-ray players, computers and notebooks, have coatingsmetallic that work like cagesinfaraday to protect their internal circuitry.
power of tips
The power of the tips is the characteristic of the conductors that makes there more accumulation of charges in sharp regions, or of great curvature. This is because every conductor in electrostatic equilibrium has a null internal electric field and, therefore, the entire its surface is under the same electrical potential, in other words, we say that the surface of this conductor é equipotential.
Lookalso: What are electrical circuits for?
Once potentialelectric é inverselyproportionalto lightning (r), so that this electrical potential remains constant across the entire surface of the conductor, different load modules are necessary in the sharp regions, where the radius of curvature of the conductor surface is greater in relation to the flat regions of the conductor.

This makes the rays more likely to hit the lightning rod, which are built in materialconductor and they are pointed at their ends so that they can accumulate a greater amount of electrical charges, thus facilitating the passage of electrical current.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-blindagem-eletrostatica.htm